Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (11): 988-998.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.11.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Development and validation of a machine learning-based prognostic model for H3K27 mmutant diffuse midline glioma
Wang Zhuangzhuang1, Yang Qingjun1, Ren Huan2, Liu Yanting3, Tian Chunlei3( )
)
- 1. Department of Surgery, People's Hospital of Gucheng County, Xiangyang 441700, China
2. Shiyan Aier Eye Hospital, Shiyan 442000, China
3. Department of Neurosurgery,the First Clinical Medical College of China Three Gorges University (Yichang Central People's Hospital), Yichang 443003, China
-
Received:2025-09-23Online:2025-11-20Published:2025-12-02 -
Contact:Tian Chunlei E-mail:cltianyc@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Zhuangzhuang, Yang Qingjun, Ren Huan, Liu Yanting, Tian Chunlei. Development and validation of a machine learning-based prognostic model for H3K27 mmutant diffuse midline glioma[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(11): 988-998.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.lchc.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.11.004
| 项目 | 训练集( | 验证集( | χ2/ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | ||||
| <30 | 58(59.8) | 24(58.5) | ||
| 30~60 | 33(34.0) | 12(29.3) | 0.980 | 0.613 |
| >60 | 6(6.2) | 5(12.2) | ||
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||
| 女性 男性 | 52(53.6) 45(46.4) | 19(46.3) 22(53.7) | 0.620 | 0.431 |
| 种族[例(%)] | ||||
| 黑种人 | 7(7.2) | 3(7.3) | ||
| 白种人 | 83(85.6) | 33(80.5) | 0.720 | 0.698 |
| 黄种人 | 7(7.2) | 5(12.2) | ||
| 肿瘤侧别[例(%)] | ||||
| 左侧 | 8(8.2) | 5(12.2) | ||
| 右侧 | 12(12.4) | 8(19.5) | 1.850 | 0.396 |
| 中线结构 | 77(79.4) | 28(68.3) | ||
| 肿瘤分期[例(%)] | ||||
| 局部浸润 | 74(76.30) | 28(68.30) | ||
| 临近侵袭 | 12(12.40) | 5(12.20) | 1.930 | 0.381 |
| 远处转移 | 11(11.30) | 8(19.50) | ||
| 放疗[例(%)] | ||||
| 否 是 | 16(16.5) 81(83.5) | 8(19.5) 33(80.5) | 0.180 | 0.674 |
| 化疗[例(%)] | ||||
| 否 是 | 43(44.3) 54(55.7) | 16(39.0) 25(61.0) | 0.350 | 0.554 |
| WHO分级[例(%)] | ||||
| 低(Ⅰ-Ⅱ) 高(Ⅲ-Ⅳ) | 73(75.3) 24(24.7) | 28(68.3) 13(31.7) | 0.750 | 0.387 |
| 肿瘤数量[例(%)] | ||||
| 单发 多发 | 1(1.0) 96(99.0) | 0 41(100.0) | - | 1.000 |
| 肿瘤体积(cm3) | 41(33, 48) | 42(30, 50) | -0.120 | 0.903 |
Tab.1 Comparison of baseline characteristics between the two groups
| 项目 | 训练集( | 验证集( | χ2/ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | ||||
| <30 | 58(59.8) | 24(58.5) | ||
| 30~60 | 33(34.0) | 12(29.3) | 0.980 | 0.613 |
| >60 | 6(6.2) | 5(12.2) | ||
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||
| 女性 男性 | 52(53.6) 45(46.4) | 19(46.3) 22(53.7) | 0.620 | 0.431 |
| 种族[例(%)] | ||||
| 黑种人 | 7(7.2) | 3(7.3) | ||
| 白种人 | 83(85.6) | 33(80.5) | 0.720 | 0.698 |
| 黄种人 | 7(7.2) | 5(12.2) | ||
| 肿瘤侧别[例(%)] | ||||
| 左侧 | 8(8.2) | 5(12.2) | ||
| 右侧 | 12(12.4) | 8(19.5) | 1.850 | 0.396 |
| 中线结构 | 77(79.4) | 28(68.3) | ||
| 肿瘤分期[例(%)] | ||||
| 局部浸润 | 74(76.30) | 28(68.30) | ||
| 临近侵袭 | 12(12.40) | 5(12.20) | 1.930 | 0.381 |
| 远处转移 | 11(11.30) | 8(19.50) | ||
| 放疗[例(%)] | ||||
| 否 是 | 16(16.5) 81(83.5) | 8(19.5) 33(80.5) | 0.180 | 0.674 |
| 化疗[例(%)] | ||||
| 否 是 | 43(44.3) 54(55.7) | 16(39.0) 25(61.0) | 0.350 | 0.554 |
| WHO分级[例(%)] | ||||
| 低(Ⅰ-Ⅱ) 高(Ⅲ-Ⅳ) | 73(75.3) 24(24.7) | 28(68.3) 13(31.7) | 0.750 | 0.387 |
| 肿瘤数量[例(%)] | ||||
| 单发 多发 | 1(1.0) 96(99.0) | 0 41(100.0) | - | 1.000 |
| 肿瘤体积(cm3) | 41(33, 48) | 42(30, 50) | -0.120 | 0.903 |
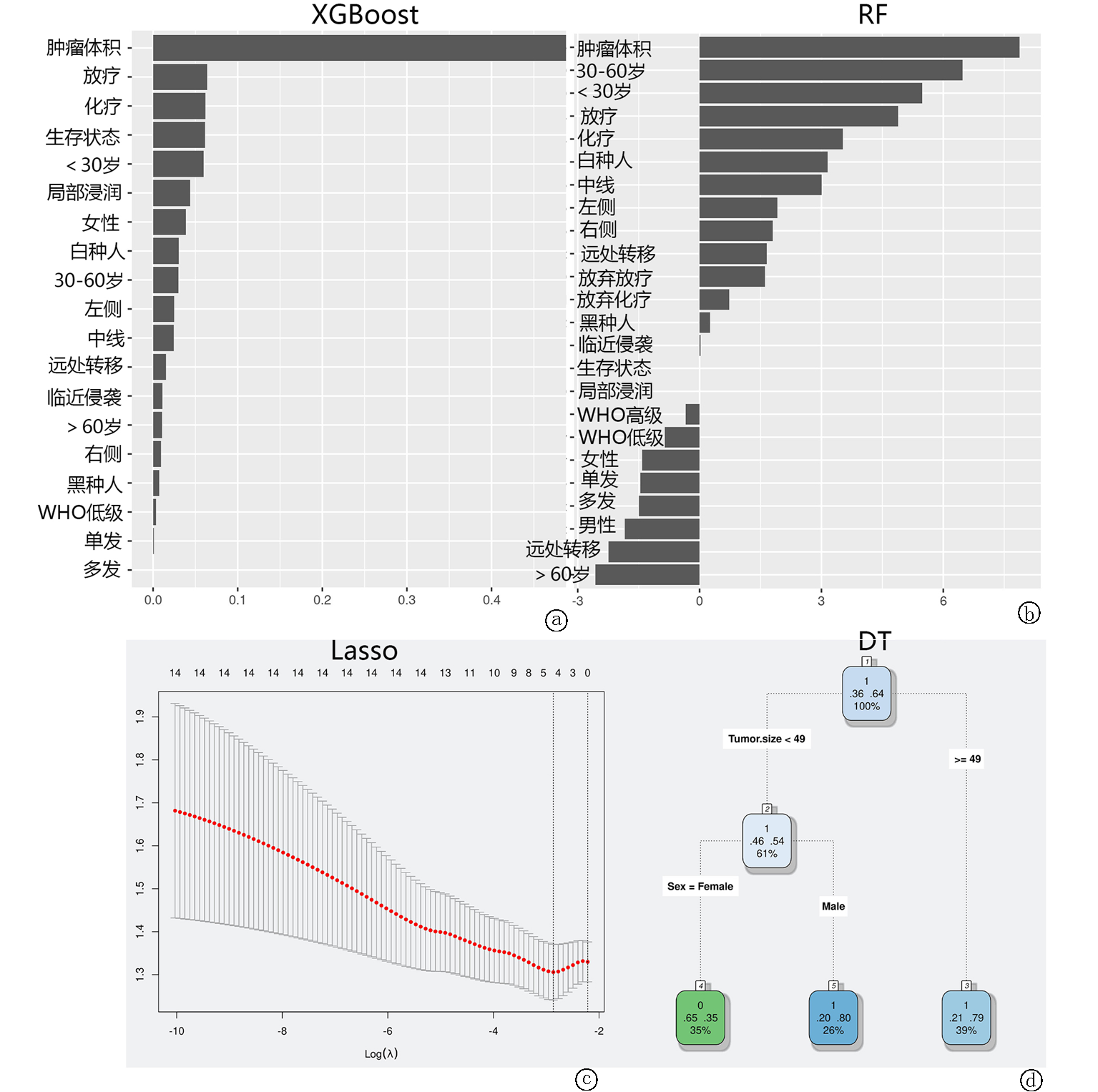
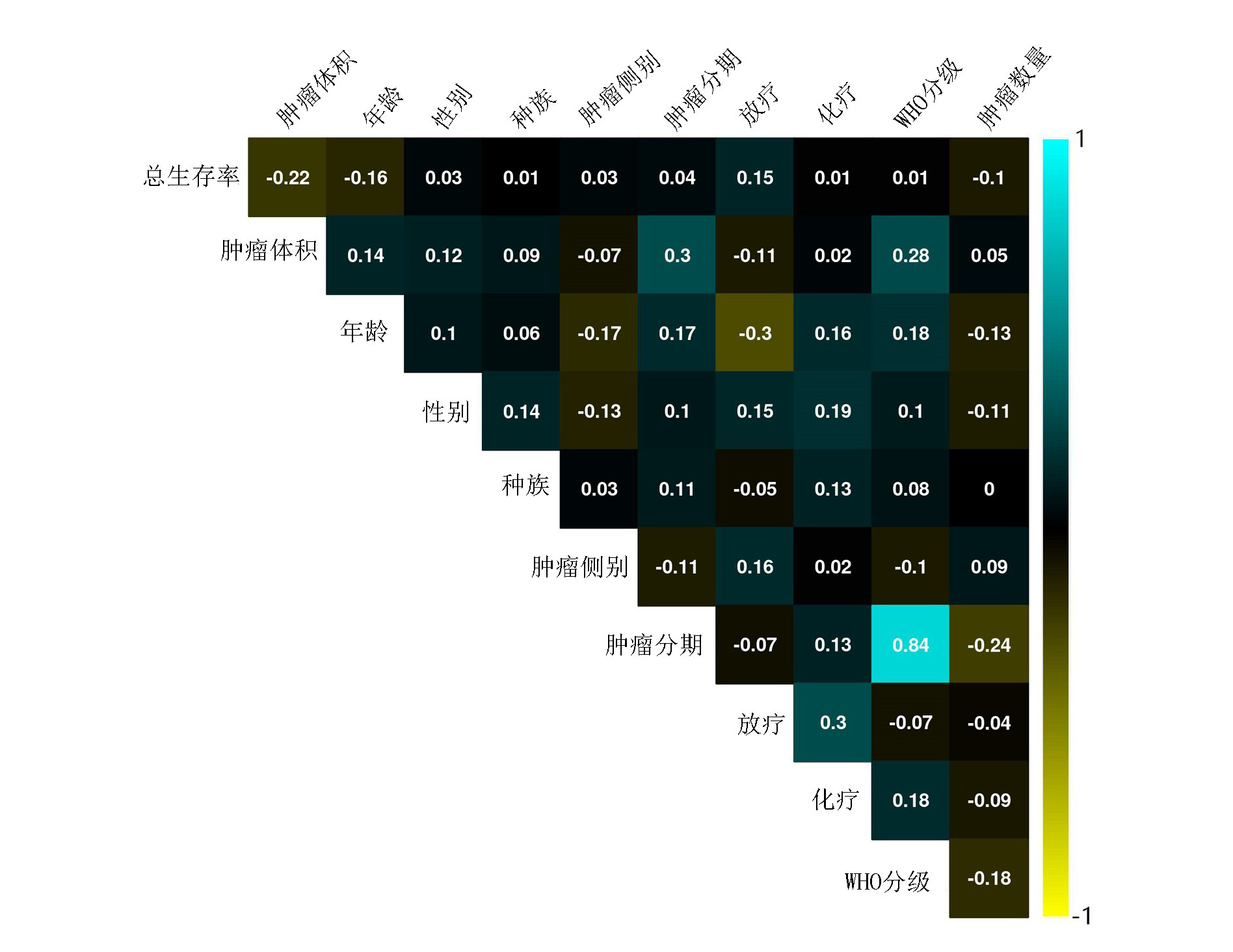
Fig.2 Prognostic variables for H3K27M mutant DMG patients screened using four machine learning algorithms a. The importance score of prognostic variables identified by XGBoost model; b. The importance score of the prognostic variables identified by the RF model; c. The importance score of the prognostic impact variables identified by the Lasso regression model; d. The importance score of prognostic variables identified by the DT model
| 模型 | 分类 | AUC(95% | Brier值 | 灵敏度 | 特异度 | 阳性预测值 | 阴性预测值 | 平衡准确性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 训练集 | Lasso | 0.82(0.76~0.87) | 0.150 | 0.780 | 0.840 | 0.810 | 0.820 | 0.810 |
| XGBoost | 0.91(0.87~0.94) | 0.110 | 0.870 | 0.820 | 0.840 | 0.860 | 0.850 | |
| RF | 0.95(0.92~0.97) | 0.080 | 0.910 | 0.880 | 0.890 | 0.900 | 0.900 | |
| DT | 0.88(0.83~0.92) | 0.130 | 0.830 | 0.800 | 0.820 | 0.810 | 0.820 | |
| 验证集 | Lasso | 0.76(0.68~0.83) | 0.180 | 0.720 | 0.790 | 0.750 | 0.760 | 0.760 |
| XGBoost | 0.80(0.73~0.86) | 0.160 | 0.760 | 0.810 | 0.780 | 0.790 | 0.790 | |
| RF | 0.78(0.70~0.85) | 0.170 | 0.740 | 0.770 | 0.760 | 0.750 | 0.760 | |
| DT | 0.72(0.64~0.79) | 0.190 | 0.680 | 0.740 | 0.710 | 0.710 | 0.710 |
Tab.2 Accuracy evaluation of different algorithm models in training set and validation set
| 模型 | 分类 | AUC(95% | Brier值 | 灵敏度 | 特异度 | 阳性预测值 | 阴性预测值 | 平衡准确性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 训练集 | Lasso | 0.82(0.76~0.87) | 0.150 | 0.780 | 0.840 | 0.810 | 0.820 | 0.810 |
| XGBoost | 0.91(0.87~0.94) | 0.110 | 0.870 | 0.820 | 0.840 | 0.860 | 0.850 | |
| RF | 0.95(0.92~0.97) | 0.080 | 0.910 | 0.880 | 0.890 | 0.900 | 0.900 | |
| DT | 0.88(0.83~0.92) | 0.130 | 0.830 | 0.800 | 0.820 | 0.810 | 0.820 | |
| 验证集 | Lasso | 0.76(0.68~0.83) | 0.180 | 0.720 | 0.790 | 0.750 | 0.760 | 0.760 |
| XGBoost | 0.80(0.73~0.86) | 0.160 | 0.760 | 0.810 | 0.780 | 0.790 | 0.790 | |
| RF | 0.78(0.70~0.85) | 0.170 | 0.740 | 0.770 | 0.760 | 0.750 | 0.760 | |
| DT | 0.72(0.64~0.79) | 0.190 | 0.680 | 0.740 | 0.710 | 0.710 | 0.710 |
| 项目 | 95% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | |||
| 30~60 vs <30 | 0.630 | 0.65~2.28 | 0.382 |
| >60 vs <30 | 3.018 | 1.15~7.91 | 0.025 |
| 肿瘤体积 | 1.039 | 1.01~1.06 | 0.004 |
| WHO分级 | 2.057 | 1.21~3.49 | 0.008 |
| 肿瘤侧别 | |||
| 右侧vs左侧 | 0.739 | 0.61~2.42 | 0.739 |
| 中线vs左侧 | 2.101 | 1.32~3.34 | 0.002 |
| 放疗 | 0.410 | 0.23~0.75 | 0.004 |
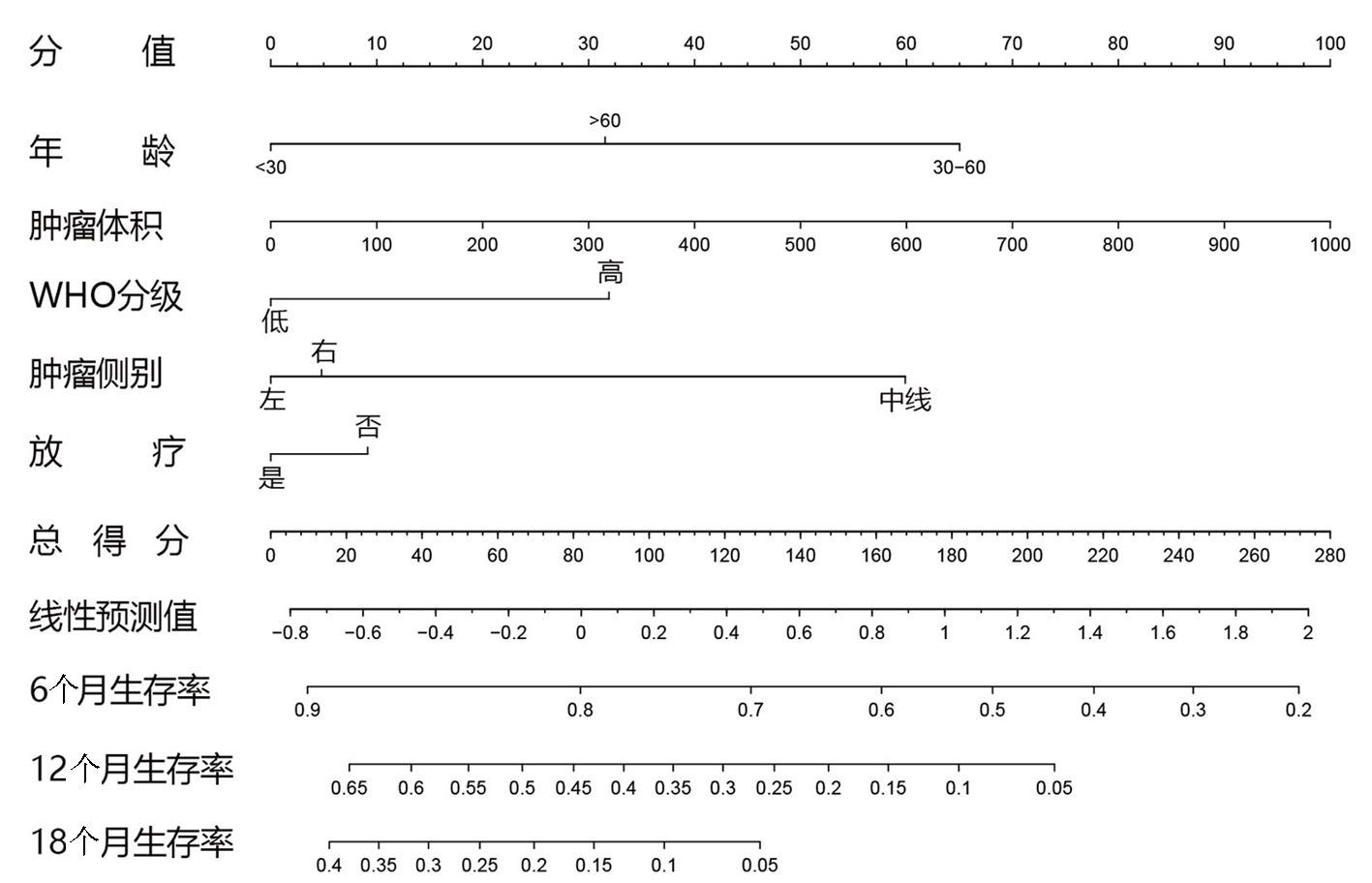
Tab.3 Multivariate Cox regression analysis of prognosis in patients with H3K27M mutant DMG
| 项目 | 95% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | |||
| 30~60 vs <30 | 0.630 | 0.65~2.28 | 0.382 |
| >60 vs <30 | 3.018 | 1.15~7.91 | 0.025 |
| 肿瘤体积 | 1.039 | 1.01~1.06 | 0.004 |
| WHO分级 | 2.057 | 1.21~3.49 | 0.008 |
| 肿瘤侧别 | |||
| 右侧vs左侧 | 0.739 | 0.61~2.42 | 0.739 |
| 中线vs左侧 | 2.101 | 1.32~3.34 | 0.002 |
| 放疗 | 0.410 | 0.23~0.75 | 0.004 |
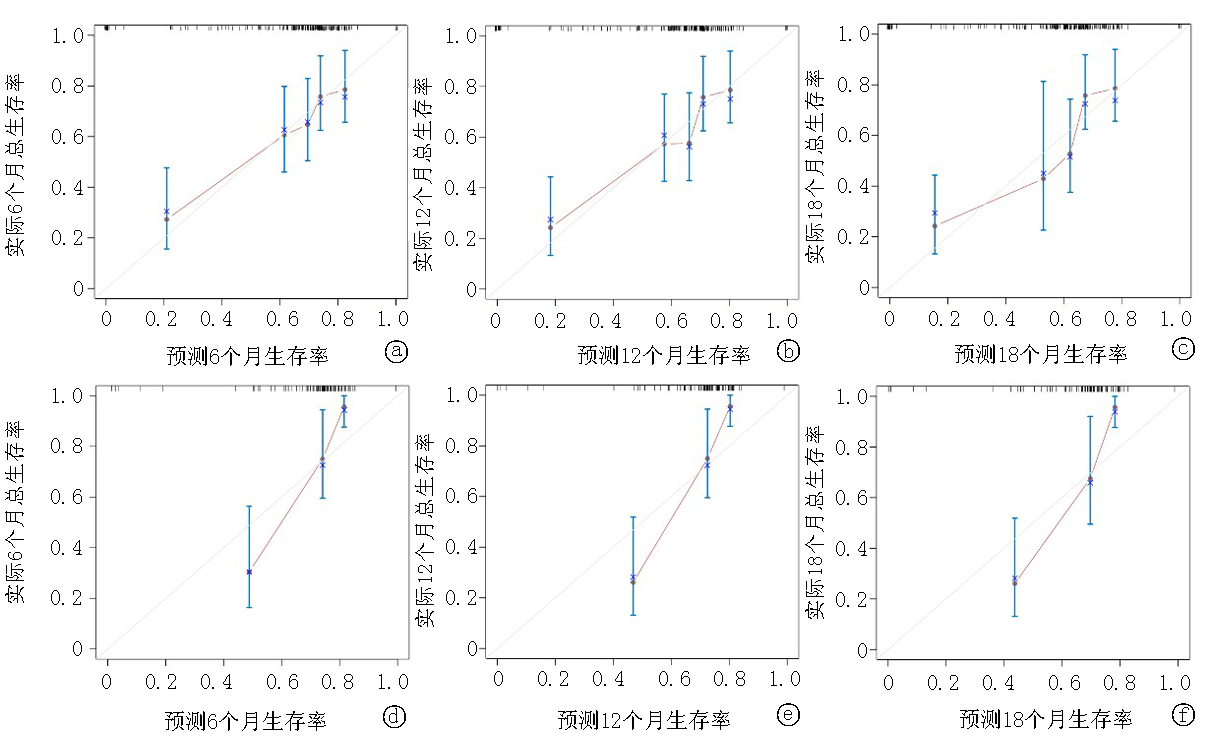
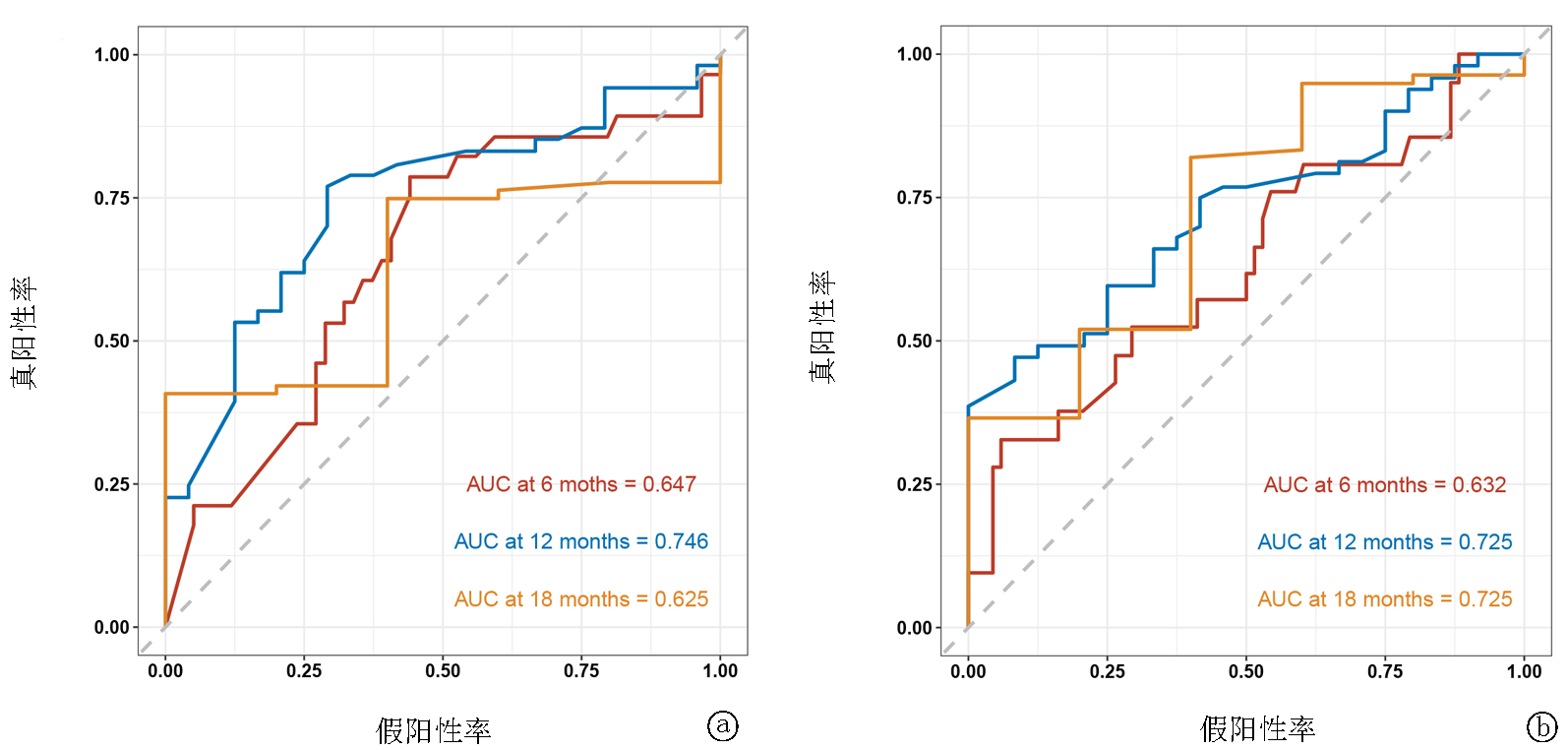
Fig.5 Calibration calibration curve of 6-, 12-, and 18-month OS in training set and validation set a. Calibration calibration curve of 6-month OS in training set; b. Calibration calibration curve of 12-month OS in training set; c. Calibration calibration curve of the 18-month OS of the training set; d. Calibration calibration curve of 6-month OS in validation set; e. Calibration calibration curve of 12-month OS in validation set; f. Calibration calibration curve for 18-month OS of the validation set
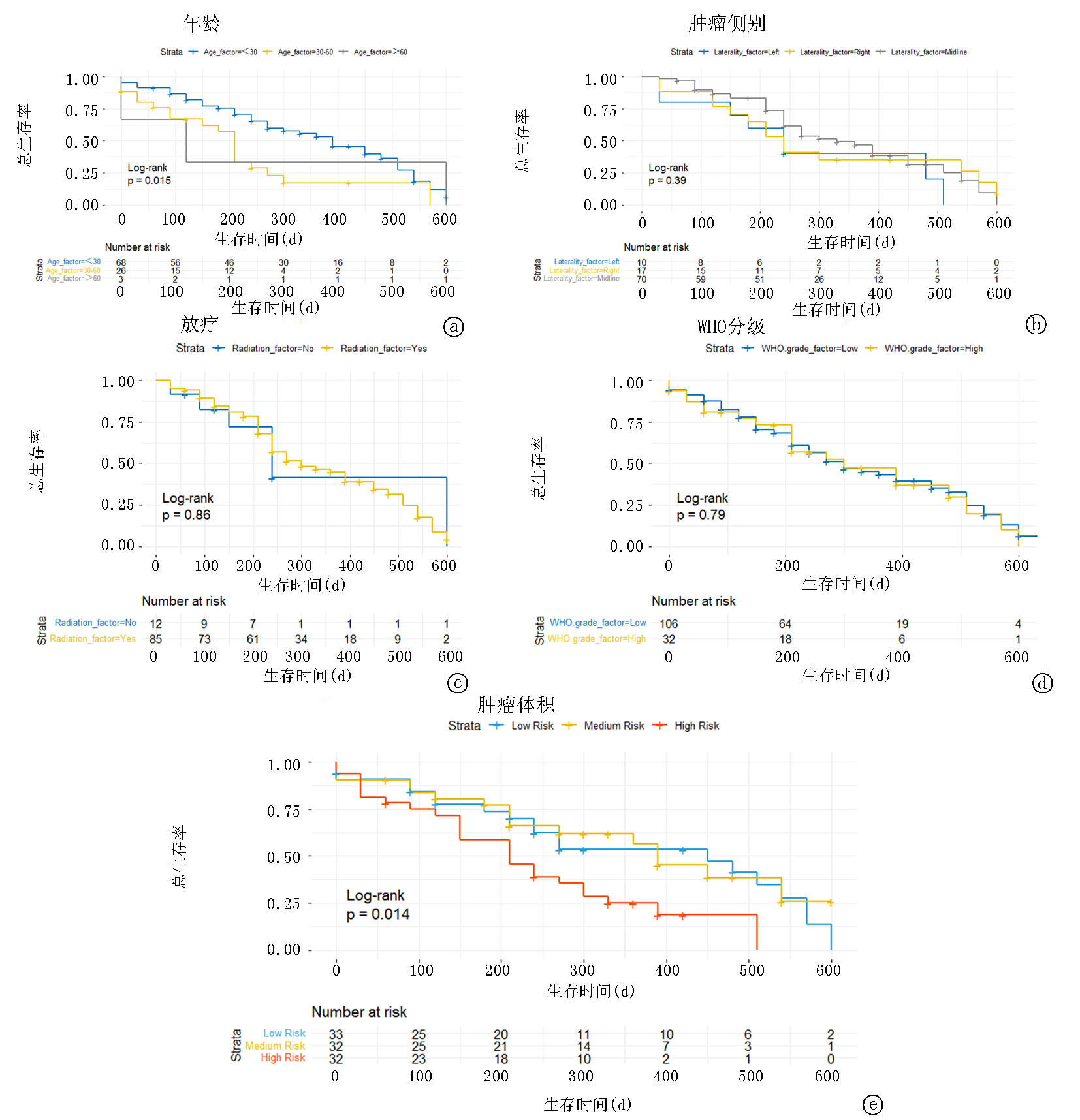
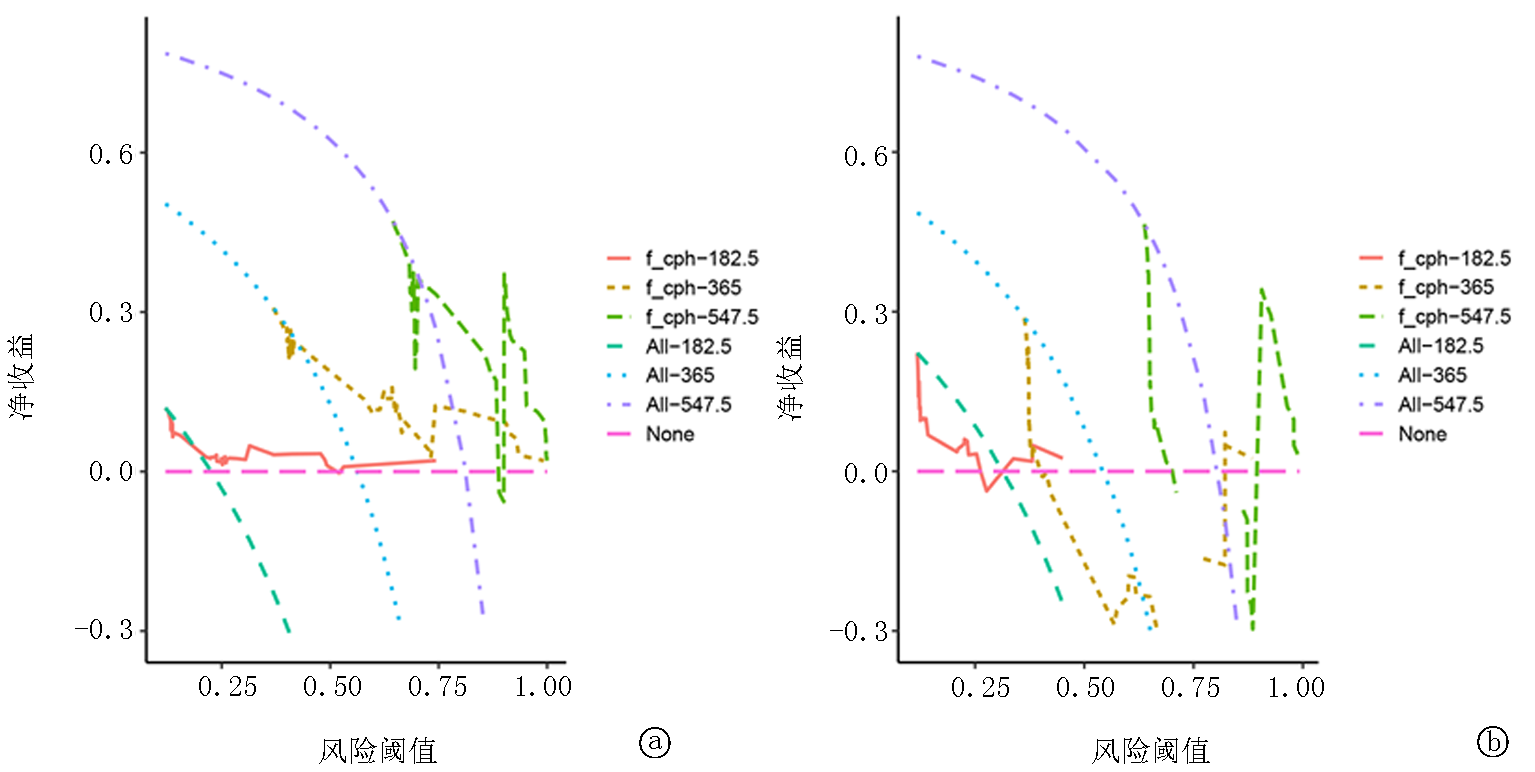
Fig. 7 Kaplan-Meier survival analysis curves of prognostic factors in H3K27M mutant DMG a. Age; b. Tumor laterality; c. Radiotherapy; d. WHO grade; e. Tumor size
| [1] | 胡鹏, 毛佳颖, 赵淦, 等. MAGED2、EMP2表达与H3K27M突变型弥漫性中线胶质瘤预后的关系研究[J]. 中华神经外科疾病研究杂志, 2025, 19(3): 52-57. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5807.2019.03.005. |
| [2] | 杨沁怡, 李明娜, 陈天羽, 等. 成人H3K27M变异型弥漫性中线胶质瘤临床病理学分析[J]. 中华病理学杂志, 2023, 52(4): 376-383.doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn112151-20220926-00810. |
| [3] | 杜娟, 李永晴, 崔文丽, 等. 弥漫性中线胶质瘤伴H3K27变异型的临床病理学及分子遗传学特征[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志, 2025, 41(9): 1187-1193.doi:10.13315/j.cnki.cjcep.2025.09.011. |
| [4] | Sarnow K, Majercak E, Qurbonov Q, et al. Neuroimmune-competent human brain organoid model of diffuse midline glioma[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2025, 27(2): 369-382.doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noae245. |
| [5] | Van den BM, Saratsis AM, Geurts M, et al. H3 K27M-altered glioma and diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma: Semi-systematic review of treatment landscape and future directions[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2024, 26(2): S110-S124.doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noad220. |
| [6] | Daoud EV, Rajaram V, Cai C, et al. Adult brainstem gliomas with H3K27M mutation: Radiology, pathology, and prognosis[J]. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol, 2018, 77(4): 302-311.doi: 10.1093/jnen/nly006. |
| [7] | 蒋会, 苏晓然, 吴玲, 等. 基于全域ADC直方图评估儿童高级别弥漫性中线胶质瘤H3K27M突变[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2024, 43(2): 251-256.doi:10.13437/j.cnki.jcr.2024.02.020. |
| [8] | 李海南, 李智, 赖名耀, 等. H3K27M突变型中线胶质瘤的病理学特征及其预后影响因素分析[J]. 中华神经外科杂志, 2022, 38(10): 1001-1006.doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn112050-20220226-00115. |
| [9] | Cheng L, Zhou M, Luo T, et al. H3F3B p.K27I-mutant diffuse midline glioma is a distinct subtype of H3K27-altered diffuse midline glioma[J]. Acta Neuropathol Commun, 2025, 13(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s40478-025-02101-0. |
| [10] | Li X, Sun W, Guo Z, et al. Identification of urinary metabolic biomarkers for histone 3 lysine27-to-methionine mutation diagnosis in brainstem gliomas[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2025, 27(6): 1536-1549.doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noaf038. |
| [11] | Lo Greco MC, Marano G, La RM, et al. Latest Advancements in the management of H3K27M-mutant diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma: A narrative review[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2025, 17(3): 420.doi: 10.3390/cancers17030420. |
| [12] | Sheikh SR, Recinos VMR, Thompson EM, et al. The role of brainstem biopsy and targeted therapies in pediatric diffuse midline glioma/diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma[J]. Front Oncol, 2024, 14((10): 1504440.doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1504440. |
| [13] | Angelico G, Mazzucchelli M, Attanasio G, et al. H3K27me3 loss in central nervous system tumors: Diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic implications[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2024, 16(20): 3451. doi: 10.3390/cancers16203451. |
| [14] | Chaturvedi A, Sadashiva N, Shukla D, et al. Thalamic H3K27M altered diffuse midline gliomas: Clinicopathological and outcome analysis[J]. Clin Neurol Neurosurg, 2024, 244(12):108449.doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2024.108449. |
| [15] | 潘昱辰, 黄国栋, 张协军, 等. H3K27M突变型弥漫性中线胶质瘤的诊治分析[J]. 中国临床神经外科杂志, 2021, 26(10):761-763.doi:10.13798/j.issn.1009-153X.2021.10.006. |
| [16] | 周江芬, 赖名耀, 邓官华, 等. 成人脑干胶质瘤临床特点及预后:单中心10年81例患者回顾性分析[J]. 临床神经外科杂志, 2022, 19(1):70-73. |
| [17] | 梁博, 梁庭毓, 王芳, 等. 弥漫性中线胶质瘤伴H3K27M突变的临床诊疗及预后分析[J]. 中国微侵袭神经外科杂志, 2019, 24(7): 299-302. |
| [18] | Nonnenbroich LF, Bouchal SM, Millesi E, et al. H3K27-altered diffuse midline glioma of the brainstem: From molecular mechanisms to targeted interventions[J]. Cells, 2024, 13(13):1122. doi: 10.3390/cells13131122. |
| [19] | Liu C, Kuang S, Huang T, et al. Radiotherapy plus temozolomide with or without anlotinib in H3K27M-mutant diffuse midline glioma: A retrospective cohort study[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2024, 30(4): e14730. doi: 10.1111/cns.14730. |
| [20] |
Zang D, Dong Z, Liu Y, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing of anaplastic ependymoma and H3K27M-mutant diffuse midline glioma[J]. BMC Neurol, 2024, 24(1):74.doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-03558-7.
pmid: 38383423 |
| [21] | Yang Z, Sun L, Chen H, et al. New progress in the treatment of diffuse midline glioma with H3K27M alteration[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(2): e24877.doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24877. |
| [22] | Huang B, Chen T, Zhang Y, et al. Deep learning for the prediction of the survival of midline diffuse glioma with an H3K27M alteration[J]. Brain Sci, 2023, 13(10):1483.doi: 10.3390/brainsci13101483. |
| [23] | Adhikari S, Bhutada AS, Ladner L, et al. Prognostic indicators for H3K27M-mutant diffuse midline glioma: A population-based retrospective surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database analysis[J]. World Neurosurg, 2023, 178(14): e113-e121. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2023.07.001. |
| [24] |
罗敏捷, 陈嘉志, 张旺明. 儿童H3 K27M突变型弥漫性中线胶质瘤治疗进展[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志, 2020, 20(4):270-276.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6731.2020.04.005 |
| [25] | 王佳, 许朗宁, 葛明, 等. 伴H3 K27M突变的儿童弥漫性中线胶质瘤的临床特点、治疗及预后[J]. 中华神经外科杂志, 2021, 37(2):118-122.doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn112050-20200717-00408. |
| [26] |
Gong X, Kuang S, Deng D, et al. Differences in survival prognosticators between children and adults with H3K27M-mutant diffuse midline glioma[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2023, 29(12): 3863-3875.doi: 10.1111/cns.14307.
pmid: 37311690 |
| [27] | Xu K, Sun Z, Wang L, et al. Bilateral thalamic gliomas harboring alterations of EGFR and H3K27M: An integrated clinicopathological characteristics case series[J]. World Neurosurg, 2022, 168(21): e442-e450. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2022.09.118. |
| [28] | Bin-Alamer O, Jimenez AE, Azad TD, et al. H3K27M-altered diffuse midline gliomas among adult patients: A systematic review of clinical features and survival analysis[J]. World Neurosurg, 2022, 165(14): e251-e264.doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2022.06.020. |
| [29] | Vuong HG, Ngo TNM, Le HT, et al. The prognostic significance of HIST1H3B/C and H3F3A K27M mutations in diffuse midline gliomas is influenced by patient age[J]. J Neurooncol, 2022, 158(3): 405-412.doi: 10.1007/s11060-022-04027-2. |
| [30] | Grimaldi S, Harlay V, Appay R, et al. Adult H3K27M mutated thalamic glioma patients display a better prognosis than unmutated patients[J]. J Neurooncol, 2022, 156(3): 615-623.doi: 10.1007/s11060-022-03943-7. |
| [31] | Gu Q, Huang Y, Zhang H, et al. Case report: Five adult cases of H3K27-altered diffuse midline glioma in the spinal cord[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11(10): 701113.doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.701113. |
| [1] | Zhao Xueting, Bai Jiawen, Sun Jun. Analysis of risk factors for liver fibrosis in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and construction of a nomogram [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(5): 417-422. |
| [2] | Wang Zhuangzhuang, Ren Huan, Liu Yanting, Tian Chunlei. Construction of a nomogram to predict postoperative hydrocephalus in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage based on the Dryad database and its validation [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(4): 313-319. |
| [3] | Wang Zhuangzhuang, Ren Huan, Liu Yanting, Tian Chunlei, Ai Wenbing. Construction of a nomogram to predict the risk of lung metastasis in extremity osteosarcomas based on the SEER database and its validation [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(5): 413-419. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||