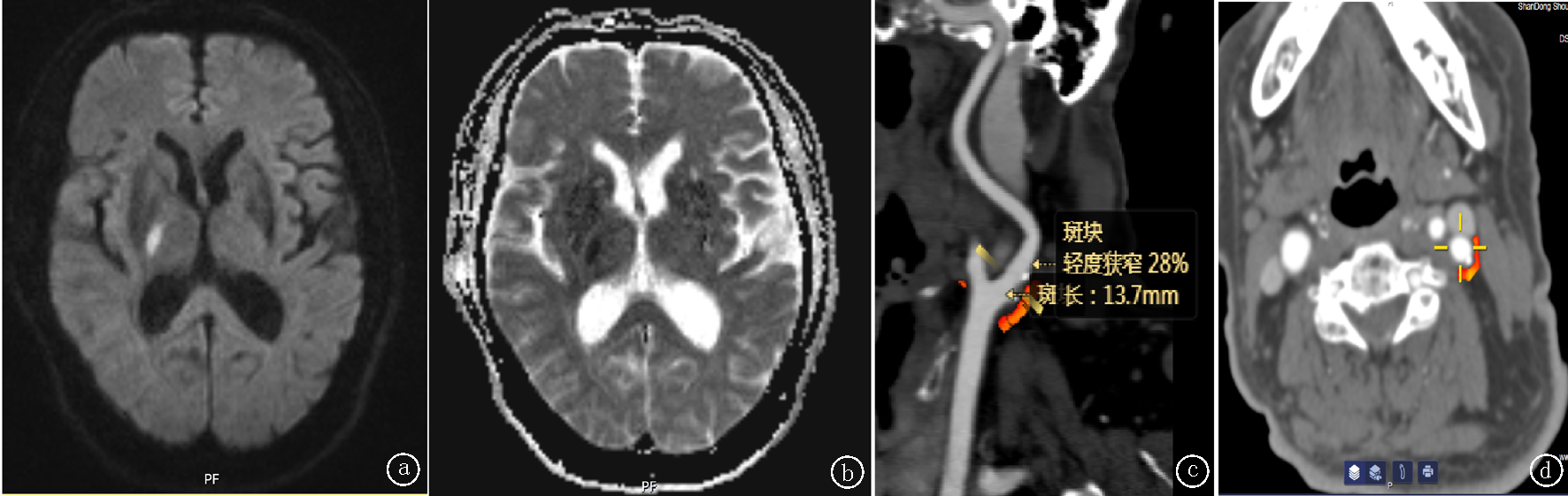
Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (9): 790-795.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.09.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
The association of imaging indicators on computed tomography angiography of the carotid arteries and blood lipid indicators with ischemic stroke
Wang Huia, Xia Xinjiana( ), Liu Saia, Wei Xifua, Zhang Shuzhongb
), Liu Saia, Wei Xifua, Zhang Shuzhongb
- a.Imaging Center; b.Department of Neurology,Shouguang People's Hospital,Weifang 262700,China
-
Received:2025-07-02Online:2025-09-20Published:2025-09-26 -
Contact:Xia Xinjian E-mail:xxjxhm@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Hui, Xia Xinjian, Liu Sai, Wei Xifu, Zhang Shuzhong. The association of imaging indicators on computed tomography angiography of the carotid arteries and blood lipid indicators with ischemic stroke[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(9): 790-795.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.lchc.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.09.003
| 特征 | 非卒中组( | 卒中组( | 统计值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 颈内动脉斑块性质[例(%)] | ||||
| 无斑块 | 12(16.9) | 0(0.0) | ||
| 非钙化斑块 | 12(16.9) | 13(25.5) | 10.57 | 0.014 |
| 钙化斑块 | 8(11.3) | 9(17.6) | ||
| 混合斑块 | 39(54.9) | 29(56.9) | ||
| 颈内动脉狭窄程度[例(%)] | ||||
| 无狭窄 | 12(16.9) | 0(0.0) | ||
| 轻度狭窄 | 23(32.4) | 12(23.5) | 15.08 | 0.002 |
| 中度狭窄 | 23(32.4) | 18(35.3) | ||
| 重度狭窄 | 13(18.3) | 21(41.2) | ||
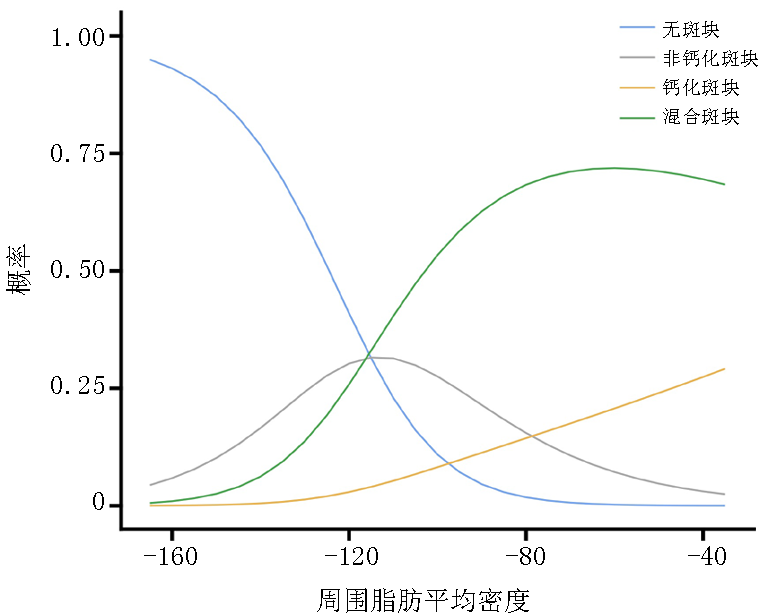
| 周围脂肪 | ||||
| 平均密度 | -96.20±13.98 | -81.67±16.58 | -5.09 | <0.001 |
| 峰值 | -38.18±14.55 | -35.84±14.81 | -0.87 | 0.388 |
| 谷值 | -137.99±18.55 | -117.39±25.98 | -4.84 | <0.001 |
| 总胆固醇 | 5.27±1.06 | 5.39±1.34 | -0.55 | 0.586 |
| 甘油三酯 | 1.74±1.11 | 1.88±0.93 | -0.76 | 0.447 |
| 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇 | 1.35±0.31 | 1.39±0.33 | -0.55 | 0.583 |
| 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇 | 2.66±0.65 | 3.39±0.82 | -5.25 | <0.001 |
Tab.1 Differences in imaging indicators and lipid indicators between the two groups
| 特征 | 非卒中组( | 卒中组( | 统计值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 颈内动脉斑块性质[例(%)] | ||||
| 无斑块 | 12(16.9) | 0(0.0) | ||
| 非钙化斑块 | 12(16.9) | 13(25.5) | 10.57 | 0.014 |
| 钙化斑块 | 8(11.3) | 9(17.6) | ||
| 混合斑块 | 39(54.9) | 29(56.9) | ||
| 颈内动脉狭窄程度[例(%)] | ||||
| 无狭窄 | 12(16.9) | 0(0.0) | ||
| 轻度狭窄 | 23(32.4) | 12(23.5) | 15.08 | 0.002 |
| 中度狭窄 | 23(32.4) | 18(35.3) | ||
| 重度狭窄 | 13(18.3) | 21(41.2) | ||
| 周围脂肪 | ||||
| 平均密度 | -96.20±13.98 | -81.67±16.58 | -5.09 | <0.001 |
| 峰值 | -38.18±14.55 | -35.84±14.81 | -0.87 | 0.388 |
| 谷值 | -137.99±18.55 | -117.39±25.98 | -4.84 | <0.001 |
| 总胆固醇 | 5.27±1.06 | 5.39±1.34 | -0.55 | 0.586 |
| 甘油三酯 | 1.74±1.11 | 1.88±0.93 | -0.76 | 0.447 |
| 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇 | 1.35±0.31 | 1.39±0.33 | -0.55 | 0.583 |
| 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇 | 2.66±0.65 | 3.39±0.82 | -5.25 | <0.001 |
| 特征 | 单因素 | 多因素 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 比值比 | 95%置信区间 | 比值比 | 95%置信区间 | ||||
| 颈内动脉斑块性质 | 1.28 | 0.90~1.82 | 0.167 | 0.77 | 0.43~1.37 | 0.368 | |
| 颈内动脉狭窄程度 | 2.21 | 1.43~3.41 | <0.001 | 3.28 | 1.68~6.42 | <0.001 | |
| 周围脂肪 | |||||||
| 平均密度 | 1.08 | 1.04~1.11 | <0.001 | 1.06 | 1.01~1.12 | 0.029 | |
| 峰值 | 1.01 | 0.99~1.04 | 0.385 | 0.98 | 0.94~1.03 | 0.464 | |
| 谷值 | 1.05 | 1.03~1.07 | <0.001 | 1.03 | 0.99~1.07 | 0.108 | |
| 总胆固醇 | 1.09 | 0.80~1.49 | 0.568 | 0.53 | 0.26~1.09 | 0.086 | |
| 甘油三酯 | 1.14 | 0.81~1.61 | 0.459 | 1.81 | 0.97~3.38 | 0.064 | |
| 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇 | 1.38 | 0.45~4.25 | 0.577 | 10.31 | 1.00~105.85 | 0.051 | |
| 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇 | 3.86 | 2.13~6.99 | <0.001 | 6.06 | 2.26~16.26 | <0.001 | |
Tab.2 Results of univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses
| 特征 | 单因素 | 多因素 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 比值比 | 95%置信区间 | 比值比 | 95%置信区间 | ||||
| 颈内动脉斑块性质 | 1.28 | 0.90~1.82 | 0.167 | 0.77 | 0.43~1.37 | 0.368 | |
| 颈内动脉狭窄程度 | 2.21 | 1.43~3.41 | <0.001 | 3.28 | 1.68~6.42 | <0.001 | |
| 周围脂肪 | |||||||
| 平均密度 | 1.08 | 1.04~1.11 | <0.001 | 1.06 | 1.01~1.12 | 0.029 | |
| 峰值 | 1.01 | 0.99~1.04 | 0.385 | 0.98 | 0.94~1.03 | 0.464 | |
| 谷值 | 1.05 | 1.03~1.07 | <0.001 | 1.03 | 0.99~1.07 | 0.108 | |
| 总胆固醇 | 1.09 | 0.80~1.49 | 0.568 | 0.53 | 0.26~1.09 | 0.086 | |
| 甘油三酯 | 1.14 | 0.81~1.61 | 0.459 | 1.81 | 0.97~3.38 | 0.064 | |
| 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇 | 1.38 | 0.45~4.25 | 0.577 | 10.31 | 1.00~105.85 | 0.051 | |
| 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇 | 3.86 | 2.13~6.99 | <0.001 | 6.06 | 2.26~16.26 | <0.001 | |
| 特征 | 估算 | 标准误 | 95%置信区间 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 颈内动脉狭窄程度 | 1.19 | 0.34 | 3.469 | <0.001 | 3.28 | 0.52~1.86 |
| 周围脂肪平均密度 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 2.178 | 0.029 | 1.06 | 0.01~0.12 |
| 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇 | 1.80 | 0.50 | 3.574 | <0.001 | 6.06 | 0.81~2.79 |
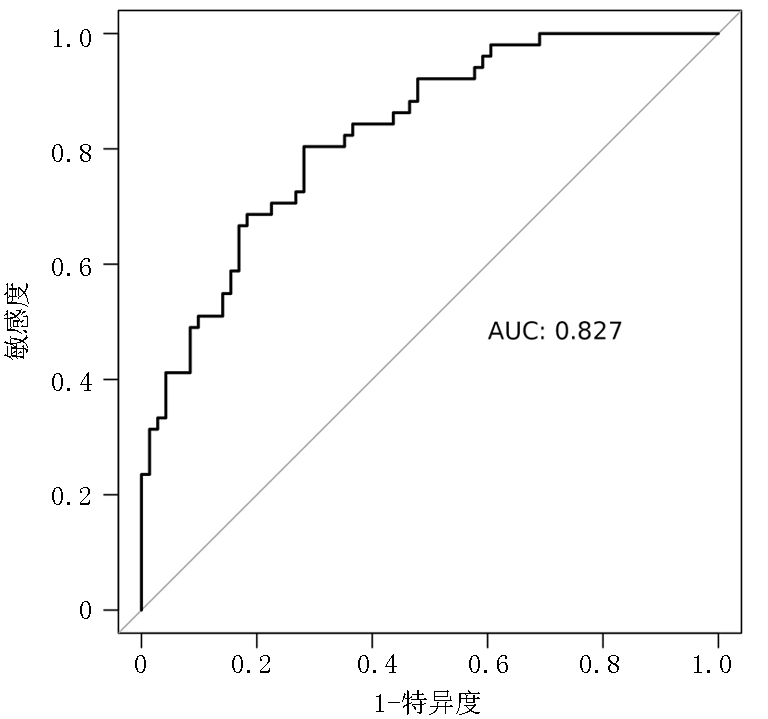
Tab.3 Model coefficients for predicting ischemic stroke by combining imaging indicators with lipid indicators
| 特征 | 估算 | 标准误 | 95%置信区间 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 颈内动脉狭窄程度 | 1.19 | 0.34 | 3.469 | <0.001 | 3.28 | 0.52~1.86 |
| 周围脂肪平均密度 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 2.178 | 0.029 | 1.06 | 0.01~0.12 |
| 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇 | 1.80 | 0.50 | 3.574 | <0.001 | 6.06 | 0.81~2.79 |
| 特征 | 血管斑块性质 | 血管狭窄程度 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ2值 | df | χ2值 | df | ||||
| 周围脂肪平均密度 | 20.84 | 3 | <0.001 | 1.17 | 1 | 0.278 | |
| 总胆固醇 | 1.69 | 3 | 0.637 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.965 | |
| 甘油三酯 | 3.50 | 3 | 0.320 | 0.11 | 1 | 0.736 | |
| 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇 | 5.93 | 3 | 0.115 | 1.05 | 1 | 0.304 | |
| 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇 | 1.56 | 3 | 0.668 | 0.91 | 1 | 0.340 | |
Tab.4 Likelihood ratio test table for the nature and degree of stenosis of vascular plaques
| 特征 | 血管斑块性质 | 血管狭窄程度 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ2值 | df | χ2值 | df | ||||
| 周围脂肪平均密度 | 20.84 | 3 | <0.001 | 1.17 | 1 | 0.278 | |
| 总胆固醇 | 1.69 | 3 | 0.637 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.965 | |
| 甘油三酯 | 3.50 | 3 | 0.320 | 0.11 | 1 | 0.736 | |
| 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇 | 5.93 | 3 | 0.115 | 1.05 | 1 | 0.304 | |
| 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇 | 1.56 | 3 | 0.668 | 0.91 | 1 | 0.340 | |
| [1] | 罗彤, 高阳, 吴琼, 等. 颈动脉高分辨磁共振血管壁成像对缺血性脑卒中发生及复发诊断价值的Meta分析[J]. 磁共振成像, 2024, 15(7):70-75.doi:10.12015/issn.1674-8034.2024.07.012. |
| [2] | 娄昕, 马林. 缺血性脑卒中影像学发展现状及展望[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2024, 58(11):1129-1136. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn112149-20240715-00409. |
| [3] | Agnieszka WK, Edyta B, Zbigniew K, et al. The effect of noninvasive bariatric surgery on the levels of certain adipokines and atherosclerosis risk factors in patients with metabolic syndrome[J]. J Am Coll Nutr, 2020, 39(6):481-487. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2019.1695017. |
| [4] | 周瑞银, 周强. 数字减影血管造影在缺血性脑卒中患者颈部血管狭窄诊断及治疗中的价值[J]. 浙江医学, 2023, 45(11):1198-1202.doi:10.12056/j.issn.1006-2785.2023.45.11.2022-2964. |
| [5] |
Foroughinia F, Morovati N, Safari A, et al. Association between Fok1 and TaqI polymorphisms of vitamin D receptor gene with the severity of stenosis and calcification in carotid bulb in patients with ischemic stroke[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2022, 97:115-120. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2022.01.009.
pmid: 35091316 |
| [6] | Kešnerová P, Školoudík D, Herzig R, et al. Peripheral vascular resistance in cerebral arteries in patients with carotid atherosclerosis-substudy results of the atherosclerotic plaque characteristics associated with a progression rate of the plaque and a risk of stroke in patients with the carotid bifurcation plaque study(ANTIQUE)[J]. J Ultrasound Med, 2022, 41(1):237-246. doi:10.1002/jum.15703. |
| [7] | 胡艳波, 高峰, 刘尚奇, 等. 血管周围脂肪组织与动脉粥样硬化的关系[J]. 医学综述, 2022, 28(13):2523-2528.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2022.13.005. |
| [8] | 殷珵烨, 袁佳栎, 葛卓望, 等. 血管周围脂肪组织在动脉粥样硬化炎症发展中的作用[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志, 2022, 30(8):719-724. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-3949.2022.08.013. |
| [9] |
Nammas W, Saraste A. Perivascular fat attenuation, inflammation, and coronary artery function[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2020, 21(6):606-607. doi:10.1093/ehjci/jeaa051.
pmid: 32335673 |
| [10] | Rami AZA, Hamid AA, Anuar NNM, et al. Exploring the relationship of perivascular adipose tissue inflammation and the development of vascular pathologies[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2022, 2022: 2734321.doi:10.1155/2022/2734321. |
| [11] | 赵芳, 赵源征, 周晨光, 等. 颈动脉周围脂肪衰减指数与缺血性脑卒中的关系[J]. 中国实用神经疾病杂志, 2024, 27(4):420-424. doi:10.12083/SYSJ.240095. |
| [12] | 余苗, 孟闫凯, 徐含波, 等. 颈动脉周围脂肪密度与急性缺血性脑卒中事件的相关性研究[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2023, 42(6):910-914. |
| [13] | 林培良. 血管周围脂肪与心血管疾病的研究进展[J]. 黑龙江医学, 2024, 48(15):1912-1914.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-5775.2024.15.037. |
| [14] | 赵丰, 徐志云. 老年急性缺血性脑卒中患者炎症因子、血脂和氧化应激水平的变化[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2020, 40(21):4515-4517.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2020.21.010. |
| [15] |
Philip HK, Laura F, Alexander DM, et al. Antibody-mediated inhibition of tissue-type plasminogen activator binding to the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 as a potential beneficial modulator for stroke therapy[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2023, 124(7):1040-1049.doi:10.1002/jcb.30431.
pmid: 37288821 |
| [16] | 罗恩斯, 陈国永, 王杰英. 急性缺血性脑卒中患者血脂、血清胱抑素C及脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2水平与颈动脉粥样硬化的关系[J]. 中国医学创新, 2021, 18(6):55-58. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2021.06.013. |
| [17] | 景文君, 刘华坤, 郭智鹏. 脂质标志物与颈动脉粥样硬化[J]. 国际脑血管病杂志, 2024, 32(2):140-144. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4165.2024.02.011. |
| [18] | 王益松, 赵沨, 张红珍. 基于血常规和颈动脉斑块构建缺血性脑卒中nomogram风险预测模型[J]. 包头医学院学报, 2024, 40(3):9-15. doi:10.16833/j.cnki.jbmc.2024.03.003. |
| [19] | 白帆, 王效春. 影像学预测缺血性脑卒中复发的研究进展[J]. 磁共振成像, 2024, 15(5):198-203. doi:10.12015/issn.1674-8034.2024.05.032. |
| [20] | 刘小蒙, 李俊玉, 何威, 等. 急诊急性缺血性脑卒中患者短期预后预测模型的构建及效能评估[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2024, 33(1):51-58. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0282.2024.01.009. |
| [21] | 苟于芬, 王宏宇. 动脉粥样硬化的免疫机制与治疗的研究进展[J]. 心血管病学进展, 2024, 45(10):912-917. doi:10.16806/j.cnki.issn.1004-3934.2024.10.010. |
| [22] | 郑蒙雨, 冯毅, 白潇萱, 等. 血管周围脂肪组织与动脉粥样硬化的关系及其研究进展[J]. 心血管康复医学杂志, 2024, 33(3):331-334.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-0074.2024.03.16. |
| [23] | 周茜洋, 唐春香, 张龙江, 等. 冠状动脉周围脂肪影像学的研究进展[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2021, 55(3): 320-323. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn112149-2020330-00470. |
| [24] | 王重阳, 张林波, 郭爽, 等. 计算机辅助测量颈动脉周围脂肪密度与颈动脉斑块的关系[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2024, 34(1):14-17. |
| [25] | Liu C, He X, Zhang L, et al. The correlation analysis between the degree of coronary artery stenosis and carotid atherosclerosis[J]. J Med Imaging, 2021, 31(6): 931-934. |
| [26] | Geng HQ, Shi JZ, Zhang XC, et al. Correlation analysis of average attenuation of adipose tissue around coronary artery CTA with plaque and stenosis[J]. J Med Imaging, 2023, 33(1): 16-20. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||