Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 513-518.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.06.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Association of poor living habits and smoking with primary membranous nephropathy
Song Chenlu1, Qi Xiaojing2, Chen Yipeng1, Xing Guangqun2( )
)
- 1. Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, China
2. Department of Nephrology,the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266555, China
-
Received:2025-02-07Online:2025-06-20Published:2025-07-01 -
Contact:Xing Guangqun E-mail:xinggq@qdu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Song Chenlu, Qi Xiaojing, Chen Yipeng, Xing Guangqun. Association of poor living habits and smoking with primary membranous nephropathy[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(6): 513-518.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.lchc.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.06.006
| 项目 | PMN组(n=227) | MCD组(n=58) | t/Z/χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性[例(%)] | 164(72.2) | 30(51.7) | 9.262 | 0.002 |
| 年龄(年) | 49.4±13.1 | 44.7±18.9 | 2.200 | 0.029 |
| 24 h尿蛋白(g/24 h) | 5.0±3.6 | 8.2±10.9 | -3.638 | <0.001 |
| 血白蛋白(g/L) | 33.5±13.1 | 27.7±11.9 | 2.971 | 0.003 |
| 血前白蛋白(mg/L) | 280.4±76.0 | 227.4±71.8 | 3.998 | <0.001 |
| 血肌酐(μmol/L) | 77.0±23.6 | 79.6±30.5 | -0.686 | 0.493 |
| 血尿素氮(mmol/L) | 5.9±2.5 | 6.2±1.2 | -0.196 | 0.846 |
| 血尿酸(μmol/L) | 385.0±105.3 | 382.3±118.5 | 0.159 | 0.874 |
| 补体C3(g/L) | 1.1±0.2 | 1.3±0.2 | -4.280 | <0.001 |
| 丙氨酸氨基转移酶(U/L) | 24.4±16.6 | 34.9±45.4 | -2.815 | 0.005 |
| 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(U/L) | 20.6±11.3 | 27.7±23.3 | -3.197 | 0.002 |
| 红细胞沉降率(mm/h) | 27.4±25.0 | 42.2±25.9 | -3.578 | <0.001 |
| D-二聚体(g/L) | 330(200, 565) | 430(310, 565) | -0.317 | 0.752 |
| 血小板(×109/L) | 245.5±67.3 | 248.7±58.6 | -0.312 | 0.755 |
| 血红蛋白(g/L) | 138.6±17 | 132.6±21.3 | 0.774 | 0.440 |
Tab.1 Comparison of clinical data between the two groups in the single-center cohort
| 项目 | PMN组(n=227) | MCD组(n=58) | t/Z/χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男性[例(%)] | 164(72.2) | 30(51.7) | 9.262 | 0.002 |
| 年龄(年) | 49.4±13.1 | 44.7±18.9 | 2.200 | 0.029 |
| 24 h尿蛋白(g/24 h) | 5.0±3.6 | 8.2±10.9 | -3.638 | <0.001 |
| 血白蛋白(g/L) | 33.5±13.1 | 27.7±11.9 | 2.971 | 0.003 |
| 血前白蛋白(mg/L) | 280.4±76.0 | 227.4±71.8 | 3.998 | <0.001 |
| 血肌酐(μmol/L) | 77.0±23.6 | 79.6±30.5 | -0.686 | 0.493 |
| 血尿素氮(mmol/L) | 5.9±2.5 | 6.2±1.2 | -0.196 | 0.846 |
| 血尿酸(μmol/L) | 385.0±105.3 | 382.3±118.5 | 0.159 | 0.874 |
| 补体C3(g/L) | 1.1±0.2 | 1.3±0.2 | -4.280 | <0.001 |
| 丙氨酸氨基转移酶(U/L) | 24.4±16.6 | 34.9±45.4 | -2.815 | 0.005 |
| 天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(U/L) | 20.6±11.3 | 27.7±23.3 | -3.197 | 0.002 |
| 红细胞沉降率(mm/h) | 27.4±25.0 | 42.2±25.9 | -3.578 | <0.001 |
| D-二聚体(g/L) | 330(200, 565) | 430(310, 565) | -0.317 | 0.752 |
| 血小板(×109/L) | 245.5±67.3 | 248.7±58.6 | -0.312 | 0.755 |
| 血红蛋白(g/L) | 138.6±17 | 132.6±21.3 | 0.774 | 0.440 |
| 项目 | 单中心 | 多中心 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMN组 (n=227) | MCD组 (n=58) | t/χ2值 | P值 | PMN组 (n=304) | MCD组 (n=78) | t/χ2值 | P值 | |||
| 男性[例(%)] | 165(72.7) | 30(51.7) | 9.396 | 0.002 | 220(72.1) | 40(51.3) | 12.385 | <0.001 | ||
| 年龄(年) | 49.4±13.1 | 44.7±18.9 | 2.184 | 0.030 | 48.0±13.7 | 42.8±18.4 | 2.758 | 0.006 | ||
| 体质量指数(kg/m2) | 25.9±3.6 | 25.4±4.6 | 0.847 | 0.398 | 25.1±3.9 | 25.2±4.4 | -0.030 | 0.976 | ||
| 高血压史[例(%)] | 125(55.3) | 18(31.0) | 10.880 | 0.001 | 169(55.6) | 23(29.5) | 16.921 | <0.001 | ||
| 收缩压(mmHg) | 137.1±17.7 | 130.1±20.3 | 2.589 | 0.010 | 136.5±17.4 | 129.5±19.6 | 3.054 | 0.002 | ||
| 舒张压(mmHg) | 81.1±12.1 | 76.3±11.3 | 2.726 | 0.007 | 82.7±12.9 | 78.2±11.9 | 2.777 | 0.006 | ||
| 高盐饮食[例(%)] | 86(58.5) | 17(29.3) | 14.178 | <0.001 | 152(67.9) | 33(42.3) | 15.913 | <0.001 | ||
| 糖尿病史[例(%)] | 31(13.7) | 3(5.2) | 3.165 | 0.075 | 58(19.0) | 5(6.4) | 7.182 | 0.007 | ||
| 高糖饮食[例(%)] | 77(36.8) | 19(32.8) | 0.329 | 0.566 | 111(38.7) | 28(38.4) | 0.003 | 0.960 | ||
| 高脂血症[例(%)] | 202(89.0) | 57(98.3) | 4.808 | 0.028 | 268(88.2) | 73(93.6) | 1.912 | 0.167 | ||
| 高甘油三酯血症[例(%)] | 78(55.7) | 27(52.9) | 0.116 | 0.733 | 142(65.4) | 40(56.3) | 1.905 | 0.168 | ||
| 高胆固醇血症[例(%)] | 108(77.7) | 51(100.0) | 13.592 | <0.001 | 167(77.3) | 62(87.3) | 3.320 | 0.068 | ||
| 高脂饮食[例(%)] | 101(50.5) | 16(27.6) | 9.525 | 0.002 | 148(54.0) | 23(29.9) | 14.025 | <0.001 | ||
| 餐馆或外卖[例(%)] | 54(33.1) | 11(19.0) | 4.133 | 0.042 | 94(40.7) | 18(24.7) | 6.130 | 0.013 | ||
| 常进食夜宵[例(%)] | 8(12.3) | 4(6.9) | 1.019 | 0.313 | 39(29.3) | 10(13.7) | 6.347 | 0.012 | ||
| 规律用餐[例(%)] | 155(73.5) | 48(82.8) | 2.125 | 0.145 | 220(76.7) | 64(82.1) | 1.034 | 0.309 | ||
| 丰盛晚餐[例(%)] | 30(46.2) | 18(31.0) | 2.944 | 0.086 | 85(61.2) | 21(26.9) | 23.426 | <0.001 | ||
| 精神压力[例(%)] | 78(37.5) | 16(28.6) | 1.534 | 0.216 | 121(42.5) | 30(39.5) | 0.219 | 0.640 | ||
| 经常熬夜[例(%)] | 2(18.2) | - | - | - | 45(51.7) | 10(50.0) | 0.019 | 0.889 | ||
| 夜班多[例(%)] | 2(16.7) | - | - | - | 35(43.8) | 5(29.4) | 1.190 | 0.275 | ||
Tab.2 Comparison of unhealthy diet and sleep habits between the two groups in the single-center and multi-center cohorts
| 项目 | 单中心 | 多中心 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMN组 (n=227) | MCD组 (n=58) | t/χ2值 | P值 | PMN组 (n=304) | MCD组 (n=78) | t/χ2值 | P值 | |||
| 男性[例(%)] | 165(72.7) | 30(51.7) | 9.396 | 0.002 | 220(72.1) | 40(51.3) | 12.385 | <0.001 | ||
| 年龄(年) | 49.4±13.1 | 44.7±18.9 | 2.184 | 0.030 | 48.0±13.7 | 42.8±18.4 | 2.758 | 0.006 | ||
| 体质量指数(kg/m2) | 25.9±3.6 | 25.4±4.6 | 0.847 | 0.398 | 25.1±3.9 | 25.2±4.4 | -0.030 | 0.976 | ||
| 高血压史[例(%)] | 125(55.3) | 18(31.0) | 10.880 | 0.001 | 169(55.6) | 23(29.5) | 16.921 | <0.001 | ||
| 收缩压(mmHg) | 137.1±17.7 | 130.1±20.3 | 2.589 | 0.010 | 136.5±17.4 | 129.5±19.6 | 3.054 | 0.002 | ||
| 舒张压(mmHg) | 81.1±12.1 | 76.3±11.3 | 2.726 | 0.007 | 82.7±12.9 | 78.2±11.9 | 2.777 | 0.006 | ||
| 高盐饮食[例(%)] | 86(58.5) | 17(29.3) | 14.178 | <0.001 | 152(67.9) | 33(42.3) | 15.913 | <0.001 | ||
| 糖尿病史[例(%)] | 31(13.7) | 3(5.2) | 3.165 | 0.075 | 58(19.0) | 5(6.4) | 7.182 | 0.007 | ||
| 高糖饮食[例(%)] | 77(36.8) | 19(32.8) | 0.329 | 0.566 | 111(38.7) | 28(38.4) | 0.003 | 0.960 | ||
| 高脂血症[例(%)] | 202(89.0) | 57(98.3) | 4.808 | 0.028 | 268(88.2) | 73(93.6) | 1.912 | 0.167 | ||
| 高甘油三酯血症[例(%)] | 78(55.7) | 27(52.9) | 0.116 | 0.733 | 142(65.4) | 40(56.3) | 1.905 | 0.168 | ||
| 高胆固醇血症[例(%)] | 108(77.7) | 51(100.0) | 13.592 | <0.001 | 167(77.3) | 62(87.3) | 3.320 | 0.068 | ||
| 高脂饮食[例(%)] | 101(50.5) | 16(27.6) | 9.525 | 0.002 | 148(54.0) | 23(29.9) | 14.025 | <0.001 | ||
| 餐馆或外卖[例(%)] | 54(33.1) | 11(19.0) | 4.133 | 0.042 | 94(40.7) | 18(24.7) | 6.130 | 0.013 | ||
| 常进食夜宵[例(%)] | 8(12.3) | 4(6.9) | 1.019 | 0.313 | 39(29.3) | 10(13.7) | 6.347 | 0.012 | ||
| 规律用餐[例(%)] | 155(73.5) | 48(82.8) | 2.125 | 0.145 | 220(76.7) | 64(82.1) | 1.034 | 0.309 | ||
| 丰盛晚餐[例(%)] | 30(46.2) | 18(31.0) | 2.944 | 0.086 | 85(61.2) | 21(26.9) | 23.426 | <0.001 | ||
| 精神压力[例(%)] | 78(37.5) | 16(28.6) | 1.534 | 0.216 | 121(42.5) | 30(39.5) | 0.219 | 0.640 | ||
| 经常熬夜[例(%)] | 2(18.2) | - | - | - | 45(51.7) | 10(50.0) | 0.019 | 0.889 | ||
| 夜班多[例(%)] | 2(16.7) | - | - | - | 35(43.8) | 5(29.4) | 1.190 | 0.275 | ||
| 项目 | 单中心 | 多中心 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMN组 (n=227) | MCD组 (n=58) | t/χ2值 | P值 | PMN组 (n=304) | MCD组 (n=78) | t/χ2值 | P值 | ||
| 饮酒史[例(%)] | 99(43.6) | 9(15.5) | 15.494 | <0.001 | 134(44.2) | 14(17.9) | 18.028 | <0.001 | |
| 饮酒累积时间(年) | 23.7±11.6 | 25.6±15 | -0.435 | 0.665 | 21.4±13.2 | 22.1±13.5 | -0.163 | 0.870 | |
| 每日消耗酒精(g) | 150(100, 250) | 200(100, 375) | -0.295 | 0.769 | 100(100, 250) | 100(75, 325) | -0.432 | 0.667 | |
| 饮酒指数 | 4500(2000, 7500) | 4500(2000, 9375) | -0.201 | 0.841 | 3000(1500, 7125) | 4000(1500, 7600) | -0.453 | 0.652 | |
| 吸烟史[例(%)] | 105(46.3) | 18(31.0) | 4.363 | 0.037 | 140(45.9) | 20(25.6) | 10.483 | 0.001 | |
| 吸烟累积时间(年) | 25.0±13.0 | 21.6±13.5 | 0.942 | 0.348 | 22.3±14.2 | 21.4±12.7 | 0.246 | 0.806 | |
| 偶尔[例(%)] | 122(57.8) | 40(71.4) | 165(57.3) | 58(76.4) | |||||
| 1~15年[例(%)] | 21(10.0) | 5(8.9) | 3.767 | 0.152 | 40(13.9) | 5(6.6) | 9.280 | 0.010 | |
| >15年[例(%)] | 68(30.0) | 11(19.6) | 83(28.8) | 13(17.1) | |||||
| 每日吸烟量(支) | 21.1±12.7 | 21.8±11.7 | -0.222 | 0.825 | 19.4±12.4 | 20.9±11.6 | -0.513 | 0.609 | |
| 偶尔[例(%)] | 122(56.5) | 40(69.0) | 165(57.3) | 58(74.4) | |||||
| 1~20支/d[例(%)] | 32(14.8) | 5(8.6) | 3.165 | 0.205 | 48(16.7) | 6(7.7) | 7.938 | 0.019 | |
| >20支/d[例(%)] | 62(28.7) | 13(22.4) | 75(26.0) | 14(17.9) | |||||
| 吸烟指数 | 450(200, 800) | 500(110, 800) | 0.415 | 0.679 | 400(103.8, 800) | 400(95, 800) | 0.100 | 0.921 | |
| 偶尔[例(%)] | 122(58.9) | 40(71.4) | 165(59.1) | 58(76.3) | |||||
| 1~400[例(%)] | 34(16.4) | 7(12.5) | 2.970 | 0.227 | 52(18.6) | 8(10.5) | 7.550 | 0.023 | |
| >400[例(%)] | 51(24.6) | 9(16.1) | 62(22.2) | 10(13.2) | |||||
Tab.3 Comparison of smoking and drinking habits between the two groups in the survey questionnaire
| 项目 | 单中心 | 多中心 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMN组 (n=227) | MCD组 (n=58) | t/χ2值 | P值 | PMN组 (n=304) | MCD组 (n=78) | t/χ2值 | P值 | ||
| 饮酒史[例(%)] | 99(43.6) | 9(15.5) | 15.494 | <0.001 | 134(44.2) | 14(17.9) | 18.028 | <0.001 | |
| 饮酒累积时间(年) | 23.7±11.6 | 25.6±15 | -0.435 | 0.665 | 21.4±13.2 | 22.1±13.5 | -0.163 | 0.870 | |
| 每日消耗酒精(g) | 150(100, 250) | 200(100, 375) | -0.295 | 0.769 | 100(100, 250) | 100(75, 325) | -0.432 | 0.667 | |
| 饮酒指数 | 4500(2000, 7500) | 4500(2000, 9375) | -0.201 | 0.841 | 3000(1500, 7125) | 4000(1500, 7600) | -0.453 | 0.652 | |
| 吸烟史[例(%)] | 105(46.3) | 18(31.0) | 4.363 | 0.037 | 140(45.9) | 20(25.6) | 10.483 | 0.001 | |
| 吸烟累积时间(年) | 25.0±13.0 | 21.6±13.5 | 0.942 | 0.348 | 22.3±14.2 | 21.4±12.7 | 0.246 | 0.806 | |
| 偶尔[例(%)] | 122(57.8) | 40(71.4) | 165(57.3) | 58(76.4) | |||||
| 1~15年[例(%)] | 21(10.0) | 5(8.9) | 3.767 | 0.152 | 40(13.9) | 5(6.6) | 9.280 | 0.010 | |
| >15年[例(%)] | 68(30.0) | 11(19.6) | 83(28.8) | 13(17.1) | |||||
| 每日吸烟量(支) | 21.1±12.7 | 21.8±11.7 | -0.222 | 0.825 | 19.4±12.4 | 20.9±11.6 | -0.513 | 0.609 | |
| 偶尔[例(%)] | 122(56.5) | 40(69.0) | 165(57.3) | 58(74.4) | |||||
| 1~20支/d[例(%)] | 32(14.8) | 5(8.6) | 3.165 | 0.205 | 48(16.7) | 6(7.7) | 7.938 | 0.019 | |
| >20支/d[例(%)] | 62(28.7) | 13(22.4) | 75(26.0) | 14(17.9) | |||||
| 吸烟指数 | 450(200, 800) | 500(110, 800) | 0.415 | 0.679 | 400(103.8, 800) | 400(95, 800) | 0.100 | 0.921 | |
| 偶尔[例(%)] | 122(58.9) | 40(71.4) | 165(59.1) | 58(76.3) | |||||
| 1~400[例(%)] | 34(16.4) | 7(12.5) | 2.970 | 0.227 | 52(18.6) | 8(10.5) | 7.550 | 0.023 | |
| >400[例(%)] | 51(24.6) | 9(16.1) | 62(22.2) | 10(13.2) | |||||
| 项目 | PMN(n=227) | MCD(n=58) | t值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
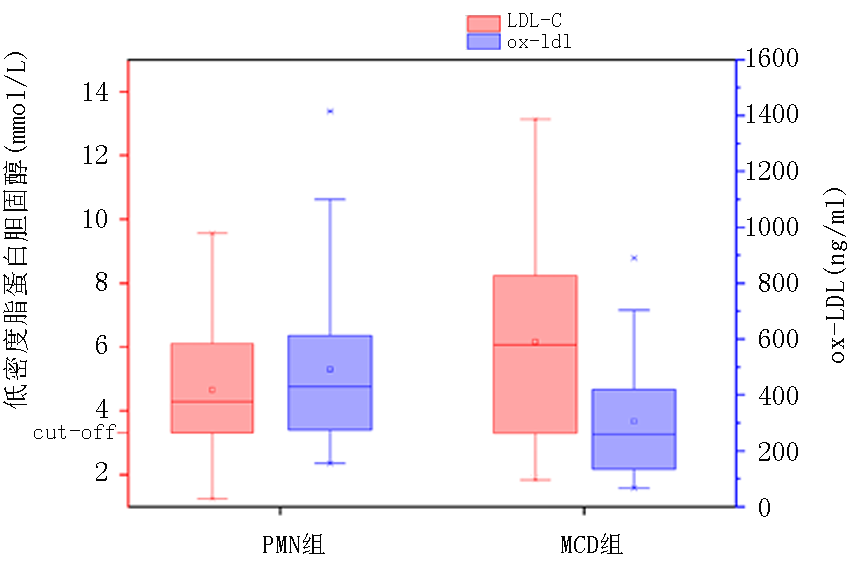
| 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(mmol/L) | 5.0±2.2 | 6.1±2.4 | -2.730 | 0.007 |
| 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(mmol/L) | 1.6±0.5 | 2±0.6 | -2.944 | 0.004 |
| 甘油三酯(mmol/L) | 2.5±2.0 | 2.3±1.2 | 0.693 | 0.489 |
| 总胆固醇(mmol/L) | 7.6±3.1 | 9.3±3.2 | -3.410 | 0.001 |
| 脂蛋白α(mg/L) | 528.4±471.1 | 741.5±573.2 | -2.008 | 0.046 |
| 载脂蛋白β(g/L) | 1.5±0.5 | 1.6±0.5 | -1.528 | 0.128 |
Tab.4 Comparison of blood lipids between the two groups in the single-center cohort
| 项目 | PMN(n=227) | MCD(n=58) | t值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(mmol/L) | 5.0±2.2 | 6.1±2.4 | -2.730 | 0.007 |
| 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(mmol/L) | 1.6±0.5 | 2±0.6 | -2.944 | 0.004 |
| 甘油三酯(mmol/L) | 2.5±2.0 | 2.3±1.2 | 0.693 | 0.489 |
| 总胆固醇(mmol/L) | 7.6±3.1 | 9.3±3.2 | -3.410 | 0.001 |
| 脂蛋白α(mg/L) | 528.4±471.1 | 741.5±573.2 | -2.008 | 0.046 |
| 载脂蛋白β(g/L) | 1.5±0.5 | 1.6±0.5 | -1.528 | 0.128 |
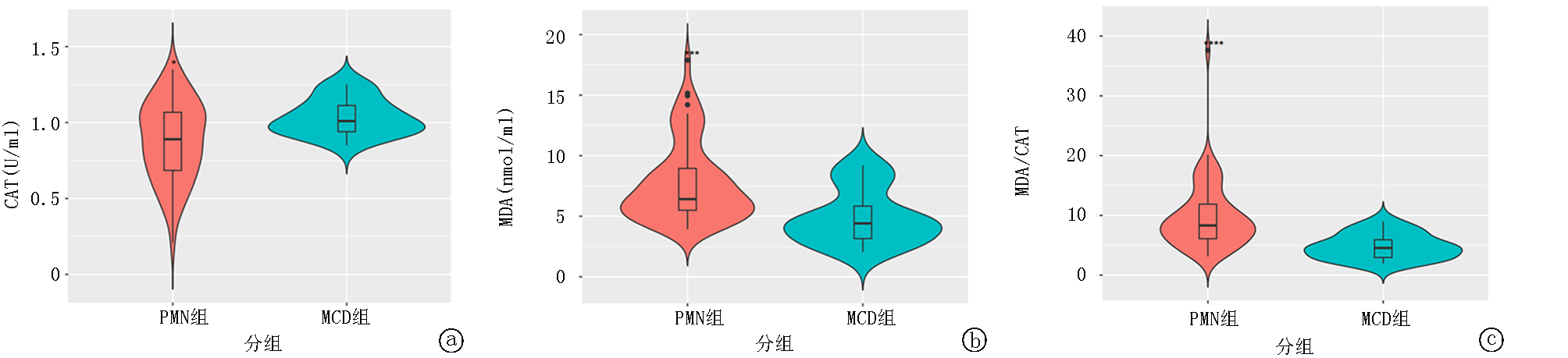
Fig.2 Comparison of serum lipid oxidation product MDA and antioxidant enzyme CAT levels between the two groups in the single-center cohort a.CAT; b.MDA; c.MDA/CAT
| [1] |
Canetta PA, Troost JP, Mahoney S, et al. Health-related quality of life in glomerular disease[J]. Kidney Int, 2019, 95(5): 1209-1224.
doi: S0085-2538(19)30046-8 pmid: 30898342 |
| [2] |
Ronco P, Debiec H. Molecular pathogenesis of membranous nephropathy[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2020, 15: 287-313.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-020117-043811 pmid: 31622560 |
| [3] | Fogo AB, Lusco MA, Najafian B, et al. AJKD atlas of renal pathology: Membranous nephropathy[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2015, 66(3): e15-17. |
| [4] | Couser WG. Primary membranous nephropathy[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2017, 12(6): 983-997. |
| [5] | Beck LH Jr, Bonegio RG, Lambeau G, et al. M-type phospholipase A2 receptor as target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy[J]. N Engl J Med, 2009, 361(1): 11-21. |
| [6] | Tomas NM, Beck LH Jr, Meyer-Schwesinger C, et al. Thrombospondin type-1 domain-containing 7A in idiopathic membranous nephropathy[J]. N Engl J Med, 2014, 371(24): 2277-2287. |
| [7] | Sethi S, Debiec H, Madden B, et al. Neural epidermal growth factor-like 1 protein (NELL-1) associated membranous nephropathy[J]. Kidney Int, 2020, 97(1): 163-174. |
| [8] |
Reinhard L, Machalitza M, Wiech T, et al. Netrin G1 is a novel target antigen in primary membranous nephropathy[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2022, 33(10): 1823-1831.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2022050608 pmid: 35985817 |
| [9] | Zhu P, Zhou FD, Wang SX, et al. Increasing frequency of idiopathic membranous nephropathy in primary glomerular disease: A 10-year renal biopsy study from a single Chinese nephrology centre[J]. Nephrology (Carlton), 2015, 20(8): 560-566. |
| [10] | Stanescu HC, Arcos-Burgos M, Medlar A, et al. Risk HLA-DQA1 and PLA(2)R1 alleles in idiopathic membranous nephropathy[J]. N Engl J Med, 2011, 364(7): 616-626. |
| [11] |
Coenen MJ, Hofstra JM, Debiec H, et al. Phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R1) sequence variants in idiopathic membranous nephropathy[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2013, 24(4): 677-683.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2012070730 pmid: 23431073 |
| [12] | Li SJ, Zhang SH, Chen HP, et al. Mercury-induced membranous nephropathy: Clinical and pathological features[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2010, 5(3): 439-444. |
| [13] |
Chakera A, Lasserson D, Beck LH, Jr, et al. Membranous nephropathy after use of UK-manufactured skin creams containing mercury[J]. QJM, 2011, 104(10): 893-896.
doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcq209 pmid: 21062753 |
| [14] |
Xu X, Wang G, Chen N, et al. Long-term exposure to air pollution and increased risk of membranous nephropathy in China[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2016, 27(12): 3739-3746.
pmid: 27365535 |
| [15] |
Xu X, Nie S, Ding H, et al. Environmental pollution and kidney diseases[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2018, 14(5): 313-324.
doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2018.11 pmid: 29479079 |
| [16] | Cremoni M, Agbekodo S, Teisseyre M, et al. Toxic occupational exposures and membranous nephropathy[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2022, 17(11): 1609-1619. |
| [17] |
Liu W, Gao C, Liu Z, et al. Idiopathic membranous nephropathy: Glomerular pathological pattern caused by extrarenal immunity activity[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 1846.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01846 pmid: 33042109 |
| [18] | Pollard KM. Gender differences in autoimmunity associated with exposure to environmental factors[J]. J Autoimmun, 2012, 38(2-3): J177-186. |
| [19] | Irazabal MV, Torres VE. Reactive oxygen species and redox signaling in chronic kidney disease[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(6). |
| [20] | Aranda-Rivera AK, Cruz-Gregorio A, Aparicio-Trejo OE, et al. Mitochondrial redox signaling and oxidative stress in kidney diseases[J]. Biomolecules, 2021, 11(8):1144. |
| [21] | Lee ES, Kim HM, Kang JS, et al. Oleanolic acid and N-acetylcysteine ameliorate diabetic nephropathy through reduction of oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress in a type 2 diabetic rat model[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2016, 31(3): 391-400. |
| [22] |
Vaziri ND. Disorders of lipid metabolism in nephrotic syndrome: Mechanisms and consequences[J]. Kidney Int, 2016, 90(1): 41-52.
doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.02.026 pmid: 27165836 |
| [23] | Koshi-Ito E, Koike K, Tanaka A, et al. Effect of low-density lipoprotein apheresis for nephrotic idiopathic membranous nephropathy as initial induction therapy[J]. Ther Apher Dial, 2019, 23(6): 575-583. |
| [24] | Wang X, Zhang M, Sun N, et al. Mizoribine combined with steroids and dietary sodium restriction on the treatment of primary membranous nephropathy: A prospective study[J]. Clin Exp Nephrol, 2023, 27(3): 211-217. |
| [25] | Ford ES, Giles WH, Dietz WH. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among US adults: Findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey[J]. JAMA, 2002, 287(3): 356-359. |
| [26] | Kitano H, Oda K, Kimura T, et al. Metabolic syndrome and robustness tradeoffs[J]. Diabetes, 2004, 53(Suppl 3): S6-S15. |
| [27] | Yang ML, Doyle HA, Clarke SG, et al. Oxidative modifications in tissue pathology and autoimmune disease[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2018, 29(14): 1415-1431. |
| [28] | Saint-Andre V, Charbit B, Biton A, et al. Smoking changes adaptive immunity with persistent effects[J]. Nature, 2024, 626(8000): 827-835. |
| [29] | Yamaguchi M, Ando M, Yamamoto R, et al. Smoking is a risk factor for the progression of idiopathic membranous nephropathy[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(6): e100835. |
| [30] | Nitta Y, Muraoka-Hirayama S, Sakurai K. Catalase is required for peroxisome maintenance during adipogenesis[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids, 2020, 1865(8): 158726. |
| [31] | Kum C, Kiral F, Sekkin S, et al. Effects of xylene and formaldehyde inhalations on oxidative stress in adult and developing rats livers[J]. Exp Anim, 2007, 56(1): 35-42. |
| [32] |
Di Marco E, Jha JC, Sharma A, et al. Are reactive oxygen species still the basis for diabetic complications?[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 2015, 129(2): 199-216.
doi: 10.1042/CS20150093 pmid: 25927680 |
| [33] |
Khan SR. Stress oxidative: Nephrolithiasis and chronic kidney diseases[J]. Minerva Med, 2013, 104(1): 23-30.
pmid: 23392535 |
| [34] |
Polanco N, Gutierrez E, Covarsi A, et al. Spontaneous remission of nephrotic syndrome in idiopathic membranous nephropathy[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2010, 21(4): 697-704.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2009080861 pmid: 20110379 |
| [35] |
Ponticelli C, Passerini P. Management of idiopathic membranous nephropathy[J]. Expert Opin Pharmacother, 2010, 11(13): 2163-2175.
doi: 10.1517/14656566.2010.494599 pmid: 20707756 |
| [1] | Liu Cuicui, Zhu Yafang, Lyu Wenjuan. Changes in pulmonary function, inflammatory factors, and clinical symptoms after smoking cessation in COPD patients with varied HRCT phenotypes [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(7): 625-629. |
| [2] | Liang Yi. Meta-analysis of effects of curcumin on inflammation and oxidative stress of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(11): 974-979. |
| [3] | Luo Fanglin, Guan Suying, Wu Guoxiang. Clinical effect of sacubitril-valsartan combined with activin on acute left heart failure [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(9): 782-785. |
| [4] | He Na, Li Minxian, Zhang Qi, Xu Fang, Zhang Chenfeng, Song Da. Effects of Tongxinluo Capsules on myocardial microperfusion in patients free of reflow after PCI and long-term efficacy and safety [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(2): 129-133. |
| [5] | Liu Ting, Ji Weidong, Yang Qingsong. Effects of cerebroprotein hydrolysate on Nrf2 oxidative stress signaling pathway in acute stroke patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(11): 996-1000. |
| [6] | Tong Jingjing1, Shi Kexin2, Leng Fei2, Li Fengping2. Correlation study between serum level of bilirubin and type 2 diabetic retinopathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(9): 816-822. |
| [7] | Song Chunli, Liu Hongbin, Dong Wei, Ma Like, Mo Ruixing. Effects of smoking status on longterm cardiovascular adverse events in male patients with heart failure [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(8): 697-701. |
| [8] | Zhang Cheng1,Gao Zeli2. Effects of Bifidobacterium triple viable entericcoated capsules on gastrointestinal hormones [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(7): 629-632. |
| [9] | Zhou Yuanyuan1, Wang Zhanjian2, Qiu Hongmei1, Li Wei1. Relationship between serum bilirubin and type 2 diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2017, 32(9): 767-769,773. |
| [10] | Wang Yuehui1, Wang Zhe1,Liu Jia1,Cai Lu2. Diabetic cardiomyopathy and potential intervention [J]. Clinical Focus, 2016, 31(9): 932-935. |
| [11] | Li Yuanyuan, Hua Yanfang, Zhou Junying. Pathogenesis in alcoholic liver disease [J]. Clinical Focus, 2016, 31(7): 723-726. |
| [12] | Ju Junqiang, Zhu Zhengtai, Li Hua, Teng Maorong. Noninvasive markers in patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Clinical Focus, 2016, 31(11): 1213-1217. |
| [13] | Shen Zhigang;Zhao Junhong;Zhou Jin. Relationship between receptor of advanced glycation end products and oxidative stress in prediabetes patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(8): 915-918. |
| [14] | Duan Hailing;Cui Xiangqin;Wang Zongbao;Liu Guanbin;Geng Mingliang. Clinical application of vitamin E combined with hemoperfusion in maintenance hemodialysis patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(11): 1288-1291. |
| [15] | YAO Xiao-ling;LIU Jian-jun;YANG Xiu-hua;WANG Jie-chao;LIU Wei-lin;CHANG Cui-fen;SHANG Su-liang. Ginkgo biloba extract on apoptosis of endothelial cells [J]. Clinical Focus, 2014, 29(9): 1022-1024. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||