Clinical Focus ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (2): 114-118.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.02.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Influencing factors and predictive indicators of vascular calcification
Zheng Lihua1a, Du Runsen2, Zhao Yaheng1b, Liu Peng1a( )
)
- 1a. Department of Vascular Surgery; b. Department of Trauma emergency surgery, the First Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050011, China
2. Graduate School, Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050011, China
-
Received:2021-10-04Online:2022-02-20Published:2022-03-04 -
Contact:Liu Peng E-mail:liupeng19850214@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zheng Lihua, Du Runsen, Zhao Yaheng, Liu Peng. Influencing factors and predictive indicators of vascular calcification[J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(2): 114-118.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.lchc.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.02.003
| 项目 | 对照组(n=276) | 病例组(n=191) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(例) | ||||
| 男 女 | 169 107 | 127 64 | χ2=1.346 | 0.246 |
| 年龄(岁) | 65.884±11.540 | 68.377±9.693 | t=1.172 | 0.241 |
| 身高(cm) | 169.673±28.235 | 167.037±14.870 | t=0.117 | 0.459 |
| 体重(kg) | 74.223±11.818 | 67.862±10.535 | t=0.568 | 0.136 |
| 中性粒细胞占比(%) | 0.604±0.087 | 0.679±0.108 | t=0.763 | <0.01 |
| 淋巴细胞占比(%) | 0.303±0.080 | 0.226±0.094 | t=0.877 | <0.01 |
| 纤维蛋白原(g/L) | 2.881±0.908 | 3.748±1.005 | t=0.906 | <0.01 |
| FDP(mg/L) | 0.780±1.008 | 6.215±35.884 | t=0.214 | <0.01 |
| 甘油三酯(mmol/L) | 1.530±1.165 | 1.504±1.299 | t=0.021 | 0.439 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.123±0.329 | 0.968±0.243 | t=0.536 | <0.01 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.856±0.683 | 2.705±0.758 | t=0.211 | <0.05 |
| 脂蛋白(mg/L) | 205.057±243.927 | 391.962±301.786 | t=0.681 | <0.01 |
| GGT(U/L) | 26.663±21.357 | 34.395±41.667 | t=0.234 | <0.01 |
| hs-CRP(mg/L) | 2.221±4.752 | 26.826±54.662 | t=0.634 | <0.01 |
| 白蛋白(g/L) | 41.364±3.609 | 36.864±5.376 | t=0.983 | <0.01 |
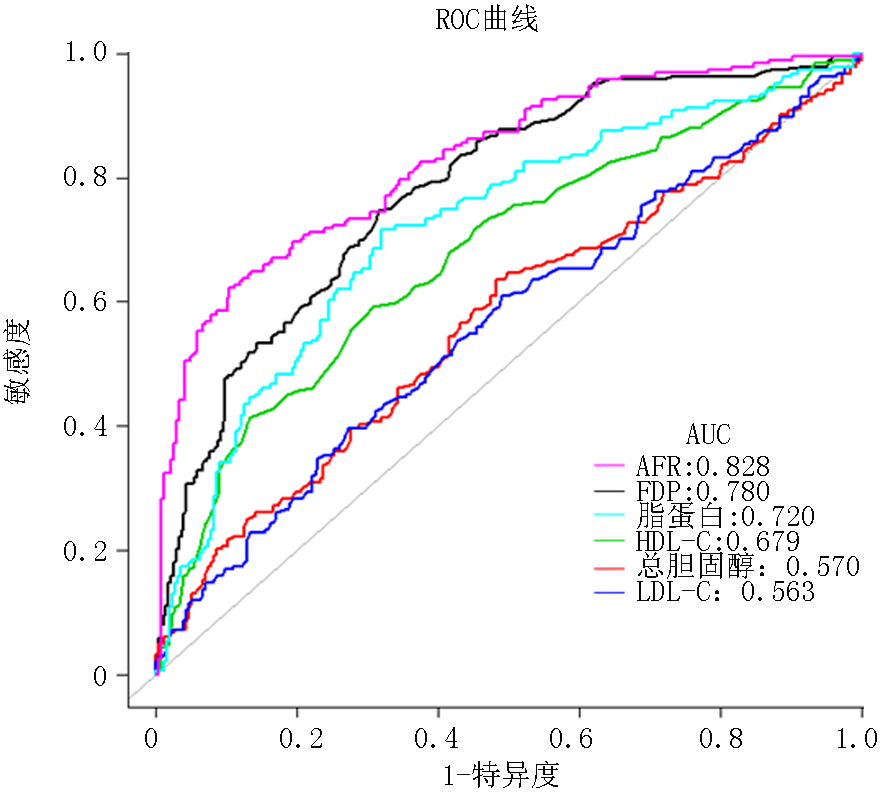
| AFR | 14.979±3.020 | 10.682±3.528 | t=1.308 | <0.01 |
| 总胆固醇(mmol/L) | 4.586±0.930 | 4.355±1.116 | t=0.224 | <0.05 |
| 项目 | 对照组(n=276) | 病例组(n=191) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(例) | ||||
| 男 女 | 169 107 | 127 64 | χ2=1.346 | 0.246 |
| 年龄(岁) | 65.884±11.540 | 68.377±9.693 | t=1.172 | 0.241 |
| 身高(cm) | 169.673±28.235 | 167.037±14.870 | t=0.117 | 0.459 |
| 体重(kg) | 74.223±11.818 | 67.862±10.535 | t=0.568 | 0.136 |
| 中性粒细胞占比(%) | 0.604±0.087 | 0.679±0.108 | t=0.763 | <0.01 |
| 淋巴细胞占比(%) | 0.303±0.080 | 0.226±0.094 | t=0.877 | <0.01 |
| 纤维蛋白原(g/L) | 2.881±0.908 | 3.748±1.005 | t=0.906 | <0.01 |
| FDP(mg/L) | 0.780±1.008 | 6.215±35.884 | t=0.214 | <0.01 |
| 甘油三酯(mmol/L) | 1.530±1.165 | 1.504±1.299 | t=0.021 | 0.439 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.123±0.329 | 0.968±0.243 | t=0.536 | <0.01 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.856±0.683 | 2.705±0.758 | t=0.211 | <0.05 |
| 脂蛋白(mg/L) | 205.057±243.927 | 391.962±301.786 | t=0.681 | <0.01 |
| GGT(U/L) | 26.663±21.357 | 34.395±41.667 | t=0.234 | <0.01 |
| hs-CRP(mg/L) | 2.221±4.752 | 26.826±54.662 | t=0.634 | <0.01 |
| 白蛋白(g/L) | 41.364±3.609 | 36.864±5.376 | t=0.983 | <0.01 |
| AFR | 14.979±3.020 | 10.682±3.528 | t=1.308 | <0.01 |
| 总胆固醇(mmol/L) | 4.586±0.930 | 4.355±1.116 | t=0.224 | <0.05 |
| 项目 | 回归 系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 中性粒细胞占比 | 1.118 | 11.828 | 0.009 | <0.01 | 3 187.985 | 356.281 | 28 525.934 |
| 淋巴细胞占比 | -0.849 | 6.035 | 0.020 | <0.01 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 纤维蛋白原 | 0.936 | 6.731 | 0.019 | 0.063 | 3.719 | 2.727 | 5.072 |
| FDP | 0.569 | 0.431 | 1.743 | <0.01 | 2.379 | 1.846 | 3.065 |
| 总胆固醇 | 1.001 | 0.342 | 8.567 | 0.020 | 0.797 | 0.659 | 0.965 |
| HDL-C | -1.932 | 0.971 | 3.960 | <0.01 | 0.074 | 0.030 | 0.182 |
| LDL-C | -1.609 | 0.546 | 8.684 | 0.030 | 0.741 | 0.566 | 0.971 |
| 脂蛋白 | 0.063 | 0.001 | 3 969 | <0.01 | 1.003 | 1.002 | 1.004 |
| GGT | 0.203 | 0.012 | 286.179 | 0.018 | 1.010 | 1.002 | 1.018 |
| hs-CRP | 0.026 | 0.023 | 1.277 | <0.01 | 1.170 | 1.109 | 1.234 |
| AFR | -0.622 | 0.723 | 0.739 | <0.01 | 0.654 | 0.600 | 0.711 |
| 白蛋白 | 0.782 | 2.134 | 0.134 | 0.132 | 0.779 | 0.736 | 0.825 |
| 项目 | 回归 系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 中性粒细胞占比 | 1.118 | 11.828 | 0.009 | <0.01 | 3 187.985 | 356.281 | 28 525.934 |
| 淋巴细胞占比 | -0.849 | 6.035 | 0.020 | <0.01 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 纤维蛋白原 | 0.936 | 6.731 | 0.019 | 0.063 | 3.719 | 2.727 | 5.072 |
| FDP | 0.569 | 0.431 | 1.743 | <0.01 | 2.379 | 1.846 | 3.065 |
| 总胆固醇 | 1.001 | 0.342 | 8.567 | 0.020 | 0.797 | 0.659 | 0.965 |
| HDL-C | -1.932 | 0.971 | 3.960 | <0.01 | 0.074 | 0.030 | 0.182 |
| LDL-C | -1.609 | 0.546 | 8.684 | 0.030 | 0.741 | 0.566 | 0.971 |
| 脂蛋白 | 0.063 | 0.001 | 3 969 | <0.01 | 1.003 | 1.002 | 1.004 |
| GGT | 0.203 | 0.012 | 286.179 | 0.018 | 1.010 | 1.002 | 1.018 |
| hs-CRP | 0.026 | 0.023 | 1.277 | <0.01 | 1.170 | 1.109 | 1.234 |
| AFR | -0.622 | 0.723 | 0.739 | <0.01 | 0.654 | 0.600 | 0.711 |
| 白蛋白 | 0.782 | 2.134 | 0.134 | 0.132 | 0.779 | 0.736 | 0.825 |
| 项目 | 回归 系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 中性粒细胞占比 | 1.228 | 6.243 | 0.039 | 0.844 | 3.413 | 0.000 | 703 933.786 |
| 淋巴细胞占比 | -0.549 | 6.943 | 0.007 | 0.937 | 0.577 | 0.000 | 469 265.822 |
| FDP | 0.486 | 0.206 | 5.565 | 0.018 | 1.626 | 1.086 | 2.433 |
| 总胆固醇 | 1.388 | 0.462 | 9.013 | 0.003 | 4.009 | 1.619 | 9.926 |
| HDL-C | -2.293 | 0.935 | 6.013 | 0.014 | 0.101 | 0.016 | 0.630 |
| LDL-C | -1.909 | 0.638 | 8.953 | 0.003 | 0.148 | 0.042 | 0.517 |
| 脂蛋白 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 9.000 | <0.01 | 1.003 | 1.002 | 1.004 |
| GGT | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.250 | 0.596 | 1.003 | 0.992 | 1.014 |
| hs-CRP | 0.026 | 0.014 | 3.500 | 0.065 | 1.026 | 0.998 | 1.054 |
| AFR | -0.322 | 0.072 | 19.800 | <0.01 | 0.725 | 0.630 | 0.834 |
| 项目 | 回归 系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 中性粒细胞占比 | 1.228 | 6.243 | 0.039 | 0.844 | 3.413 | 0.000 | 703 933.786 |
| 淋巴细胞占比 | -0.549 | 6.943 | 0.007 | 0.937 | 0.577 | 0.000 | 469 265.822 |
| FDP | 0.486 | 0.206 | 5.565 | 0.018 | 1.626 | 1.086 | 2.433 |
| 总胆固醇 | 1.388 | 0.462 | 9.013 | 0.003 | 4.009 | 1.619 | 9.926 |
| HDL-C | -2.293 | 0.935 | 6.013 | 0.014 | 0.101 | 0.016 | 0.630 |
| LDL-C | -1.909 | 0.638 | 8.953 | 0.003 | 0.148 | 0.042 | 0.517 |
| 脂蛋白 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 9.000 | <0.01 | 1.003 | 1.002 | 1.004 |
| GGT | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.250 | 0.596 | 1.003 | 0.992 | 1.014 |
| hs-CRP | 0.026 | 0.014 | 3.500 | 0.065 | 1.026 | 0.998 | 1.054 |
| AFR | -0.322 | 0.072 | 19.800 | <0.01 | 0.725 | 0.630 | 0.834 |
| [1] |
Smith ER, Hewitson TD, Holt SG. Diagnostic tests for vascular calcification[J]. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis, 2019,26(6):445-463.
doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2019.07.001 URL |
| [2] |
Shao JS, Sierra OL, Cohen R, et al. Vascular calcification and aortic fibrosis: A bifunctional role for osteopontin in diabetic arteriosclerosis[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2011,31(8):1821-1833.
doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.230011 URL |
| [3] |
Zazzeroni L, Faggioli G, Pasquinelli G. Mechanisms of arterial calcification: The role of matrix vesicles[J]. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg, 2018,55(3):425-432.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2017.12.009 URL |
| [4] |
Youssef G, Guo M, McClelland RL, et al. Risk factors for the development and progression of thoracic aorta calcification: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis[J]. Acad Radiol, 2015,22(12):1536-1545.
doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2015.08.017 pmid: 26403646 |
| [5] |
Yang W, Zou B, Hou Y, et al. Extracellular vesicles in vascular calcification[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2019,499:118-122.
doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.09.002 URL |
| [6] |
Vossen LM, Kroon AA, Schurgers LJ, et al. Pharmacological and nutritional modulation of vascular calcification[J]. Nutrients, 2019,12(1):100.
doi: 10.3390/nu12010100 URL |
| [7] |
López-Mejías R, González-Gay MA. IL-6: Linking chronic inflammation and vascular calcification[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2019,15(8):457-459.
doi: 10.1038/s41584-019-0259-x pmid: 31235835 |
| [8] |
Sun DW, An L, Lv GY. Albumin-fibrinogen ratio and fibrinogen-prealbumin ratio as promising prognostic markers for cancers: An updated meta-analysis[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2020,18(1):9.
doi: 10.1186/s12957-020-1786-2 URL |
| [9] |
Demer LL, Tintut Y. Inflammatory, metabolic, and genetic mechanisms of vascular calcification[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2014,34(4):715-723.
doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302070 URL |
| [10] |
Leopold JA. Vascular calcification: Mechanisms of vascular smooth muscle cell calcification[J]. Trends Cardiovasc Med, 2015,25(4):267-274.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2014.10.021 URL |
| [11] |
Raggi P, Bellasi A, Bushinsky D, et al. Slowing progression of cardiovascular calcification with SNF472 in patients on hemodialysis: Results of a randomized phase 2b study[J]. Circulation, 2020,141(9):728-739.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044195 URL |
| [12] |
Akers EJ, Nicholls SJ, Di Bartolo BA. Plaque calcification: Do lipoproteins have a role?[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2019,39(10):1902-1910.
doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.311574 pmid: 31462089 |
| [13] |
Sánchez-Duffhues G, García de Vinuesa A, van de Pol V, et al. Inflammation induces endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and promotes vascular calcification through downregulation of BMPR2[J]. J Pathol, 2019,247(3):333-346.
doi: 10.1002/path.2019.247.issue-3 URL |
| [14] |
Arefin S, Buchanan S, Hobson S, et al. Nrf2 in early vascular ageing: Calcification, senescence and therapy[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2020,505:108-118.
doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.02.026 URL |
| [15] |
Lee SJ, Lee IK, Jeon JH. Vascular calcification-New insights into its mechanism[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020,21(8):2685.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21082685 URL |
| [16] |
Naito M. Effects of fibrinogen, fibrin and their degradation products on the behaviour of vascular smooth muscle cells[J]. Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi, 2000,37(6):458-463.
doi: 10.3143/geriatrics.37.458 URL |
| [17] |
Yakovlev S, Zhang L, Ugarova T, et al. Interaction of fibrin(ogen) with leukocyte receptor alpha M beta 2 (Mac-1): Further characterization and identification of a novel binding region within the central domain of the fibrinogen gamma-module[J]. Biochemistry, 2005,44(2):617-626.
pmid: 15641787 |
| [18] |
Fiuza M. Lipoprotein(a) as a novel therapeutic target for preventing cardiovascular disease:A whiter shade of pale?[J]. Rev Port Cardiol, 2019,38(7):495-496.
doi: 10.1016/j.repc.2019.08.006 URL |
| [19] |
Arques S. Human serum albumin in cardiovascular diseases[J]. Eur J Intern Med, 2018,52:8-12.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2018.04.014 URL |
| [20] |
Choi SR, Lee YK, Cho AJ, et al. Malnutrition, inflammation, progression of vascular calcification and survival: Inter-relationships in hemodialysis patients[J]. PLoS One, 2019,14(5):e0216415.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216415 URL |
| [21] |
Liu SL, Wu NQ, Shi HW, et al. Fibrinogen is associated with glucose metabolism and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2020,19(1):36.
doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01012-9 URL |
| [22] |
Dellegrottaglie S, Saran R, Rajagopalan S. Vascular calcification in patients with renal failure: Culprit or innocent bystander[J]. Cardiol Clin, 2005,23(3):373-384.
pmid: 16084285 |
| [23] |
Lia SQ, Jianga YH, Lin J, et al. Albumin-to- fibrinogen ratio as a promising biomarker to predict clinical outcome of non-small cell lung cancer individuals[J]. Cancer Med, 2018,7(4):1221-1231.
doi: 10.1002/cam4.2018.7.issue-4 URL |
| [24] |
Tsujino T, Komura K, Hashimoto T, et al. C-reactive protein-albumin ratio as prognostic factor in renal cell carcinoma-A data from multi-institutional study in Japan[J]. Urol Oncol, 2019,37(11):812.e1-812.e8.
doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2019.04.002 URL |
| [25] |
Özdemir M, Yurtdaᶊ M, Asoğlu R, et al. Fibrinogen to albumin ratio as a powerful predictor of the exaggerated morning blood pressure surge in newly diagnosed treatment-naive hypertensive patients[J]. Clin Exp Hypertens, 2020,42(8):692-699.
doi: 10.1080/10641963.2020.1779282 URL |
| [26] | Afifi NM, Medhat B, Abdel Ghani AM, et al. Value of albumin-fibrinogen ratio and CRP-albumin ratio as predictor marker of disease activity in egyptian RA patients, correlated with musculoskeletal sonography[J]. Open Access Rheumatol, 2020,12:241-248. |
| [27] | Kayapinar O, Ozde C, Kaya A. Relationship between the reciprocal change in inflammation-related biomarkers (fibrinogen-to-albumin and hs-CRP-to-albumin ratios) and the presence and severity of coronary slow flow[J]. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost, 2019,25:1076029619835383. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||