Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (10): 897-903.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.10.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Assessment value of FT4 combined with LVEF in hyperthyroid heart disease
Department of Cardiology ,Beijing Renhe Hospital Beijing 102600, China
-
Received:2025-06-05Online:2025-10-20Published:2025-10-31 -
Contact:Liu Shenghua E-mail:sci_publishing@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Shenghua. Assessment value of FT4 combined with LVEF in hyperthyroid heart disease[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(10): 897-903.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.lchc.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.10.004
| 典型症状群 | 高代谢症候群:体重进行性下降、怕热多汗、食欲亢进 |
|---|---|
| 神经兴奋性增加:手颤、失眠、易激惹等 | |
| 影像学证据 | 甲状腺肿大 |
| 实验室指标 | 血清甲状腺激素水平上升、促甲状腺激素(thyroid stimulating hormone,TSH)降低 |
Tab.1 Diagnostic criteria for hyperthyroidism
| 典型症状群 | 高代谢症候群:体重进行性下降、怕热多汗、食欲亢进 |
|---|---|
| 神经兴奋性增加:手颤、失眠、易激惹等 | |
| 影像学证据 | 甲状腺肿大 |
| 实验室指标 | 血清甲状腺激素水平上升、促甲状腺激素(thyroid stimulating hormone,TSH)降低 |
| 必要条件 | 确诊甲亢 |
|---|---|
| 次要条件 | ①明显的房性心律失常:房性心动过速、心房扑动、心房颤动;②心力衰竭;③心脏扩大 |
| 排除条件 | 其他原因导致的心脏疾病 |
Tab.2 Diagnostic criteria for HHD
| 必要条件 | 确诊甲亢 |
|---|---|
| 次要条件 | ①明显的房性心律失常:房性心动过速、心房扑动、心房颤动;②心力衰竭;③心脏扩大 |
| 排除条件 | 其他原因导致的心脏疾病 |
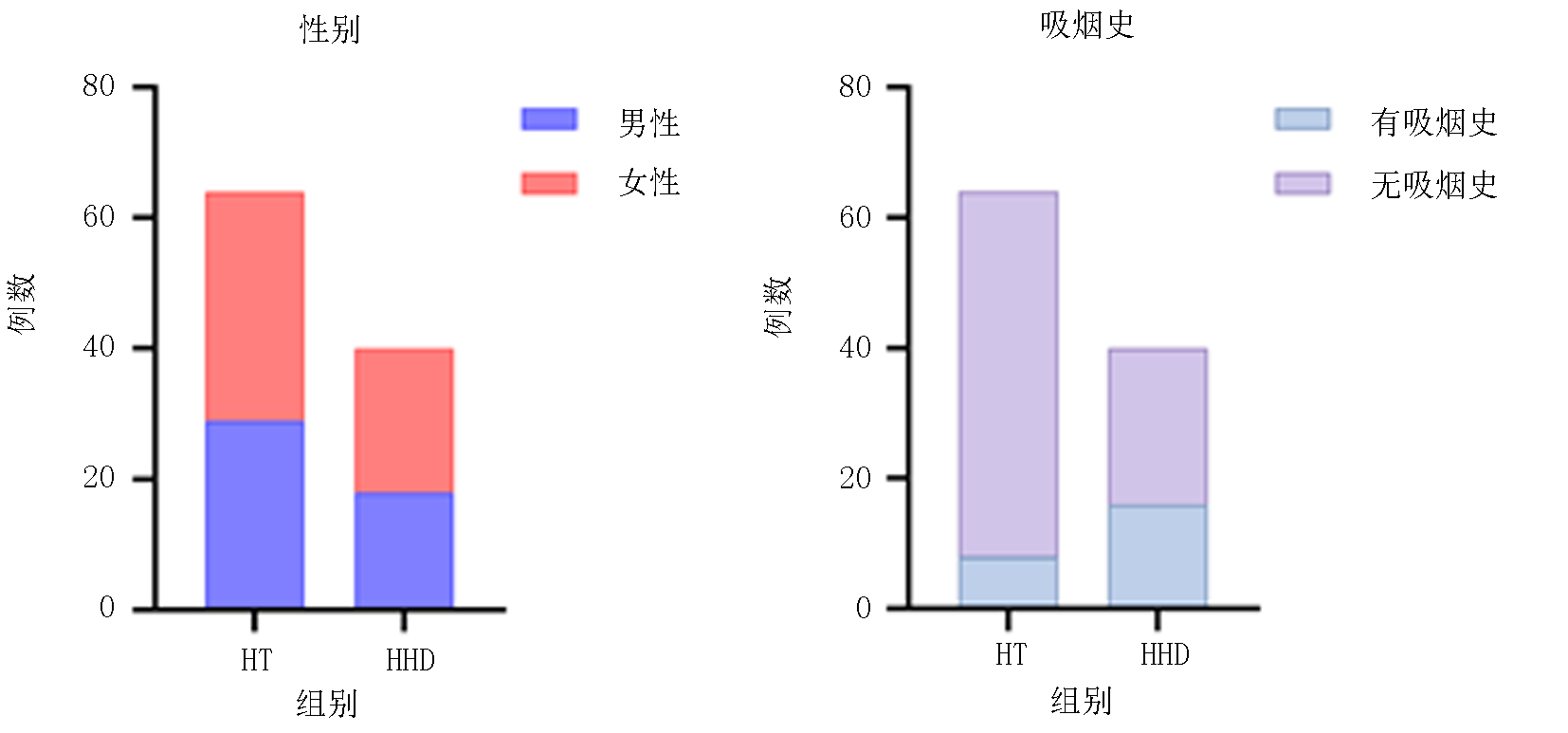
| 组别 | 例数 | 女性 [例(%)] | 年龄 (岁) | 吸烟史 [例(%)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甲亢组 | 64 | 35(54.69) | 34.78±8.37 | 8(12.50) |
| HHD组 | 40 | 22(55.00) | 40.13±10.61 | 16(40.00) |
| t/χ2值 | 0.001 | 2.853 | 10.490 | |
| P值 | 0.975 | 0.005 | 0.001 |
Tab.3 Comparison of general data between the two groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 女性 [例(%)] | 年龄 (岁) | 吸烟史 [例(%)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甲亢组 | 64 | 35(54.69) | 34.78±8.37 | 8(12.50) |
| HHD组 | 40 | 22(55.00) | 40.13±10.61 | 16(40.00) |
| t/χ2值 | 0.001 | 2.853 | 10.490 | |
| P值 | 0.975 | 0.005 | 0.001 |
| 组别 | 例数 | FT3(ng/L) | FT4(ng/L) | TSH(mIU/L) | LVEDD(mm) | LVESD(mm) | LVEF(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甲亢组 | 64 | 10.45±3.56 | 39.40±6.90 | 0.08(0.07, 0.09) | 50.09±4.26 | 39.66±3.58 | 55.43±6.63 |
| HHD组 | 40 | 12.69±2.92 | 55.10±11.80 | 0.06(0.04, 0.08) | 54.85±5.73 | 43.79±3.66 | 51.59±6.06 |
| t/Z值 | 3.340 | 5.350 | -3.971 | 4.532 | 5.681 | 2.968 | |
| P值 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.004 |
Tab.4 Comparison of clinical data between the two groups
| 组别 | 例数 | FT3(ng/L) | FT4(ng/L) | TSH(mIU/L) | LVEDD(mm) | LVESD(mm) | LVEF(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甲亢组 | 64 | 10.45±3.56 | 39.40±6.90 | 0.08(0.07, 0.09) | 50.09±4.26 | 39.66±3.58 | 55.43±6.63 |
| HHD组 | 40 | 12.69±2.92 | 55.10±11.80 | 0.06(0.04, 0.08) | 54.85±5.73 | 43.79±3.66 | 51.59±6.06 |
| t/Z值 | 3.340 | 5.350 | -3.971 | 4.532 | 5.681 | 2.968 | |
| P值 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.004 |
| 变量 | 赋值 |
|---|---|
| 因变量 | |
| 分组 | 0=甲亢,1=HHD |
| 自变量 | |
| 年龄 | 连续性变量 |
| 吸烟史 | 1=无,2=有 |
| FT3、FT4、TSH | 连续性变量 |
| LVESD、LVEDD、LVEF | 连续性变量 |
Tab.5 Coding of statistical dependent and independent variables
| 变量 | 赋值 |
|---|---|
| 因变量 | |
| 分组 | 0=甲亢,1=HHD |
| 自变量 | |
| 年龄 | 连续性变量 |
| 吸烟史 | 1=无,2=有 |
| FT3、FT4、TSH | 连续性变量 |
| LVESD、LVEDD、LVEF | 连续性变量 |
| 因素 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | 95%可信区间 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | |||||
| FT3 | 0.201 | 0.065 | 9.488 | 0.002 | 0.073 | 0.329 |
| FT4 | 1.115 | 0.251 | 19.750 | <0.001 | 0.623 | 1.606 |
| TSH | -34.220 | 9.938 | 11.857 | 0.001 | -53.698 | -14.742 |
| LVESD | 0.194 | 0.048 | 16.311 | <0.001 | 0.100 | 0.288 |
| LVEDD | 0.323 | 0.072 | 19.845 | <0.001 | 0.181 | 0.465 |
| LVEF | -0.094 | 0.034 | 7.665 | 0.006 | -0.161 | -0.028 |
| 年龄 | 0.061 | 0.023 | 7.074 | 0.008 | 0.016 | 0.106 |
| 吸烟史 | 1.540 | 0.497 | 9.606 | 0.002 | 0.566 | 2.515 |
Tab.6 Multiple logistic regression
| 因素 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | 95%可信区间 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | |||||
| FT3 | 0.201 | 0.065 | 9.488 | 0.002 | 0.073 | 0.329 |
| FT4 | 1.115 | 0.251 | 19.750 | <0.001 | 0.623 | 1.606 |
| TSH | -34.220 | 9.938 | 11.857 | 0.001 | -53.698 | -14.742 |
| LVESD | 0.194 | 0.048 | 16.311 | <0.001 | 0.100 | 0.288 |
| LVEDD | 0.323 | 0.072 | 19.845 | <0.001 | 0.181 | 0.465 |
| LVEF | -0.094 | 0.034 | 7.665 | 0.006 | -0.161 | -0.028 |
| 年龄 | 0.061 | 0.023 | 7.074 | 0.008 | 0.016 | 0.106 |
| 吸烟史 | 1.540 | 0.497 | 9.606 | 0.002 | 0.566 | 2.515 |
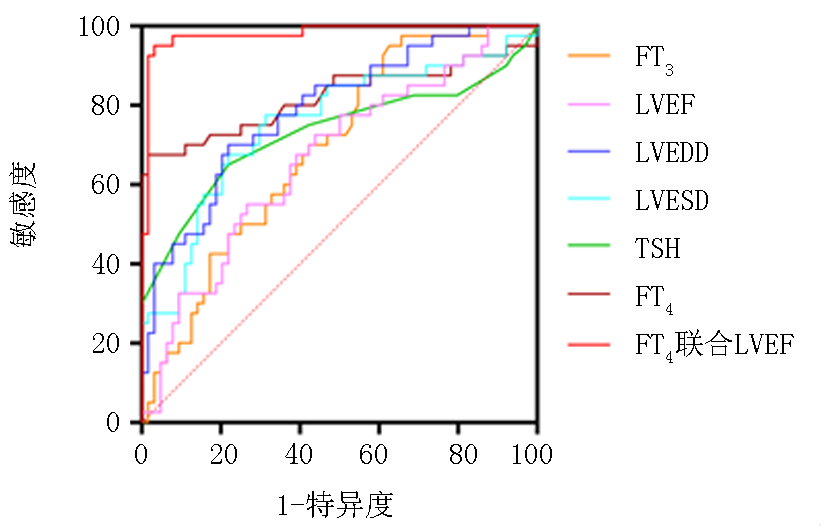
| 预测项目 | AUC | 截断值 | 95%可信区间 | 特异度(%) | 灵敏度(%) | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| FT4联合LVEF | 0.98 | -3.14 | 0.871 | 0.999 | 64.06 | 51.82 | <0.001 |
| FT4 | 0.82 | 4.98 | 0.723 | 0.920 | 96.88 | 67.50 | <0.001 |
| LVEDD | 0.79 | 44.23 | 0.698 | 0.877 | 79.10 | 89.06 | <0.001 |
| LVESD | 0.75 | 57.85 | 0.653 | 0.855 | 95.31 | 27.50 | <0.001 |
| TSH | 0.73 | 0.05 | 0.618 | 0.842 | 90.63 | 47.50 | <0.001 |
| FT3 | 0.69 | 16.20 | 0.590 | 0.791 | 96.88 | 12.50 | 0.001 |
| LVEF | 0.67 | 62.39 | 0.559 | 0.773 | 12.50 | 97.50 | <0.001 |
Tab.7 The diagnostic and predictive value of thyroid function index and cardiac function index for HHD
| 预测项目 | AUC | 截断值 | 95%可信区间 | 特异度(%) | 灵敏度(%) | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| FT4联合LVEF | 0.98 | -3.14 | 0.871 | 0.999 | 64.06 | 51.82 | <0.001 |
| FT4 | 0.82 | 4.98 | 0.723 | 0.920 | 96.88 | 67.50 | <0.001 |
| LVEDD | 0.79 | 44.23 | 0.698 | 0.877 | 79.10 | 89.06 | <0.001 |
| LVESD | 0.75 | 57.85 | 0.653 | 0.855 | 95.31 | 27.50 | <0.001 |
| TSH | 0.73 | 0.05 | 0.618 | 0.842 | 90.63 | 47.50 | <0.001 |
| FT3 | 0.69 | 16.20 | 0.590 | 0.791 | 96.88 | 12.50 | 0.001 |
| LVEF | 0.67 | 62.39 | 0.559 | 0.773 | 12.50 | 97.50 | <0.001 |
| [1] | 许波进, 彭文芳, 黄珊. 2022版《中国甲状腺功能亢进症和其他原因所致甲状腺毒症诊治指南》解读[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2023, 28(6): 512-519. doi:10.16139/j.1007-9610.2023.06.05. |
| [2] | 蔡丹阳, 李洁, 李运伦. 以线粒体自噬为靶点的益气活血类中药保护心肌缺血再灌注损伤研究进展[J]. 环球中医药, 2023, 16(9): 1913-1919. doi:CNKI:SUN:HQZY.0.2023-09-041. |
| [3] |
Rhodes MA, Adams CS, Bragg S, et al. Thyroid and parathyroid conditions: Hyperthyroidism[J]. FP Essent, 2022, 514: 11-17.
pmid: 35235281 |
| [4] | 徐鑫, 赵锴, 杨孜. 131I联合生脉注射液治疗甲亢性心脏病的临床研究[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2018, 16(18): 2612-2615. |
| [5] |
Polikar R, Burger AG, Scherrer U, et al. The thyroid and the heart[J]. Circulation, 1993, 87(5): 1435-1441. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.87.5.1435.
pmid: 8490997 |
| [6] | Liu J, Wu G, Li S, et al. The genetic association between hyperthyroidism and heart failure: A Mendelian randomization study[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2024, 15: 1344282. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1344282. |
| [7] | 王双. 甲亢性心脏病相关临床检验指标探析[J]. 中西医结合心血管病电子杂志, 2022, 10(22): 139-141+130. doi:10.16282/j.cnki.cn11-9336/r.2022.22.014. |
| [8] | 吴清原, 郭思佳, 孙增涛, 等. 基于线粒体功能探讨培宗气理论治疗慢性阻塞性肺疾病的机制研究[J]. 天津中医药, 2024, 41(1): 117-122. doi:CNKI:SUN:TJZY.0.2024-01-020. |
| [9] | 任艳茹, 马俊, 刘萍, 等. 甲状腺功能亢进性心脏病相关危险因素分析[J]. 宁夏医学杂志, 2020, 42(5): 406-408. doi:10.13621/j.1001-5949.2020.05.0406. |
| [10] | Haidous M, Al Armashi AR, Balozian P, et al. A case of severe dilated cardiomyopathy and hyperthyroidism[J]. Cureus, 2022, 14(3): e22968. doi:10.7759/cureus.22968. |
| [11] | 中华医学会内分泌学分会《中国甲状腺疾病诊治指南》编写组. 中国甲状腺疾病诊治指南——甲状腺功能亢进症[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2007, 46(10): 876-882. doi:CNKI:SUN:ZHNK.0.2007-10-044. |
| [12] |
Li H, Zeng RL, Liao YF, et al. Association of plasma connective tissue growth factor levels with hyperthyroid heart disease[J]. Curr Med Sci, 2021, 41(2): 348-355. doi: 10.1007/s11596-021-2354-x. Epub 2021 Apr 20.
pmid: 33877553 |
| [13] | 张成伟, 马慧慧, 魏琴, 等. 老年甲亢性心脏病患者血清TPO-Ab、BNP、Tg-Ab水平与心肌损伤标志物的关系[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2024, 44(20): 4865-4869. doi:CNKI:SUN:ZLXZ.0.2024-20-001. |
| [14] |
Zubair Khan M, Gupta A, Hodge J, et al. Clinical outcomes of atrial fibrillation with hyperthyroidism[J]. J Arrhythm, 2021, 37(4): 942-948. doi: 10.1002/joa3.12550.
pmid: 34386120 |
| [15] | Huang PS, Cheng JF, Chen JJ, et al. Higher risk of incident hyperthyroidism in patients with atrial fibrillation[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2023, 109(1): 92-99. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgad448. |
| [16] | Petrie MA, Taylor EB, Suneja M, et al. Genomic and epigenomic evaluation of electrically induced exercise in people with spinal cord injury: Application to precision rehabilitation[J]. Phys Ther, 2022, 102(1):pzab243. doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzab243. |
| [17] | Okafor EN, Ugonabo MC, Chukwukelu EE, et al. Prevalence and pattern of thyroid disorders among patients attending University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital, Enugu, Southeastern Nigeria[J]. Niger Med J, 2019, 60(2): 62-67. doi: 10.4103/nmj.NMJ_34_19. |
| [18] |
Fages-Masmiquel E, Ponjoan A, Blanch J, et al. The effect of age and sex on factors associated with dementia[J]. Rev Neurol, 2021, 73(12): 409-415. Spanish. doi: 10.33588/rn.7312.2021301.
pmid: 34877643 |
| [19] | Naz F, Malik S, Asif K, et al. Unravelling atrial fibrillation aetiology and anticoagulation trends in stroke: Where do we stand? A study from Northern Pakistan[J]. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad, 2024, 36(3): 470-4747. doi: 10.55519/JAMC-03-13418. |
| [20] |
Kim HJ, Kang T, Kang MJ, et al. Incidence and mortality of myocardial infarction and stroke in patients with hyperthyroidism: A nationwide cohort study in Korea[J]. Thyroid, 2020, 30(7): 955-965. doi: 10.1089/thy.2019.0543. Epub 2020 Mar 26.
pmid: 32093587 |
| [21] | Zhang X, Chen L, Sheng J, et al. The association of autoantibodies in hyperthyroid heart disease combined with pulmonary hypertension[J]. Int J Endocrinol, 2019:9325289. doi: 10.1155/2019/9325289. |
| [22] |
Sönmez E, Bulur O, Ertugrul DT, et al. Hyperthyroidism influences renal function[J]. Endocrine, 2019, 65(1): 144-148. doi: 10.1007/s12020-019-01903-2. Epub 2019 Mar 23.
pmid: 30904999 |
| [23] | Janus I, Noszczyk-Nowak A, Bubak J, et al. Comparative cardiac macroscopic and microscopic study in cats with hyperthyroidism vs. cats with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy[J]. Vet Q, 2023, 43(1): 1-11. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2023.2234436. |
| [24] | Nie D, Xia C, Wang Z, et al. CaMKII inhibition protects against hyperthyroid arrhythmias and adverse myocardial remodeling[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2022, 615: 136-142. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.04.082. Epub 2022 Apr 20. |
| [25] | Lin C, Kuo FC, Chau T, et al. Artificial intelligence-enabled electrocardiography contributes to hyperthyroidism detection and outcome prediction[J]. Commun Med (Lond), 2024, 4(1): 42. doi:10.1038/s43856-024-00472-4. |
| [26] | Bektur Aykanat NE, Şahin E, Kaçar S, et al. Investigation of the effect of hyperthyroidism on endoplasmic reticulum stress and tran- sient receptor potential canonical 1 channel in the kidney[J]. Turk J Med Sci, 2021, 51(3): 1554-1563. doi: 10.3906/sag-2007-109. |
| [27] | Fan SWD, Ong LT. Prevalence and risk factors of heart failure in patients diagnosed with hyperthyroidism: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. touchREV Endocrinol, 2024, 20(2): 91-99. doi: 10.17925/EE.2024.20.2.12. Epub 2024 Jul 22. |
| [28] | Naser JA, Pislaru S, Stan MN, et al. Incidence, risk factors, natural history and outcomes of heart failure in patients with Graves' disease[J]. Heart, 2022, 108(11): 868-874. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2021-319752. |
| [29] |
Mastroianno S, Di Stolfo G, Maggio A, et al. Role of Subclinical iatrogenic hyperthyroidism in the setting of heart disease and arrhythmic burden[J]. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets, 2020, 20(6):959-962. doi: 10.2174/1871530320666191227103627.
pmid: 31880254 |
| [30] | 刘盼茹, 郭玺, 唐乙朝, 等. 自身免疫性疾病与肠道菌群互作及中药干预研究进展[J]. 南京中医药大学学报, 2023, 39(7): 693-700. doi:10.14148/j.issn.1672-0482.2023.0693. |
| [31] | 李丹, 黄峰. 血清FT3、FT4水平对甲亢患者并发甲亢性心脏病的评估价值[J]. 医学临床研究, 2024, 41(3): 368-370+374. doi:CNKI:SUN:HNYZ.0.2024-03-013. |
| [32] | 王竹英. 分析甲亢性心脏病患者血浆B型脑钠肽水平的变化及意义[J]. 心血管病防治知识, 2020, 10(24): 42-44. doi:CNKI:SUN:XUGB.0.2020-24-014. |
| [33] | 朱莉, 祝国华, 张斌, 等. 血清T3、T4、H-TSH、FT3、FT4在甲亢和甲减诊断中的评价探讨[J]. 解放军预防医学杂志, 2019, 37(5): 49-50. doi:10.13704/j.cnki.jyyx.2019.05.024. |
| [34] | 田永波, 孙敏, 金安林, 等. 血清TPO-Ab、NT-proBNP及CRP在甲亢性心脏病早期诊断中的临床价值[J]. 临床医学研究与实践, 2021, 6(26): 109-112. doi:10.19347/j.cnki.2096-1413.202126037. |
| [35] | 黄玉婵, 阎施杜, 张帆, 等. 活血利水方药理论与应用探讨[J]. 中草药, 2024, 55(14): 4978-4990. doi:CNKI:SUN:ZCYO.0.2024-14-030. |
| [36] | 孙可心, 项莹. 甲状腺功能亢进及其药物在心血管疾病中的作用[J]. 心血管康复医学杂志, 2023, 32(1): 73-77. doi:CNKI:SUN:XXGK.0.2023-01-019. |
| [37] | Merkx R, Leerink JM, Feijen ELAM, et al. Extensive cardiac function analyses using contemporary echocardiography in childhood cancer survivors: A DCCSS LATER study[J]. JACC CardioOncol, 2023, 5(4): 472-485. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2023.06.003. |
| [38] | Zhang Y, Jiang H, Cui J, et al. Ablation of ventricular preexcitation to cure preexcitation-induced dilated cardiomyopathy in infants: Diagnosis and outcome[J]. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2023, 16(4):e011569. doi:10.1161/CIRCEP.122.011569. Epub 2023 Mar 9. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||