Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (11): 1016-1021.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.11.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
Tocilizumab enables glucocorticoid reduction in refractory adult-onset Still’s disease: A case report and literature review
Luo Lunju1, Deng Yiyao2, Li Zhengsheng3, Xue Qiuling1, Zha Yan2, Yuan Jing2( )
)
- 1. Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guiyang 550005, China
2. Department of Nephrology/NHC Key Laboratory of Pulmonary Immunological Disease/Guizhou Provincial Key Laboratory of Pathogenesis and Prevention of Common Chronic Diseases Research, Guizhou Provincial People's Hospital, Guiyang 550002, China
3. Department of Nephrology, the 2nd Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou University of TCM, Guiyang 550003, China
-
Received:2025-09-11Online:2025-11-20Published:2025-12-02 -
Contact:Yuan Jing E-mail:yuanjinger@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Luo Lunju, Deng Yiyao, Li Zhengsheng, Xue Qiuling, Zha Yan, Yuan Jing. Tocilizumab enables glucocorticoid reduction in refractory adult-onset Still’s disease: A case report and literature review[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(11): 1016-1021.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.lchc.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.11.008

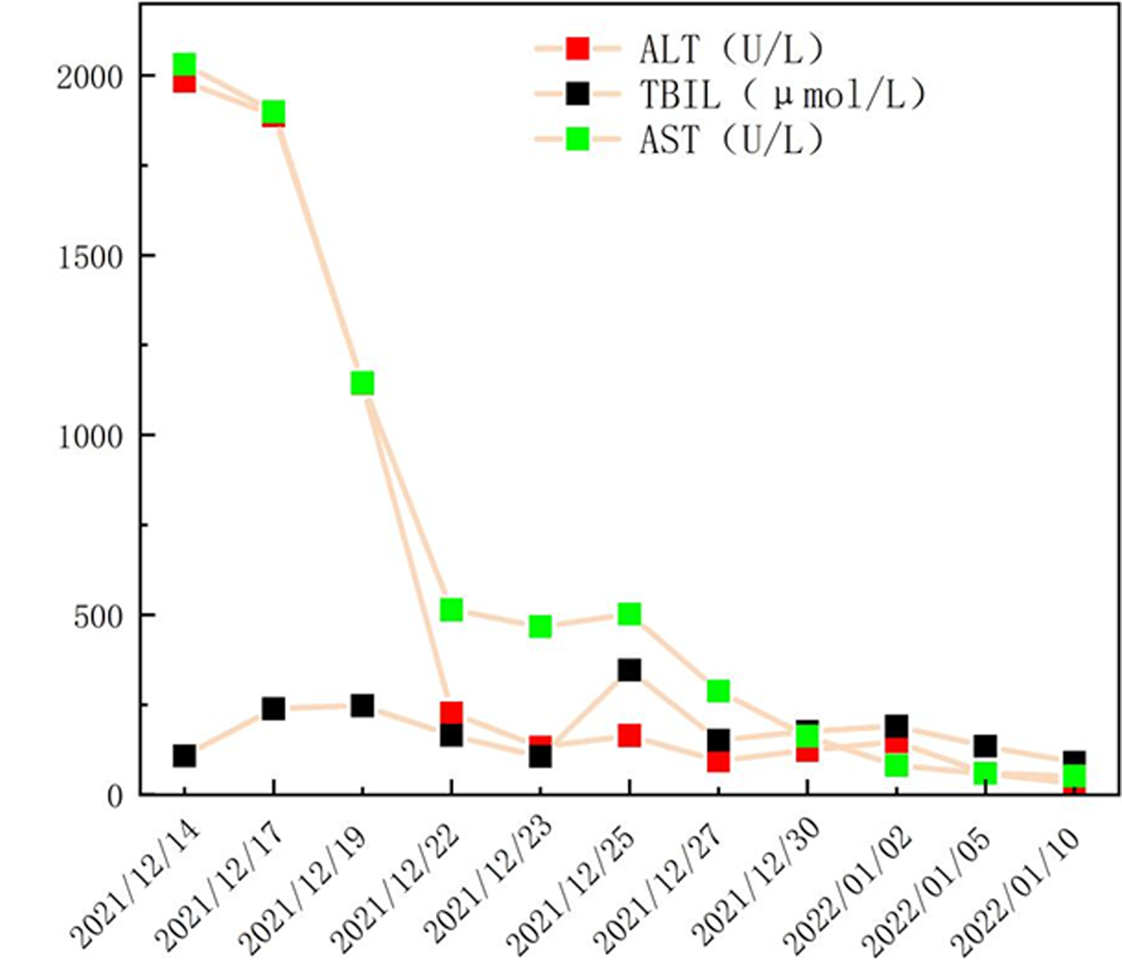
Fig.2 After treatment with methylprednisolone, CsA, and tocilizumab, the above-mentioned indicators decreased. After treatment with tocilizumab, the levels of ferritin, CRP, WBC, and ESR increased for the first time with the reduction of tocilizumab during the course of the disease. The second increase in laboratory indicators was considered to be due to the patient's irregular use of tocilizumab.
| [1] | Huang Z, You X, Chen L, et al. mTORC1 links pathology in experimental models of Still’s disease and macrophage activation syndrome[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1):6915. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34480-6. |
| [2] | Bita S, Ashley G, Marta W, et al. The 2022 EULAR/ACR points to consider at the early stages of diagnosis and management of suspected haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis/macrophage activation syndrome (HLH/MAS)[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2023, 75(10):1714-1732. doi:10.1002/ART.42636. |
| [3] |
Piero R, Onorina B, Ilenia CD, et al. The hyper-expression of NLRP4 characterizes the occurrence of macrophage activation syndrome assessing STING pathway in adult-onset Still's disease[J]. Clin Exp Immunol., 2022, 208(1):95-102. doi: 10.1093/CEI/UXAC014.
pmid: 35467709 |
| [4] |
Ma Y, Meng J, Jia J, et al. Current and emerging biological therapy in adult-onset Still's disease[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2021, 60(9):3986-4000. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keab485.
pmid: 34117886 |
| [5] |
Ruscitti P, McGonagle D, Garcia VC, et al. Systematic review and metaanalysis of pharmacological interventions in adult-onset still disease and the role of biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs[J]. J Rheumatol, 2024, 51:442. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.2023-0995.
pmid: 38302170 |
| [6] | Yurttas B, Egeli B, Ozkose GG, et al. POS1381 biologic treatment of adult-onset Still's disease: A single center experience[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2021, 80(S1):974-974. doi:10.1136/ANNRHEUMDIS-2021-EULAR.3968. |
| [7] |
Yamaguchi M, Ohta A, Tsunematsu T, et al. Preliminary criteria for classification of adult Still's disease[J]. J Rheumatol, 1992, 19:424-430.
pmid: 1578458 |
| [8] | Henter JI, Horne A, Aricó M, et al. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis[J]. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 2007, 48(2):124-131. doi: 10.1002/pbc.21039. |
| [9] | van de Putte LB, Wouters JM. Adult-onset Still's disease[J]. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol, 1991, 5(2):263-275.doi: 10.1016/s0950-3579(05)80283-3. |
| [10] |
Zhou D, Xie J, Wang J, et al. Establishment of a differential diagnosis method and an online prediction platform for AOSD and sepsis based on gradient boosting decision trees algorithm[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2023, 25(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03207-3.
pmid: 37974244 |
| [11] | Beatrice M, Giovanni C, Marcello G. Adult-onset Still’s disease: Novel biomarkers of specific subsets, disease activity, and relapsing forms[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(24):13320. doi:10.3390/ijms222413320. |
| [12] |
Jordan MB. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: A disorder of T cell activation, immune regulation, and distinctive immunopathology[J]. Immunol Rev, 2023, 322(1):339-350. doi:10.1111/imr.13298.
pmid: 38100247 |
| [13] | Braun A, Otoukesh S, Tinajero J, et al. Blinatumomab-induced macrophage activating syndrome (MAS) in adult with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL)[J]. Ann Hematol, 2024, 103(7):2541-2543. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-05795-9. |
| [14] | Jia J, Wang M, Meng J, et al. Ferritin triggers neutrophil extracellular trap-mediated cytokine storm through Msr1 contributing to adult-onset Still’s disease pathogenesis[J]. Nat. Commun, 2022, 13(1):6804. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34560-7. |
| [15] |
Ogasawara Y, Kogiso T, Kotera Y, et al. The utility of liver transplantation to treat acute liver failure caused by adult-onset Still’s disease: Case reports[J]. Clin J Gastroenterol, 2021, 14(3):866-875. doi: 10.1007/s12328-021-01398-3.
pmid: 33797038 |
| [16] |
Ruscitti P, Iacono D, Ciccia F, et al. Macrophage activation syndrome in patients affected by adult-onset still disease: Analysis of survival rates and predictive factors in the gruppo italiano diricerca in reumatologia clinicae sperimentale cohort[J]. J Rheumatol, 2018, 45(6):864-872. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.170955.
pmid: 29657144 |
| [17] | Chi H, Wang Z, Meng J, et al. A cohort study of liver involvement in patients with adult-onset Still's disease: Prevalence, characteristics and impact on prognosis[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2020, 7:621005. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.621005. |
| [18] |
Fautrel B, Mitrovic S, Matteis DA, et al. EULAR/PReS recommendations for the diagnosis and management of Still's disease, comprising systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and adult-onset Still's disease[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2024, 83(12):1614-1627. doi: 10.1136/ard-2024-225851.
pmid: 39317417 |
| [19] | Sola D, Smirne C, Bruggi F, et al. Unveiling the mystery of adult-onset Still’s disease: A compelling case report[J]. Life, 2024, 14(2):195. doi: 10.3390/life14020195. |
| [20] | De Matteis A, Bindoli S, De Benedetti F, et al. Systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and adult-onset Still’s disease are the same disease: Evidence from systematic reviews and meta-analyses informing the 2023 EULAR/PReS recommendations for the diagnosis and management of Still’s disease[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2024, 83:1748. doi: 10.1136/ard-2024-225853. |
| [21] | Eloseily EM, Weiser P, Crayne CB, et al. Benefit of anakinra in treating pediatric secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2020, 72(2):326-334. doi: 10.1002/art.41103. |
| [22] | Mehta P, Cron QR, Hartwell J, et al. Silencing the cytokine storm: The use of intravenous anakinra in haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis or macrophage activation syndrome[J]. Lancet Rheumatol, 2020, 2(6):e358-e367. doi: 10.1016/s2665-9913(20)30096-5. |
| [23] |
Bindoli S, Baggio C, Doria A, et al. Adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD): Advances in understanding pathophysiology, genetics and emerging treatment options[J]. Drugs, 2024, 84(3):257-274. doi: 10.1007/s40265-024-01993-x.
pmid: 38441807 |
| [24] | Wang MJ, Zhang HL, Chen F, et al. The double-edged effects of IL-6 in liver regeneration, aging, inflammation, and diseases[J]. Exp Hematol Oncol, 2024, 13(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s40164-024-00527-1. |
| [25] | Zhang Y, Zhou F, Wu Z, et al. Timing of tocilizumab administration under the guidance of IL-6 in CAR-T therapy for R/R acute lymphoblastic leukemia[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13:914959. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.914959. |
| [26] | Dufranc E, Del Bello A, Belliere J, et al. IL6-R blocking with tocilizumab in critically ill patients with hemophagocytic syndrome[J]. Crit Care, 2020, 24(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02878-7. |
| [27] | Ma Y, Wu M, Zhang X, et al. Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab with inhibition of interleukin-6 in adult-onset Still’s disease: A meta-analysis[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2018, 28(5):849-857. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2017.1416924. |
| [28] | Fung WW, Chao AC, Pang WF, et al. An unusual case of adult-onset Still’s disease complicated with anti-complement factor H antibodies associated atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome[J]. BMC Nephrol, 2024, 25(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03548-4. |
| [29] | Horiuchi Y, Hashimoto K, Horikoshi H, et al. Fulminant elderly adult-onset Still’s disease effectively treated with tocilizumab and methotrexate: A case report[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2022, 101(28):e29354. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000029354. |
| [30] | Lee JH, Ha YJ, Kang EH, et al. A case of macrophage activation syndrome during the treatment of adult-onset Still’s disease with tocilizumab[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2022, 29(2):123-128. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2022.29.2.123. |
| [31] | Ohmura SI, Uehara K, Yamabe T, et al. Successful use of short-term add-on tocilizumab for refractory adult-onset Still’s disease with macrophage activation syndrome despite treatment with high-dose glucocorticoids, cyclosporine, and etoposide[J]. Mod Rheumatol Case Rep, 2020, 4(2):202-207. doi: 10.1080/24725625.2020.1741073. |
| [32] | Sautner J. Makrophagenaktivierungssyndrom-eine seltene komplikation bei adultem morbus still[J]. Rheuma Plus, 2020, 19:28-31. doi: 10.1007/s12688-019-00292-8. |
| [33] |
Kaneko Y, Kameda H, Ikeda K, et al. Tocilizumab in patients with adult-onset Still's disease refractory to glucocorticoid treatment: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial[J]. Ann Rheum Dis., 2018, 77(12):1720-1729. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213920.
pmid: 30279267 |
| [34] |
de Boysson H, Février J, Nicolle A, et al. Tocilizumab in the treatment of the adult-onset Still's disease: Current clinical evidence[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2013, 32(1):141-147. doi:10.1007/s10067-012-2105-2.
pmid: 23108887 |
| [35] |
Ciprani P, Ruscitti P, Carubbi F, et al. Tocilizumab for the treatment of adult-onset Still's disease: Results from a case series[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2014, 33(1):49-55. doi:10.1007/s10067-013-2381-5.
pmid: 24005839 |
| [1] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(10): 954-960. |
| [2] | Li Ying, Cao Tingting, Wang Cuicui, Li Yanxia, Yang Dongliang. Causal relationship between virus infection characterized by skin and mucosal lesions and dermatomyositis based on Mendelian randomization [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(9): 811-815. |
| [3] | Guo Yifan, Ren Hua, Bai Jing, Liu Sanjiao, Li Yanjuan. Incidence of sleep disorders in rheumatoid arthritis patients and influencing factors: A meta-analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(8): 677-683. |
| [4] | Shen Xuejiao, Wang Ting, Wang Yuan, Li Yan, Wei Jiaqi. Role of musculoskeletal ultrasound in the early diagnosis of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(8): 705-710. |
| [5] | Li Shaoning, Liu Xiaoxue, Li Chongwei, Ma Jijun. A case of pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus complicated with myasthenia gravis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(6): 537-540. |
| [6] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(5): 477-480. |
| [7] | Zhan Yaping, Zhang Ke, Li Wengen, He Chunmei, Yang Dashan. Clinical value of serum DKK-1 detection in carotid intima-media thickening in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(2): 138-142. |
| [8] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(1): 86-89. |
| [9] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(12): 1135-1140. |
| [10] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(11): 1052-1056. |
| [11] | Dong Hong, Li Zhenbin, Ma Xu, Luo Yaping, Jiao Aijun, Zhang Xufei, Sun Caixia. Rheumatoid arthritis combined with insomnia: A multicenter cross-sectional survey [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(10): 882-888. |
| [12] | Xie Jianli, Wang Junxiang, Chen Haiying. Application of musculoskeletal ultrasound in ankylosing spondylitis with peripheral osteophytes [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(9): 787-791. |
| [13] | Wang Yun, Wang Dandan. Bioinformatic analysis of differentially expressed genes of primary Sjögren's syndrome [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(9): 792-797. |
| [14] | Han Kaiyang, Feng Tongtong, Bao Ying. Analysis of clinical characteristics and risk factors of lupus nephritis combined with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus in children [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(9): 812-815. |
| [15] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(8): 763-768. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||