Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 504-508.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.06.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation of JP2 with atrial fibrillation in patients with essential hypertension
Si Huili1,2, Guo Shuang2, Dong Haocheng1, Li Shuren2( )
)
- 1. Department of Internal Medicine, Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050017, China
2. Department of Cardiology, Hebei General Hospital, Shijiazhuang 050051, China
-
Received:2025-04-22Online:2025-06-20Published:2025-07-01 -
Contact:Li Shuren E-mail:lsr64@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Si Huili, Guo Shuang, Dong Haocheng, Li Shuren. Correlation of JP2 with atrial fibrillation in patients with essential hypertension[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(6): 504-508.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.lchc.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.06.004
| 项目 | EH+AF组(n=52) | EH组(n=75) | χ2/t/Z值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | 70.1±11.3 | 64.2±12.4 | -3.042 | 0.003 |
| 女性[例(%)] | 27(51.9) | 40(53.3) | 0.025 | 0.876 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 26.2(4.6) | 26.0(4.4) | -0.691 | 0.489 |
| 饮酒史[例(%)] | 12(23.1) | 10(13.3) | 2.036 | 0.154 |
| 吸烟史[例(%)] | 15(28.8) | 14(18.7) | 1.806 | 0.179 |
| 糖尿病史[例(%)] | 12(23.1) | 28(37.3) | 2.893 | 0.089 |
| 冠心病史[例(%)] | 24(46.2) | 40(53.3) | 0.633 | 0.426 |
| 空腹血糖(mmol/L) | 5.4(1.0) | 5.1(1.6) | -1.897 | 0.058 |
| 尿酸(μmol/L) | 333.8(102.0) | 310.9(111.4) | -1.657 | 0.097 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.3(1.2) | 2.7(1.0) | -1.630 | 0.103 |
| eGFR(ml/min) | 80.4(23.3) | 91.4(14.5) | -3.731 | <0.001 |
| WBC(×109/L) | 6.4(2.4) | 6.1(2.3) | -0.613 | 0.540 |
| HB(g/L) | 135.3±17.8 | 134.6±16.2 | 0.220 | 0.826 |
| NT-proBNP (ng/L) | 278.0(720.0) | 71.0(69.0) | -5.334 | <0.001 |
| JP2 (ng/L) | 43.8(11.0) | 60.3(24.3) | -6.306 | <0.001 |
| LAD (mm) | 44(7) | 38(5) | -5.812 | <0.001 |
| LVESD (mm) | 31.0(4.0) | 29.5(5.0) | -2.635 | 0.008 |
| LVEDD (mm) | 47.0(7.0) | 46.5(5.0) | -1.367 | 0.171 |
| LVEF (%) | 62.0(5.0) | 65.0(6.8) | -2.785 | 0.005 |
Tab. 1 Comparison of clinical data between the two groups
| 项目 | EH+AF组(n=52) | EH组(n=75) | χ2/t/Z值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | 70.1±11.3 | 64.2±12.4 | -3.042 | 0.003 |
| 女性[例(%)] | 27(51.9) | 40(53.3) | 0.025 | 0.876 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 26.2(4.6) | 26.0(4.4) | -0.691 | 0.489 |
| 饮酒史[例(%)] | 12(23.1) | 10(13.3) | 2.036 | 0.154 |
| 吸烟史[例(%)] | 15(28.8) | 14(18.7) | 1.806 | 0.179 |
| 糖尿病史[例(%)] | 12(23.1) | 28(37.3) | 2.893 | 0.089 |
| 冠心病史[例(%)] | 24(46.2) | 40(53.3) | 0.633 | 0.426 |
| 空腹血糖(mmol/L) | 5.4(1.0) | 5.1(1.6) | -1.897 | 0.058 |
| 尿酸(μmol/L) | 333.8(102.0) | 310.9(111.4) | -1.657 | 0.097 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.3(1.2) | 2.7(1.0) | -1.630 | 0.103 |
| eGFR(ml/min) | 80.4(23.3) | 91.4(14.5) | -3.731 | <0.001 |
| WBC(×109/L) | 6.4(2.4) | 6.1(2.3) | -0.613 | 0.540 |
| HB(g/L) | 135.3±17.8 | 134.6±16.2 | 0.220 | 0.826 |
| NT-proBNP (ng/L) | 278.0(720.0) | 71.0(69.0) | -5.334 | <0.001 |
| JP2 (ng/L) | 43.8(11.0) | 60.3(24.3) | -6.306 | <0.001 |
| LAD (mm) | 44(7) | 38(5) | -5.812 | <0.001 |
| LVESD (mm) | 31.0(4.0) | 29.5(5.0) | -2.635 | 0.008 |
| LVEDD (mm) | 47.0(7.0) | 46.5(5.0) | -1.367 | 0.171 |
| LVEF (%) | 62.0(5.0) | 65.0(6.8) | -2.785 | 0.005 |
| 自变量 | 单因素logistic回归分析 | 多因素logistic回归分析 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR值 | 95%CI | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | P值 | ||
| 年龄 | 1.048 | 1.015~1.082 | 0.004 | 0.989 | 0.937~1.044 | 0.685 | |
| eGFR | -0.959 | 0.936~0.983 | 0.001 | -0.997 | 0.959~1.036 | 0.864 | |
| NT-proBNP | 1.005 | 1.002~1.007 | <0.001 | 1.002 | 0.999~1.005 | 0.179 | |
| JP2 | -0.912 | 0.881~0.944 | <0.001 | -0.901 | 0.860~0.944 | <0.001 | |
| LAD | 1.300 | 1.173~1.441 | <0.001 | 1.339 | 1.130~1.586 | 0.001 | |
| LVESD | 1.155 | 1.039~1.284 | 0.008 | 0.957 | 0.778~1.177 | 0.676 | |
| LVEF | -0.906 | 0.843~0.974 | 0.007 | -0.902 | 0.795~1.023 | 0.109 | |
Tab.2 Logistic regression analysis of risk factors for AF in EH patients
| 自变量 | 单因素logistic回归分析 | 多因素logistic回归分析 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR值 | 95%CI | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | P值 | ||
| 年龄 | 1.048 | 1.015~1.082 | 0.004 | 0.989 | 0.937~1.044 | 0.685 | |
| eGFR | -0.959 | 0.936~0.983 | 0.001 | -0.997 | 0.959~1.036 | 0.864 | |
| NT-proBNP | 1.005 | 1.002~1.007 | <0.001 | 1.002 | 0.999~1.005 | 0.179 | |
| JP2 | -0.912 | 0.881~0.944 | <0.001 | -0.901 | 0.860~0.944 | <0.001 | |
| LAD | 1.300 | 1.173~1.441 | <0.001 | 1.339 | 1.130~1.586 | 0.001 | |
| LVESD | 1.155 | 1.039~1.284 | 0.008 | 0.957 | 0.778~1.177 | 0.676 | |
| LVEF | -0.906 | 0.843~0.974 | 0.007 | -0.902 | 0.795~1.023 | 0.109 | |
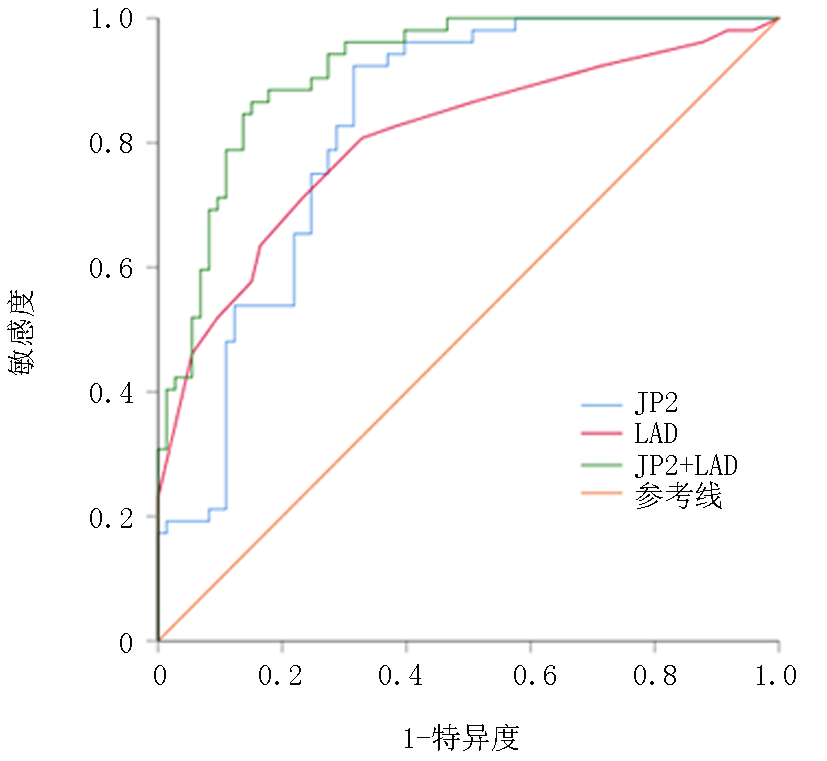
| 因素 | AUC | 95%CI | P值 | 截断值 | 特异度 | 敏感度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2 | 0.825 | 0.753~0.897 | <0.001 | 57.02 ng/L | 68.5% | 92.3% |
| LAD | 0.805 | 0.724~0.886 | <0.001 | 39.5 mm | 67.1% | 80.8% |
| JP2+LAD | 0.918 | 0.871~0.964 | <0.001 | - | 84.9% | 86.5% |
Tab.3 The predictive value of JP2 and LAD in predicting AF in EH patients
| 因素 | AUC | 95%CI | P值 | 截断值 | 特异度 | 敏感度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2 | 0.825 | 0.753~0.897 | <0.001 | 57.02 ng/L | 68.5% | 92.3% |
| LAD | 0.805 | 0.724~0.886 | <0.001 | 39.5 mm | 67.1% | 80.8% |
| JP2+LAD | 0.918 | 0.871~0.964 | <0.001 | - | 84.9% | 86.5% |
| [1] |
Gorenek B, Pelliccia A, Benjamin EJ, et al. European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA)/European Association of Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation (EACPR) position paper on how to prevent atrial fibrillation endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) and Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS)[J]. Europace, 2017, 19(2): 190-225.
doi: 10.1093/europace/euw242 pmid: 28175283 |
| [2] | 中华医学会心血管病学分会, 中国生物医学工程学会心律分会. 心房颤动诊断和治疗中国指南[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2023, 51(6): 572-618. |
| [3] |
Chen B, Guo A, Zhang C, et al. Critical roles of junctophilin-2 in T-tubule and excitation-contraction coupling maturation during postnatal development[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2013, 100(1): 54-62.
doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvt180 pmid: 23860812 |
| [4] | Gross P, Johnson J, Romero CM, et al. Interaction of the joining region in junctophilin-2 with the L-type Ca(2+) channel is pivotal for cardiac dyad assembly and intracellular Ca(2+) dynamics[J]. Circ Res, 2021, 128(1): 92-114. |
| [5] | Brandenburg S, Pawlowitz J, Eikenbusch B, et al. Junctophilin-2 expression rescues atrial dysfunction through polyadic junctional membrane complex biogenesis[J]. JCI Insight, 2019, 4(12):e127116. |
| [6] | 国家卫生健康委员会疾病预防控制局, 国家心血管病中心, 中国医学科学院阜外医院, 等. 中国高血压健康管理规范(2019)[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2020, 48(1): 10-46. |
| [7] |
Andrade J, Khairy P, Dobrev D, et al. The clinical profile and pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation: Relationships among clinical features, epidemiology, and mechanisms[J]. Circ Res, 2014, 114(9): 1453-1468.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.303211 pmid: 24763464 |
| [8] |
Heijman J, Muna AP, Veleva T, et al. Atrial myocyte NLRP3/CaMKII nexus forms a substrate for postoperative atrial fibrillation[J]. Circ Res, 2020, 127(8): 1036-1055.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316710 pmid: 32762493 |
| [9] | De Mello WC. Local renin angiotensin aldosterone systems and cardiovascular diseases[J]. Med Clin North Am, 2017, 101(1): 117-127. |
| [10] | Ling XX, Chen H, Fu BB, et al. Xin-Ji-Er-Kang protects myocardial and renal injury in hypertensive heart failure in mice[J]. Phytomedicine, 2021, 91: 153675. |
| [11] |
Landstrom AP, Weisleder N, Batalden KB, et al. Mutations in JPH2-encoded junctophilin-2 associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in humans[J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2007, 42(6): 1026-1035.
doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.04.006 pmid: 17509612 |
| [12] |
van Oort RJ, Garbino A, Wang W, et al. Disrupted junctional membrane complexes and hyperactive ryanodine receptors after acute junctophilin knockdown in mice[J]. Circulation, 2011, 123(9): 979-988.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.006437 pmid: 21339484 |
| [13] |
Hill JA, Diwan A. Ca(2+) leak in atrial fibrillation: Junctophilin-2 stabilizes ryanodine receptor[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2013, 62(21): 2020-2022.
doi: S0735-1097(13)03088-X pmid: 23973695 |
| [14] | Landstrom AP, Yang Q, Sun B, et al. Reduction in Junctophilin 2 expression in cardiac nodal tissue results in intracellular calcium-driven increase in nodal cell automaticity[J]. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2023, 16(2): e010858. |
| [15] |
Page E, Surdyk-Droske M. Distribution, surface density, and membrane area of diadic junctional contacts between plasma membrane and terminal cisterns in mammalian ventricle[J]. Circ Res, 1979, 45(2): 260-267.
doi: 10.1161/01.res.45.2.260 pmid: 376173 |
| [16] |
Takeshima H, Komazaki S, Nishi M, et al. Junctophilins: A novel family of junctional membrane complex proteins[J]. Mol Cell, 2000, 6(1): 11-22.
doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00003-4 pmid: 10949023 |
| [17] | Guo A, Wang Y, Chen B, et al. E-C coupling structural protein junctophilin-2 encodes a stress-adaptive transcription regulator[J]. Science, 2018, 362(6421). |
| [18] | Wu CY, Chen B, Jiang YP, et al. Calpain-dependent cleavage of junctophilin-2 and T-tubule remodeling in a mouse model of reversible heart failure[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2014, 3(3): e000527. |
| [19] |
Guo A, Hall D, Zhang C, et al. Molecular determinants of calpain-dependent cleavage of junctophilin-2 protein in cardiomyocytes[J]. J Biol Chem, 2015, 290(29): 17946-17955.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.652396 pmid: 26063807 |
| [20] |
Molkentin JD, Lu JR, Antos CL, et al. A calcineurin-dependent transcriptional pathway for cardiac hypertrophy[J]. Cell, 1998, 93(2): 215-228.
doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81573-1 pmid: 9568714 |
| [21] | Seko Y, Kato T, Haruna T, et al. Association between atrial fibrillation, atrial enlargement, and left ventricular geometric remodeling[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 6366. |
| [22] | Chahine Y, Chamoun N, Kassar A, et al. Atrial fibrillation substrate and impaired left atrial function: A cardiac MRI study[J]. Europace, 2024, 26(11): euae258. |
| [23] | Cunha PS, Laranjo S, Heijman J, et al. The atrium in atrial fibrillation-A clinical review on how to manage atrial fibrotic substrates[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9: 879984. |
| [24] |
Van Gelder IC, Rienstra M, Bunting KV, et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS)[J]. Eur Heart J, 2024, 45(36): 3314-3414.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae176 pmid: 39210723 |
| [25] |
Zhang W, Wang JG. Prevention of atrial fibrillation by intensive antihypertensive treatment[J]. Hypertension, 2020, 75(6): 1414-1416.
doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.14856 pmid: 32401649 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||