Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 428-433.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.05.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
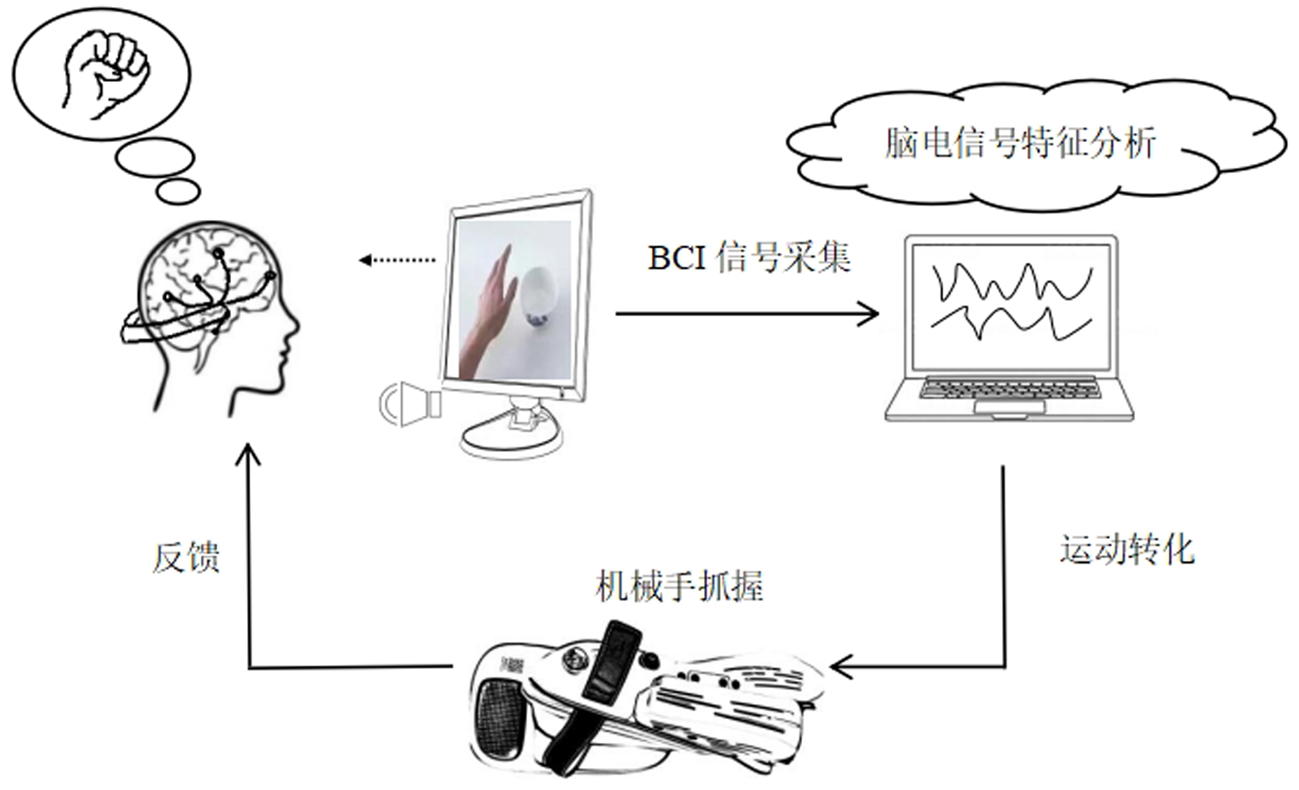
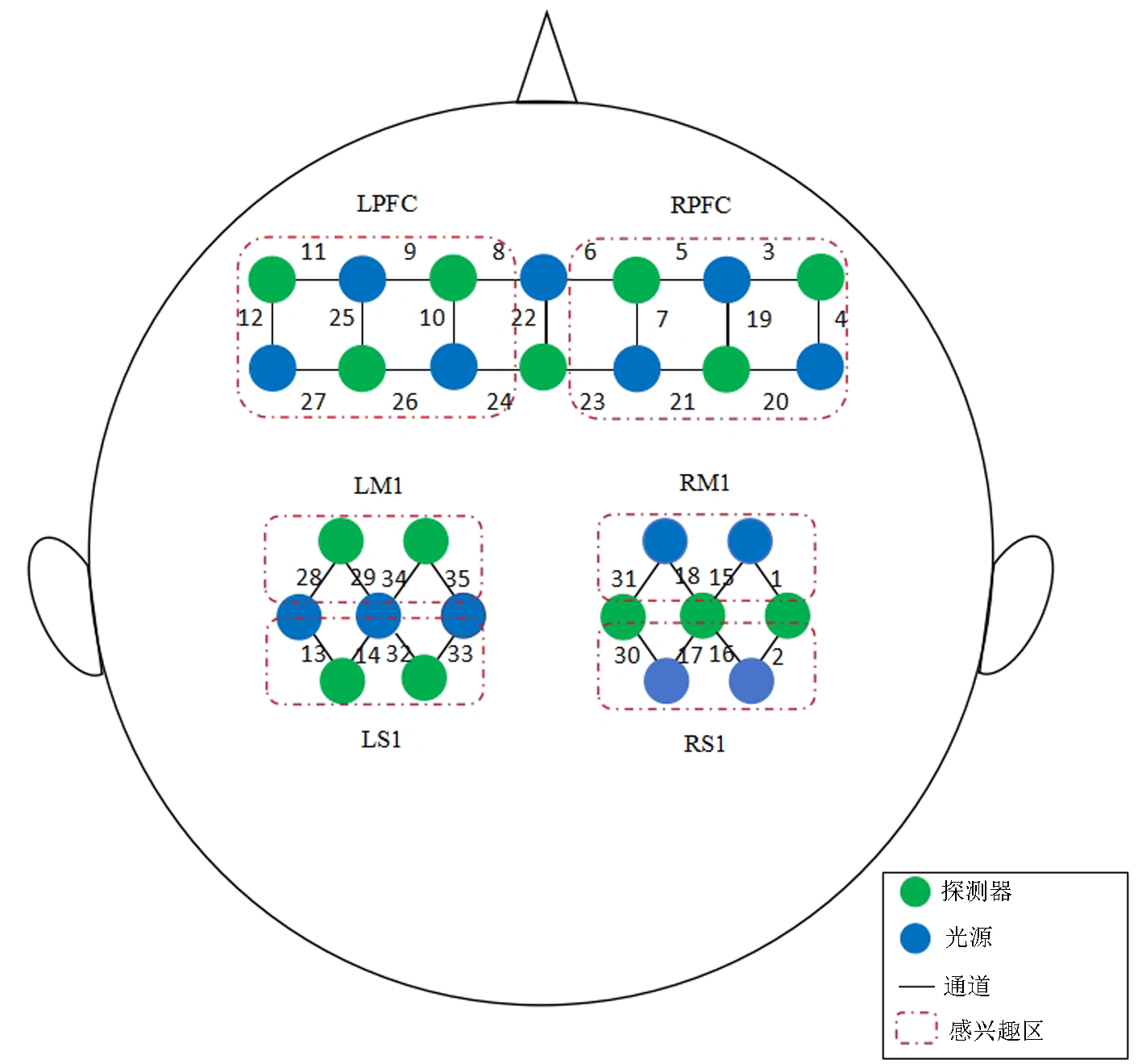
Effect of motor imagery-brain-computer interface training system on brain functional connectivity in subacute stroke patients with upper limb dysfunction by functional near infrared spectroscopy
Xu Sheng( ), Yang Qingqing, Zhang Min
), Yang Qingqing, Zhang Min
- Department of Rehabilitation, Changzhou De'an Hospital, Changzhou 213004, China
-
Received:2024-10-12Online:2025-05-20Published:2025-05-23 -
Contact:Xu Sheng E-mail:774128015@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Sheng, Yang Qingqing, Zhang Min. Effect of motor imagery-brain-computer interface training system on brain functional connectivity in subacute stroke patients with upper limb dysfunction by functional near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(5): 428-433.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.lchc.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.05.008
| 组别 | 例数 | 总体FC |
|---|---|---|
| 训练前 | 24 | 0.573±0.394 |
| 训练后 | 24 | 0.772±0.273 |
| t值 | -2.091 | |
| P值 | 0.042 |
Tab.1 Comparison of overall FC strength
| 组别 | 例数 | 总体FC |
|---|---|---|
| 训练前 | 24 | 0.573±0.394 |
| 训练后 | 24 | 0.772±0.273 |
| t值 | -2.091 | |
| P值 | 0.042 |
| 组别 | 例数 | RPFC- | RM1- | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPFC | RM1 | LM1 | RS1 | LS1 | LM1 | RS1 | LS1 | ||||||||
| 训练前 | 24 | 0.391(0.148,0.620) | 0.429(0.221,0.780) | 0.492±0.198 | 0.443(0.151,0.947) | 0.321(0.131,0.739) | 0.671±0.439 | 0.711±0.490 | 0.518(0.271,1.040) | ||||||
| 训练后 | 24 | 0.524(0.442,0.809) | 0.662(0.462,0.987) | 0.683±0.301 | 0.708(0.501,0.962) | 0.652(0.381,0.826) | 0.932±0.328 | 0.981±0.359 | 0.982(0.603,1.108) | ||||||
| t/Z值 | -2.261 | -1.939 | -1.872 | -1.868 | -1.891 | -2.301 | -2.120 | -1.921 | |||||||
| P值 | 0.021 | 0.052 | 0.071 | 0.059 | 0.062 | 0.029 | 0.038 | 0.061 | |||||||
| 组别 | LPFC- | LM1- | RS1-LS1 | ||||||||||||
| RM1 | LM1 | RS1 | LS1 | RS1 | LS1 | ||||||||||
| 训练前 | 0.429±0.361 | 0.418±0.411 | 0.453±0.381 | 0.452±0.392 | 0.523(0.322,1.217) | 0.771±0.547 | 0.780±0.431 | ||||||||
| 训练后 | 0.646±0.312 | 0.659±0.303 | 0.638±0.251 | 0.641±0.309 | 0.990(0.702,1.101) | 1.009±0.452 | 0.949±0.311 | ||||||||
| t/Z值 | -2.182 | -2.337 | -2.019 | -1.792 | -1.848 | -1.531 | -1.557 | ||||||||
| P值 | 0.032 | 0.023 | 0.051 | 0.079 | 0.058 | 0.131 | 0.130 | ||||||||
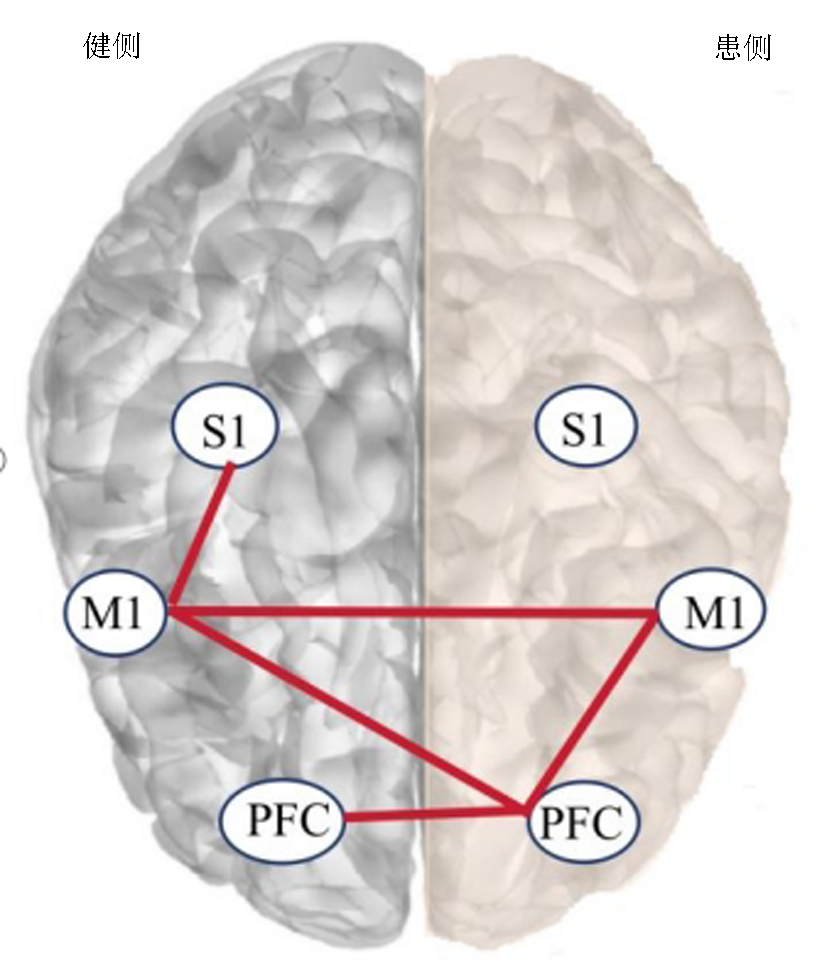
Tab.2 Comparison of FC strength between ROI
| 组别 | 例数 | RPFC- | RM1- | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPFC | RM1 | LM1 | RS1 | LS1 | LM1 | RS1 | LS1 | ||||||||
| 训练前 | 24 | 0.391(0.148,0.620) | 0.429(0.221,0.780) | 0.492±0.198 | 0.443(0.151,0.947) | 0.321(0.131,0.739) | 0.671±0.439 | 0.711±0.490 | 0.518(0.271,1.040) | ||||||
| 训练后 | 24 | 0.524(0.442,0.809) | 0.662(0.462,0.987) | 0.683±0.301 | 0.708(0.501,0.962) | 0.652(0.381,0.826) | 0.932±0.328 | 0.981±0.359 | 0.982(0.603,1.108) | ||||||
| t/Z值 | -2.261 | -1.939 | -1.872 | -1.868 | -1.891 | -2.301 | -2.120 | -1.921 | |||||||
| P值 | 0.021 | 0.052 | 0.071 | 0.059 | 0.062 | 0.029 | 0.038 | 0.061 | |||||||
| 组别 | LPFC- | LM1- | RS1-LS1 | ||||||||||||
| RM1 | LM1 | RS1 | LS1 | RS1 | LS1 | ||||||||||
| 训练前 | 0.429±0.361 | 0.418±0.411 | 0.453±0.381 | 0.452±0.392 | 0.523(0.322,1.217) | 0.771±0.547 | 0.780±0.431 | ||||||||
| 训练后 | 0.646±0.312 | 0.659±0.303 | 0.638±0.251 | 0.641±0.309 | 0.990(0.702,1.101) | 1.009±0.452 | 0.949±0.311 | ||||||||
| t/Z值 | -2.182 | -2.337 | -2.019 | -1.792 | -1.848 | -1.531 | -1.557 | ||||||||
| P值 | 0.032 | 0.023 | 0.051 | 0.079 | 0.058 | 0.131 | 0.130 | ||||||||
| [1] | Anwer S, Waris A, Gilani SO, et al. Rehabilitation of upper limb motor impairment in stroke: A narrative review on the prevalence, risk factors, and economic statistics of stroke and state of the art therapies[J]. Healthcare, 2022, 10(2):190-210. |
| [2] | Wang H, Arceo R, Chen S, et al. Effectiveness of interventions to improve hand motor function in individuals with moderate to severe stroke: A systematic review protocol[J]. BMJ open, 2019, 9(9): e032413. |
| [3] |
Lee KB, Lim SH, Kim KH, et al. Six-month functional recovery of stroke patients: A multi-time-point study[J]. Int J Rehabil Res, 2015, 38(2):173-180.
doi: 10.1097/MRR.0000000000000108 pmid: 25603539 |
| [4] | Salvalaggio S, Cacciante L, Maistrello L, et al. Clinical predictors for upper limb recovery after stroke rehabilitation: Retrospective cohort study[J]. Healthcare, 2023, 11(3):335-346. |
| [5] |
Wang H, Xiong X, Zhang K, et al. Motor network reorganization after motor imagery training in stroke patients with moderate to severe upper limb impairment[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2023, 29(2):619-632.
doi: 10.1111/cns.14065 pmid: 36575865 |
| [6] | 朱兰, 眭有昕, 王庆雷, 等. 对侧控制神经肌肉电刺激对脑卒中偏瘫患者脑功能连接的影响[J], 康复学报, 2023, 33(6):502-507. |
| [7] | Qu H, Zeng F, Tang Y, et al. The clinical effects of brain-computer interface with robot on upper-limb function for post-stroke rehabilitation: A meta-analysis and systematic review[J]. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol, 2024, 19(1):30-41. |
| [8] | 蔡楚杰, 李四楠, 刘天, 等. 运动想象脑机接口在脑卒中后上肢康复中的研究进展[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2023, 38(6):851-857. |
| [9] | Frolov AA, Olesya M, Roman L, et al. Post-stroke rehabilitation training with a motor-imagery-based brain-computer interface (BCI)-controlled hand exoskeleton: A randomized controlled multicenter trial[J]. Front Neurosci, 2017, 11(20):1-11. |
| [10] |
Ramos-Murguialday A, Broetz D, Rea M, et al. Brain-machine interface in chronic stroke rehabilitation: A controlled study[J]. Ann Neurol, 2013, 74(1):100-108.
doi: 10.1002/ana.23879 pmid: 23494615 |
| [11] | 中华医学会神经病学分会, 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 中国各类主要脑血管病诊断要点2019[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2019, 52(9):710-715. |
| [12] |
田婧, 刘珏, 何志杰, 等. 基于功能性近红外光谱技术的脑卒中后上肢运动功能障碍患者单侧上肢训练和双侧上肢训练脑网络功能连接对比研究[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2022, 28(5):497-501.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2022.05.001 |
| [13] | Abiri R, Borhani S, Sellers EW, et al. A comprehensive review of EEG-based brain-computer interface paradigms[J]. J Neural Eng, 2019, 16(1):1-21. |
| [14] |
陈树耿, 贾杰. 脑机接口在脑卒中手功能康复中的应用进展[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2017, 23(1):23-26.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2017.01.006 |
| [15] | Biasiucci A, Leeb R, Iturrate I, et al. Brain-actuated functional electrical stimulation elicits lasting arm motor recovery after stroke[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1):1-13. |
| [16] | Sun X, Li M, Li Q, et al. Poststroke cognitive impairment research progress on application of brain-computer interface[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2022, 7(14):1-16. |
| [17] | 薛超, 王敏. 脑卒中后上肢和手功能的康复治疗研究新进展[J]. 中华全科医学, 2016, 14(11):1932-1935. |
| [18] | 陈佳丽, 董继革, 黄富表. 脑机接口治疗脑卒中上肢功能及大脑可塑性的研究进展[J]. 中国老年保健医学, 2023, 21(5):22-26. |
| [19] | Rahman MA, Siddik AB, Ghosh TK, et al. A narrative review on clinical applications of fNIRS[J]. J Digit Imaging, 2020, 33(1):1167-1184. |
| [20] |
Ward NS. Functional reorganization of the cerebral motor system after stroke[J]. Curr Opin Neurol, 2004, 17(6):725-730.
doi: 10.1097/00019052-200412000-00013 pmid: 15542982 |
| [21] |
Cole MW, Ito T, Cocuzza C, et al. The functional relevance of task-state functional connectivity[J]. J Neurosci, 2021, 41(12):2684-2702.
doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1713-20.2021 pmid: 33542083 |
| [22] | James DRC, Leff DR, Orihuela-espina F, et al. Enhanced frontoparietal network architectures following “gaze-contingent” versus “free-hand” motor learning[J]. Neuroimage, 2013, 64(11):267-276. |
| [23] |
Ocklenburg S, Ball A, Wolf CC, et al. Functional cerebral lateralization and interhemispheric interaction in patients with callosal agenesis[J]. Neuropsychology, 2015, 29(5):806-815.
doi: 10.1037/neu0000193 pmid: 25798664 |
| [24] | 姜林鸿, 刘晓丹, 孙萍萍, 等. 运动想象训练对卒中后患者上肢运动功能恢复的影响及静息态fNIRS脑网络特征研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2023(11):1505-1513. |
| [25] |
Peters DM, Fridriksson J, Stewart JC, et al. Cortical disconnection of the ipsilesional primary motor cortex is associated with gait speed and upper extremity motor impairment in chronic left hemispheric stroke[J]. Hum Brain Mapp, 2018, 39(1):120-132.
doi: 10.1002/hbm.23829 pmid: 28980355 |
| [26] | 吕政, 刘世文. 初级运动区和次级运动区的作用[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2003, 18(11):702-704. |
| [27] | Ang KK, Guan C. Brain-computer interface for neurorehabilitation of upper limb after stroke[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2015, 103(6):944-953. |
| [28] |
Gardner EP, Putrino DF, Chen J. Neural representation in M1 and S1 cortex of bilateral hand actions during prehension[J]. J Neurophysiol, 2022, 127(4):1007-1025.
doi: 10.1152/jn.00374.2021 pmid: 35294304 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||