Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (7): 581-588.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.07.001
Effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on cognitive rehabilitation in patients with mild-to-moderate cognitive impairment after stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Su Guiting, Kang Yahong, Chen Ziqiong, Liu Fang( )
)
- School of Nursing, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, China
-
Received:2025-06-05Online:2025-07-20Published:2025-07-17 -
Contact:Liu Fang E-mail:liufangcn05@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Su Guiting, Kang Yahong, Chen Ziqiong, Liu Fang. Effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on cognitive rehabilitation in patients with mild-to-moderate cognitive impairment after stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(7): 581-588.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.lchc.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.07.001
| 第一作者 及时间 | 诊断标准 | 年龄 (岁) | 例数(对照 组/试验组) | 干预措施 | 电流强度 (mA) | 干预频率 (每周) | 干预周期 (周) | 结局指标 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脑卒中 | 认知障 碍程度 | 对照组 | 试验组 | |||||||
| Chen 2024[ | ①⑥ | ⑦ | E:61.06±3.08 C:62.44±2.76 | 18/18 | 计算机辅助认知训练 | 计算机辅助认知训练+tDCS | 2 | 20 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 3 | MoCA |
| 石琪2024[ | ① | ⑦ | E:72.31±3.46 C:71.05±3.17 | 31/31 | 盐酸多奈哌齐 | 盐酸多奈哌齐+tDCS | 1~2 | 20 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 4 | MoCA、RBMT |
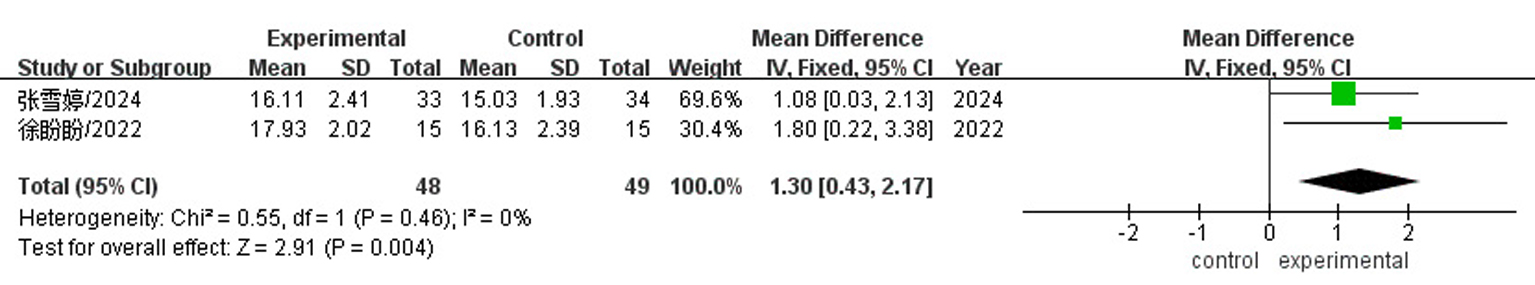
| 张雪婷2024[ | ② | ③⑦ | E:61.56±5.01 C:59.23±4.38 | 34/33 | 常规治疗 | 常规治疗+tDCS | 1.5 | 15 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 4 | MoCA、LOTCA、RBMT |
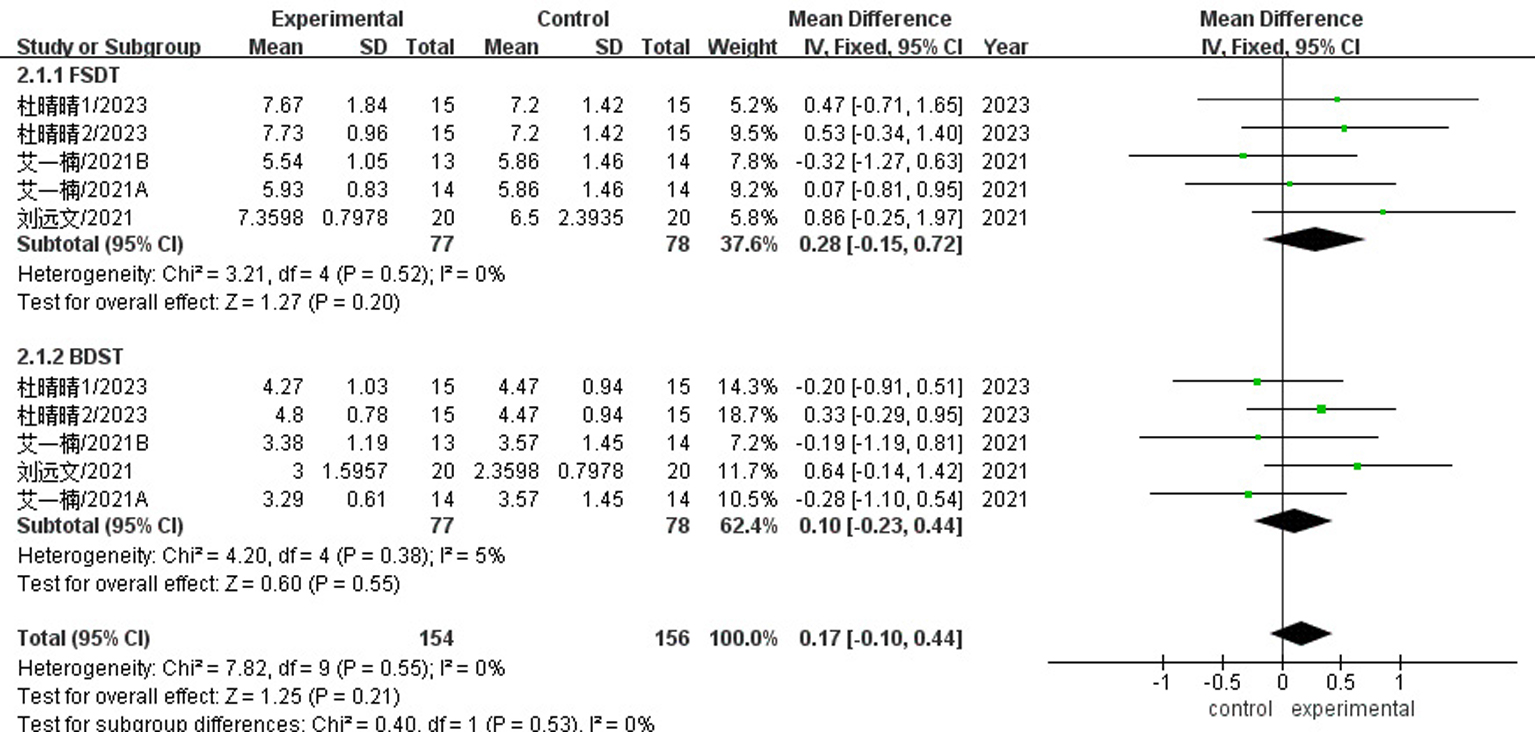
| 杜晴晴2023[ | ④⑥ | ⑧ | E1:55.67±7.75 E2:52.40±8.77 C:56.60±8.03 | 15/15/15 | 认知训练+假tDCS | E1:认知训练和tDCS同时进行 E2:先tDCS后认知训练 | 1.4 | 30 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 2 | MMSE、MoCA、DST、n-back |
| 徐盼盼2022[ | ④⑥ | ⑦ | E:59.53±5.99 C:59.80±6.86 | 15/15 | 常规康复治疗+认知功能训练+假tDCS | 常规康复治疗+认知功能训练+tDCS | 2.0 | 30 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 3 | MoCA、RBMT |
| 杨健2022[ | ⑥ | ⑧ | E:56.19±7.541 C:54.84±8.041 | 32/32 | 常规药物、康复治疗+认知训练 | 常规药物、康复治疗+认知训练+tDCS | 1.0 | 20 min/次,2次/d,5 d | 2 | MMSE、MoCA |
| Ko 2022[ | 未注明 | ⑨ | E:61.25±12.85 C:57.86±10.04 | 13/13 | 认知训练+假远程tDCS | 认知训练+远程tDCS | 2.0 | 30 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 4 | K-MoCA、SCWT、K-BNT、K-DRS-2、TMT、Go/No Go、COWAT |
| 艾一楠2021[ | ④⑥ | ⑧ | E1:61.64±10.33 E2:61.36±8.51 C:58.77±9.61 | 14/14/13 | 常规康复治疗+计算机辅助认知康复训练+假tDCS | E1:常规康复治疗+计算机辅助认知康复训练+tDCS(与认知康复同时进行) E2:常规康复治疗+计算机辅助认知康复训练+tDCS(与认知康复隔4h以上) | 2.0 | 30 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 2 | MoCA、DST |
| 刘远文2021[ | 未注明 | ⑧ | E:63.72±8.41 C:60.06±8.26 | 20/20 | 常规康复治疗+假tDCS | 常规康复治疗+tDCS | 2.0 | 20 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 4 | MMSE、DST、TMT、DS |
| 张晓杰2020[ | ⑤⑥ | ⑦ | E:53.43±10.79 C:54.37±12.21 | 15/15 | 常规康复方案+认知训练+假tDCS | 常规康复方案+认知训练+tDCS | 1.5 | 20 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 3 | MoCA、SCWT |
| Shaker 2018[ | ⑥ | ⑧ | E:54.45±4.68 C:53.05±6.32 | 20/20 | 认知功能训练+假tDCS | 认知功能训练+tDCS | 2.0 | 30 min/次,1次/d,3 d | 4 | ACL、FML、RBL、LRL |
Tab. 1 Features of the included studies
| 第一作者 及时间 | 诊断标准 | 年龄 (岁) | 例数(对照 组/试验组) | 干预措施 | 电流强度 (mA) | 干预频率 (每周) | 干预周期 (周) | 结局指标 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 脑卒中 | 认知障 碍程度 | 对照组 | 试验组 | |||||||
| Chen 2024[ | ①⑥ | ⑦ | E:61.06±3.08 C:62.44±2.76 | 18/18 | 计算机辅助认知训练 | 计算机辅助认知训练+tDCS | 2 | 20 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 3 | MoCA |
| 石琪2024[ | ① | ⑦ | E:72.31±3.46 C:71.05±3.17 | 31/31 | 盐酸多奈哌齐 | 盐酸多奈哌齐+tDCS | 1~2 | 20 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 4 | MoCA、RBMT |
| 张雪婷2024[ | ② | ③⑦ | E:61.56±5.01 C:59.23±4.38 | 34/33 | 常规治疗 | 常规治疗+tDCS | 1.5 | 15 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 4 | MoCA、LOTCA、RBMT |
| 杜晴晴2023[ | ④⑥ | ⑧ | E1:55.67±7.75 E2:52.40±8.77 C:56.60±8.03 | 15/15/15 | 认知训练+假tDCS | E1:认知训练和tDCS同时进行 E2:先tDCS后认知训练 | 1.4 | 30 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 2 | MMSE、MoCA、DST、n-back |
| 徐盼盼2022[ | ④⑥ | ⑦ | E:59.53±5.99 C:59.80±6.86 | 15/15 | 常规康复治疗+认知功能训练+假tDCS | 常规康复治疗+认知功能训练+tDCS | 2.0 | 30 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 3 | MoCA、RBMT |
| 杨健2022[ | ⑥ | ⑧ | E:56.19±7.541 C:54.84±8.041 | 32/32 | 常规药物、康复治疗+认知训练 | 常规药物、康复治疗+认知训练+tDCS | 1.0 | 20 min/次,2次/d,5 d | 2 | MMSE、MoCA |
| Ko 2022[ | 未注明 | ⑨ | E:61.25±12.85 C:57.86±10.04 | 13/13 | 认知训练+假远程tDCS | 认知训练+远程tDCS | 2.0 | 30 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 4 | K-MoCA、SCWT、K-BNT、K-DRS-2、TMT、Go/No Go、COWAT |
| 艾一楠2021[ | ④⑥ | ⑧ | E1:61.64±10.33 E2:61.36±8.51 C:58.77±9.61 | 14/14/13 | 常规康复治疗+计算机辅助认知康复训练+假tDCS | E1:常规康复治疗+计算机辅助认知康复训练+tDCS(与认知康复同时进行) E2:常规康复治疗+计算机辅助认知康复训练+tDCS(与认知康复隔4h以上) | 2.0 | 30 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 2 | MoCA、DST |
| 刘远文2021[ | 未注明 | ⑧ | E:63.72±8.41 C:60.06±8.26 | 20/20 | 常规康复治疗+假tDCS | 常规康复治疗+tDCS | 2.0 | 20 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 4 | MMSE、DST、TMT、DS |
| 张晓杰2020[ | ⑤⑥ | ⑦ | E:53.43±10.79 C:54.37±12.21 | 15/15 | 常规康复方案+认知训练+假tDCS | 常规康复方案+认知训练+tDCS | 1.5 | 20 min/次,1次/d,5 d | 3 | MoCA、SCWT |
| Shaker 2018[ | ⑥ | ⑧ | E:54.45±4.68 C:53.05±6.32 | 20/20 | 认知功能训练+假tDCS | 认知功能训练+tDCS | 2.0 | 30 min/次,1次/d,3 d | 4 | ACL、FML、RBL、LRL |
| [1] |
《中国卒中中心报告2022》概要[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2024, 21(8):565-576.
|
| [2] |
王拥军, 李子孝, 谷鸿秋, 等. 中国卒中报告2020(中文版)(1)[J]. 中国卒中杂志, 2022, 17(5):433-447.
|
| [3] |
GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2021, 20(10):795-820.
doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00252-0 pmid: 34487721 |
| [4] |
汪凯, 董强, 郁金泰, 等. 卒中后认知障碍管理专家共识2021[J]. 中国卒中杂志, 2021, 16(4):376-389.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
pmid: 26915421 |
| [7] |
doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-03613-3 pmid: 38641827 |
| [8] |
石琪, 胡丹丹, 祁伟. 盐酸多奈哌齐联合tDCS治疗老年脑梗死患者轻度认知障碍的临床效果[J]. 医药前沿, 2024, 14(31):62-64.
|
| [9] |
张雪婷, 周楠, 李晴. 针灸联合经颅直流电刺激治疗脑卒中伴认知障碍的随机对照试验[J]. 世界中医药, 2024, 19(1):52-56.
|
| [10] |
杜晴晴. 经颅直流电刺激对脑卒中后工作记忆障碍患者的影响[D]. 太原: 山西医科大学, 2023.
|
| [11] |
徐盼盼. 经颅直流电刺激对脑卒中后记忆障碍的疗效研究[D]. 太原: 山西医科大学, 2022.
|
| [12] |
杨健, 梁桂生, 廖成钜, 等. 经颅直流电刺激配合认知训练治疗卒中后认知障碍的疗效[J]. 中国实用神经疾病杂志, 2022, 25(2):160-165.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
艾一楠, 李莉莉, 尹明宇, 等. 不同治疗时机的经颅直流电刺激治疗脑卒中后认知障碍的初步研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2021, 36(3):315-321.
|
| [15] |
刘远文, 张淑娴, 黄丽, 等. 经颅直流电刺激治疗脑卒中患者注意功能障碍的随机对照单盲研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2021, 36(5):533-537+558.
|
| [16] |
张晓杰. 经颅直流电刺激治疗对脑卒中后注意障碍的疗效观察[D]. 太原: 山西医科大学, 2020.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
陈善鹏. 轻中度卒中后认知障碍与NIHSS评分及卒中危险因素的相关性分析[D]. 西宁: 青海大学, 2020.
|
| [19] |
王益言, 王东岩, 李慎微, 等. 电针治疗脑卒中后认知障碍突触可塑性机制研究进展[J]. 针灸临床杂志, 2024, 40(1):102-106.
|
| [20] |
胡延超, 李瑞青, 郝文雪, 等. 电针治疗脑卒中后认知障碍的机理研究[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志, 2021, 27(7):1186-1190.
|
| [21] |
王祯芝, 张美玲, 熊康, 等. 针刺对脑卒中后认知障碍的作用机制研究进展[J]. 江苏中医药, 2022, 54(3):73-77
|
| [22] |
常文轩, 王婷, 刘伟, 等. 脑白质高信号患者执行功能与脑血流量的相关性分析[J]. 中国当代医药, 2024, 31(14):4-7,36.
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.029221 pmid: 32521221 |
| [25] |
李晓云, 褚静, 周悦, 等. 经颅直流电刺激和认知训练对脑梗死后认知功能障碍患者认知功能恢复的作用[J]. 微循环学杂志, 2024, 34(3):55-60.
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-12457-1_38 pmid: 31646541 |
| [28] |
doi: 10.1038/ncomms11100 pmid: 27000523 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-91287-5_10 pmid: 30178324 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||