Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (7): 608-618.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.07.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bioinformatics-driven investigation into the molecular pathways of polycystic ovary syndrome
Guo Qian, Chen Jie, Ma Weirong, Zhang Yan, Yang Yingqian, Tan Yong( )
)
- Department of Gynecology, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China
-
Received:2025-04-22Online:2025-07-20Published:2025-07-17 -
Contact:Tan Yong E-mail:xijun1025@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Qian, Chen Jie, Ma Weirong, Zhang Yan, Yang Yingqian, Tan Yong. Bioinformatics-driven investigation into the molecular pathways of polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(7): 608-618.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.lchc.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.07.005
| GSE ID | 样本 | 组织 | 平台 | 试验类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE6798 | 16例病例和13例对照 | 肌肉 | GPL570 | 队列 |
| GSE10946 | 12例病例和11例对照 | 卵丘细胞 | GPL570 | 队列 |
| GSE8157 | 30例病例和13例对照 | 肌肉 | GPL570 | 队列 |
Tab.1 The characteristics of the three GEO datasets
| GSE ID | 样本 | 组织 | 平台 | 试验类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE6798 | 16例病例和13例对照 | 肌肉 | GPL570 | 队列 |
| GSE10946 | 12例病例和11例对照 | 卵丘细胞 | GPL570 | 队列 |
| GSE8157 | 30例病例和13例对照 | 肌肉 | GPL570 | 队列 |
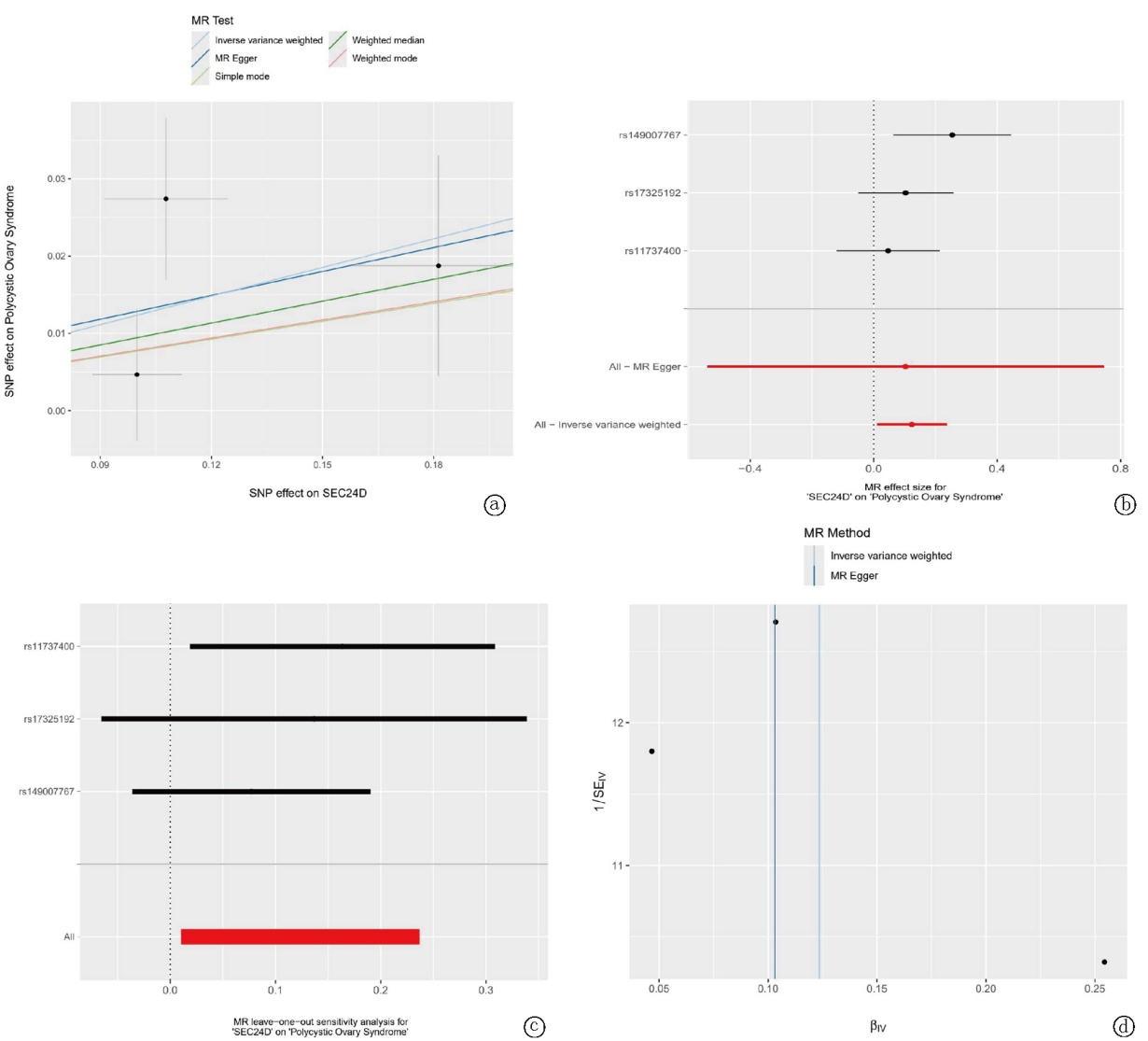
Fig.6 MR analysis of the relationship between SEC24D and PCOS a. Scatter plot; b. Forest plot; c. Leave-one-out sensitivity analysis plot; d. Funnel plot
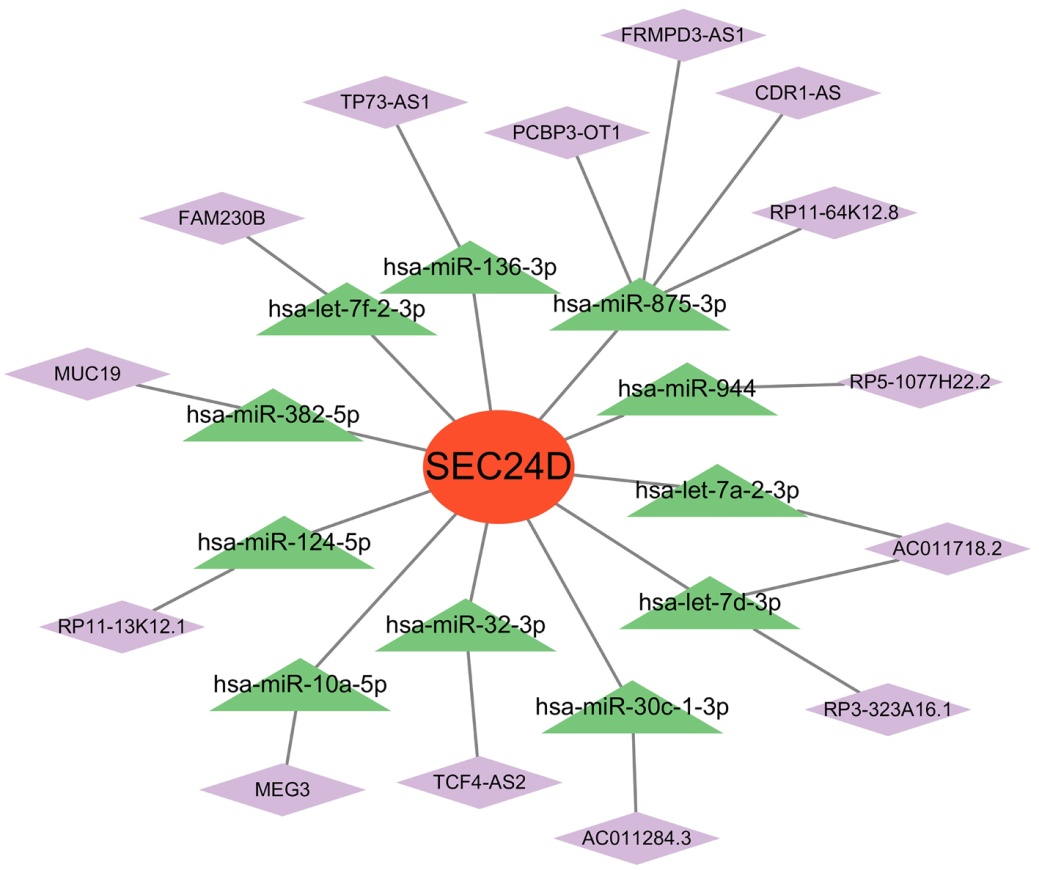
| miRNA | lncRNA | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-875-3p | CDR1-AS | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-875-3p | PCBP3-OT1 | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-875-3p | RP11-64K12.8 | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-875-3p | FRMPD3-AS1 | spongeScan |
| hsa-let-7d-3p | AC011718.2 | spongeScan |
| hsa-let-7d-3p | RP3-323A16.1 | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-382-5p | MUC19 | spongeScan |
| hsa-let-7a-2-3p | AC011718.2 | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-32-3p | TCF4-AS2 | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-10a-5p | MEG3 | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-124-5p | RP11-13K12.1 | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-944 | RP5-1077H22.2 | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-136-3p | TP73-AS1 | spongeScan |
| hsa-let-7f-2-3p | FAM230B | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-30c-1-3p | AC011284.3 | spongeScan |
Tab.2 LncRNAs that bind to miRNAs
| miRNA | lncRNA | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-875-3p | CDR1-AS | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-875-3p | PCBP3-OT1 | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-875-3p | RP11-64K12.8 | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-875-3p | FRMPD3-AS1 | spongeScan |
| hsa-let-7d-3p | AC011718.2 | spongeScan |
| hsa-let-7d-3p | RP3-323A16.1 | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-382-5p | MUC19 | spongeScan |
| hsa-let-7a-2-3p | AC011718.2 | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-32-3p | TCF4-AS2 | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-10a-5p | MEG3 | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-124-5p | RP11-13K12.1 | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-944 | RP5-1077H22.2 | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-136-3p | TP73-AS1 | spongeScan |
| hsa-let-7f-2-3p | FAM230B | spongeScan |
| hsa-miR-30c-1-3p | AC011284.3 | spongeScan |
| [1] |
doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(24)00019-1 pmid: 38552655 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7493-1_12 pmid: 29344893 |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
刘琳, 王静怡, 王欣, 等. 高通量测序应用于PCOS患者卵泡液外泌体lncRNA表达谱分析[J]. 生殖医学杂志, 2020, 29(5):620-627.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
pmid: 37693152 |
| [14] |
余涛, 李丹, 邹小娟, 等. 基于Oncomine和GEO数据库分析SEC24D基因在乳腺癌中的表达意义及穿心莲内酯的干预研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2018, 33(5):1703-1707.
|
| [15] |
蒋贤忠. 乙肝易感基因的关联分析及其功能研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017.
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00579-x pmid: 34702932 |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.5653/cerm.2023.05932 pmid: 37643835 |
| [21] |
pmid: 37303662 |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04116-4 pmid: 37062827 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2021.10.003 pmid: 34655744 |
| [25] |
孟睿, 张雯. lncRNA TP73-AS1通过调控miR-128-3p对多囊卵巢综合征卵巢颗粒细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 解剖科学进展, 2024, 30(2):212-215+219.
|
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||