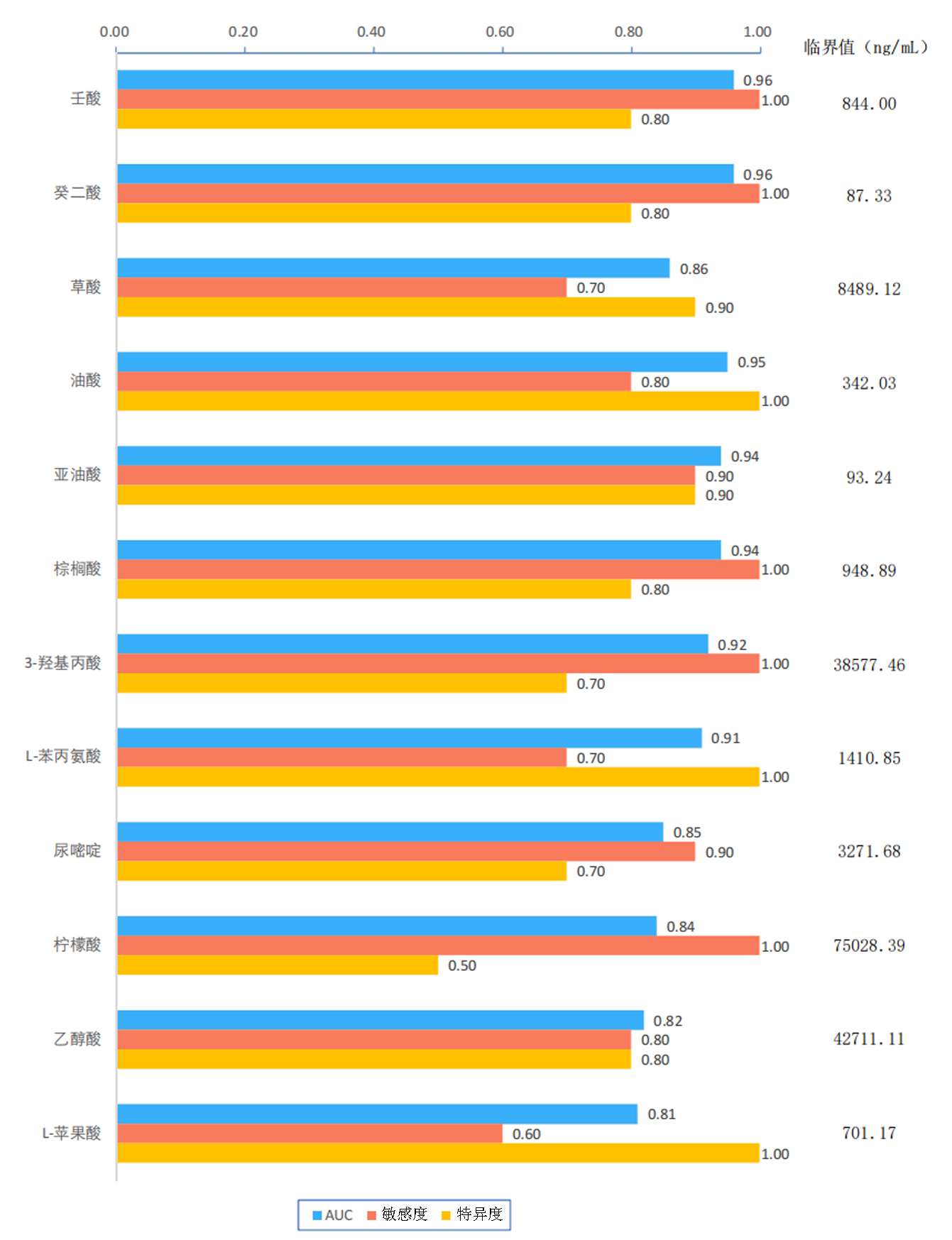
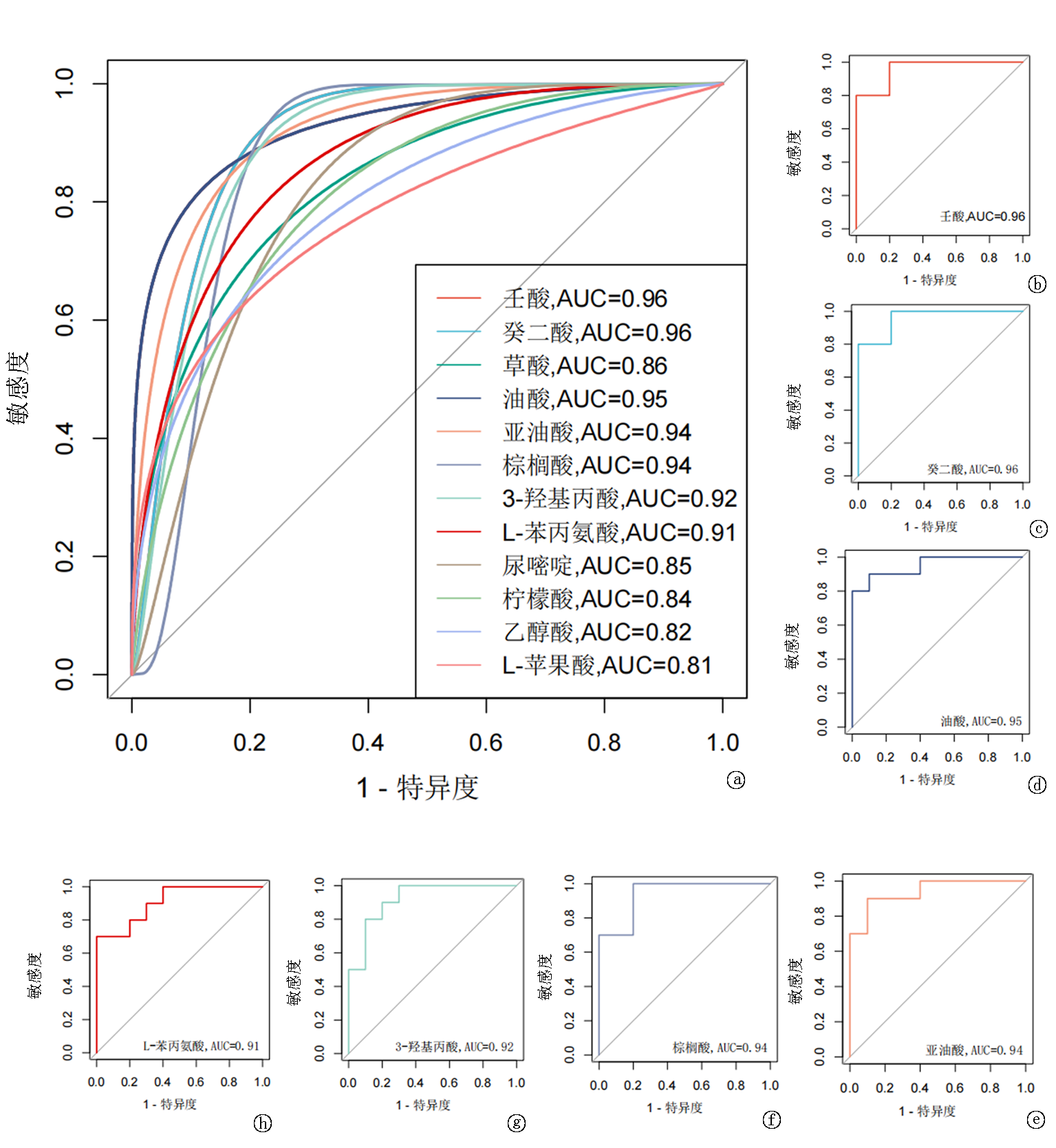
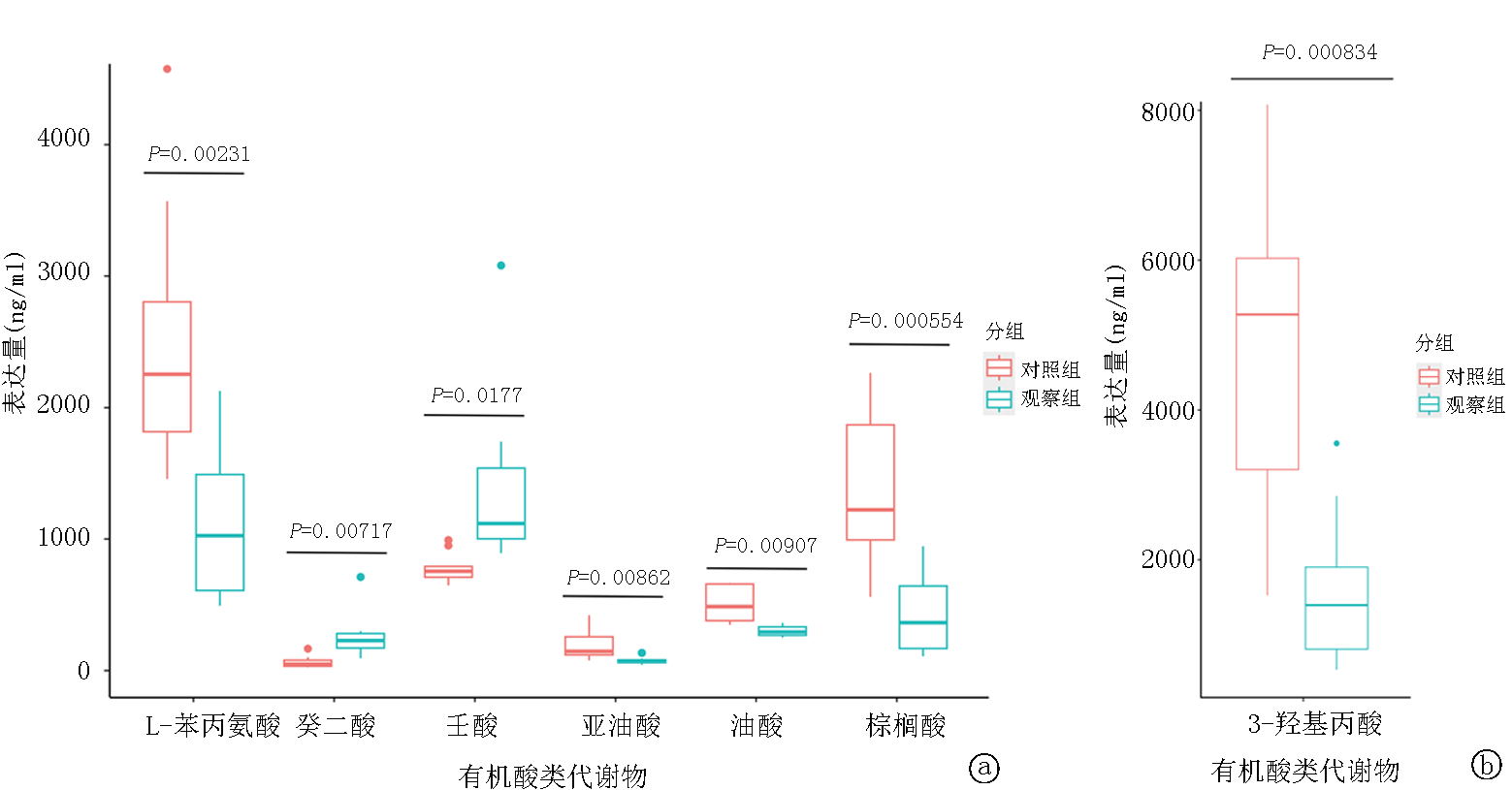
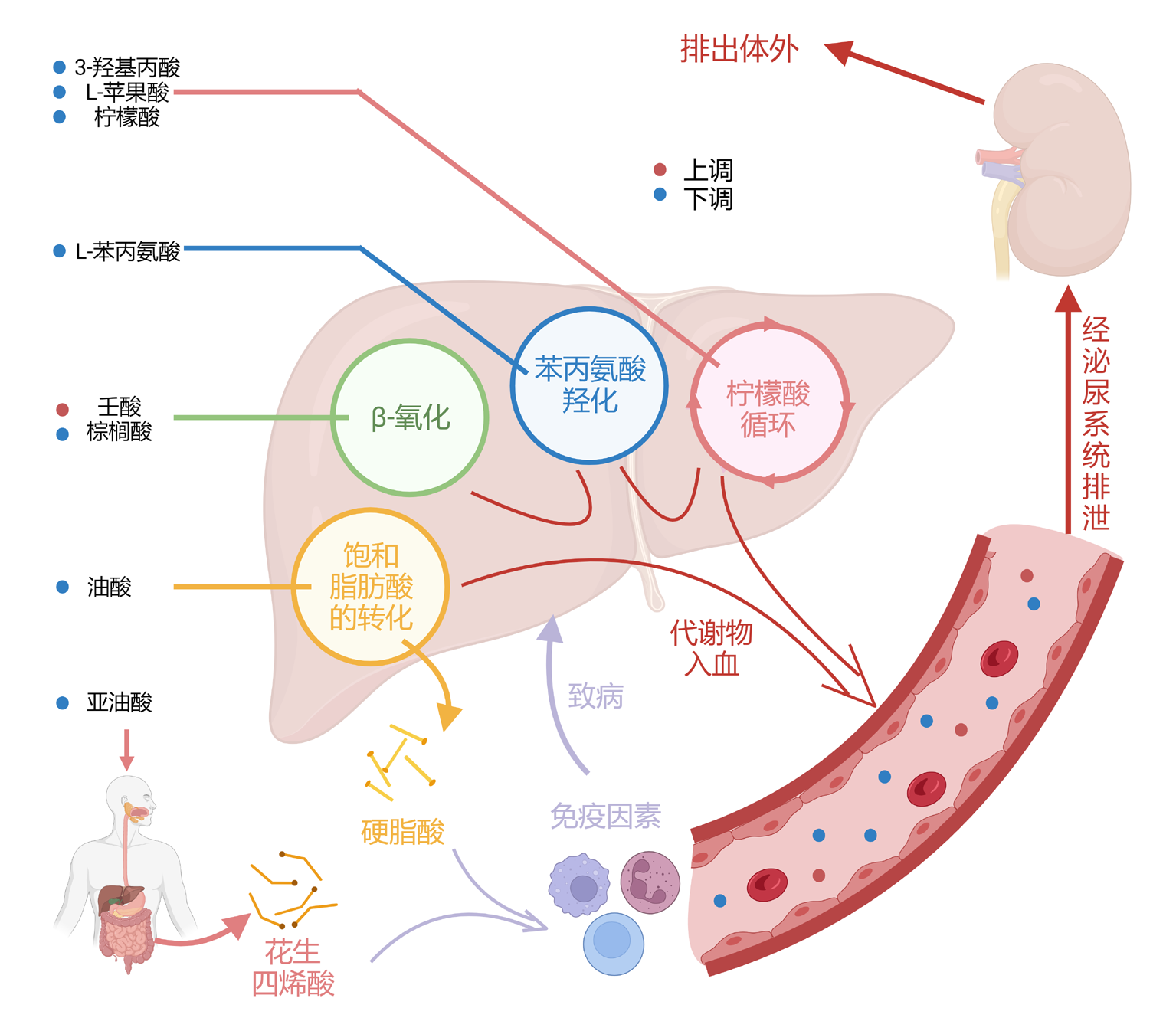
Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 519-526.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.06.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical predictive value of urine organic acid metabolites in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
You Yilan1a, Chen Lingyan1, Miao Keyan2, Ni Luohang3, Zhang Yan1, Xiao Jianping1b( )
)
- 1a. Science and Education Department; b. Department of Prenatal Diagnosis, Wuxi Maternity and Child Health Care Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214002, China
2. Medical College of Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, China
3. The First Clinical Medical College,Wuxi People's Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214023, China
-
Received:2025-03-24Online:2025-06-20Published:2025-07-01 -
Contact:Xiao Jianping E-mail:jianpingx999@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
You Yilan, Chen Lingyan, Miao Keyan, Ni Luohang, Zhang Yan, Xiao Jianping. Clinical predictive value of urine organic acid metabolites in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(6): 519-526.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.lchc.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.06.007
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(岁) | 体质指数(kg/m2) | TBA(μmol/L) | AST(IU/L) | ALT(IU/L) | ALP(IU/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 10 | 33.3±5.6 | 26.9±3.3 | 3.6±2.2 | 18.8±5.6 | 11.7±7.1 | 167.7±84.2 | ||||
| 观察组 | 10 | 31.4±4.2 | 26.6±3.0 | 61.8±40.7 | 57.6±38 | 91.8±67.9 | 227.4±47.4 | ||||
| t值 | 0.944 | 0.271 | 4.940 | 3.501 | 3.561 | 2.140 | |||||
| P值 | 0.356 | 0.789 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.047 | |||||
| 组别 | 发病孕天(d) | 分娩孕天(d) | 孕次(次) | 产次(次) | 新生儿出生体重(g) | ||||||
| 对照组 | - | 273.3±2.6 | 2.6±1.3 | 0.8±0.6 | 3430.0±455.4 | ||||||
| 观察组 | 215.6±55.9 | 256.8±8.2 | 3.1±1.6 | 0.9±0.8 | 2827.1±435.3 | ||||||
| t值 | 6.668 | 0.849 | 0.573 | 3.068 | |||||||
| P值 | 0.000 | 0.406 | 0.573 | 0.006 | |||||||
Tab.1 General information and liver function indices between the two groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(岁) | 体质指数(kg/m2) | TBA(μmol/L) | AST(IU/L) | ALT(IU/L) | ALP(IU/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 10 | 33.3±5.6 | 26.9±3.3 | 3.6±2.2 | 18.8±5.6 | 11.7±7.1 | 167.7±84.2 | ||||
| 观察组 | 10 | 31.4±4.2 | 26.6±3.0 | 61.8±40.7 | 57.6±38 | 91.8±67.9 | 227.4±47.4 | ||||
| t值 | 0.944 | 0.271 | 4.940 | 3.501 | 3.561 | 2.140 | |||||
| P值 | 0.356 | 0.789 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.047 | |||||
| 组别 | 发病孕天(d) | 分娩孕天(d) | 孕次(次) | 产次(次) | 新生儿出生体重(g) | ||||||
| 对照组 | - | 273.3±2.6 | 2.6±1.3 | 0.8±0.6 | 3430.0±455.4 | ||||||
| 观察组 | 215.6±55.9 | 256.8±8.2 | 3.1±1.6 | 0.9±0.8 | 2827.1±435.3 | ||||||
| t值 | 6.668 | 0.849 | 0.573 | 3.068 | |||||||
| P值 | 0.000 | 0.406 | 0.573 | 0.006 | |||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 油酸 | 亚油酸 | 棕榈酸 | 壬酸 | 癸二酸 | 草酸 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 10 | 488.35±155.97 | 195.68±114.64 | 1113.22±674.54 | 104.62±57.66 | 815.26±114.26 | 6542.63±3682.01 | |||||||
| 观察组 | 10 | 309.53±56.15 | 74.40±25.78 | 467.21±460.79 | 1260.79±405.67 | 159.98±67.91 | 10372.78±3894.39 | |||||||
| 变化倍数 (观察组/对照组) | 0.634 | 0.380 | 0.420 | 1.546 | 0.380 | 1.585 | ||||||||
| P值 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.022 | 0.045 | 0.039 | 0.036 | ||||||||
| 组别 | L-苯丙氨酸 | 3-羟基丙酸 | 柠檬酸 | 乙醇酸 | L-苹果酸 | 尿嘧啶 | ||||||||
| 对照组 | 2467.92±985.14 | 47372.17±20851.61 | 141568.05±70636.63 | 61405.95±29008.71 | 2442.89±1682.24 | 3950.87±1648.88 | ||||||||
| 观察组 | 1128.04±604.12 | 15732.55±10120.39 | 66582.48±32340.82 | 29776.15±22874.65 | 1034.51±967.84 | 1793.62±1123.919 | ||||||||
| 变化倍数 (观察组/对照组) | 0.457 | 0.332 | 0.470 | 0.485 | 0.423 | 0.454 | ||||||||
| P值 | 0.002 | <0.001 | 0.007 | 0.014 | 0.034 | 0.003 | ||||||||
| 组别 | L-4-羟脯氨酸 | 顺式乌头酸 | 琥珀酸 | DL-焦谷氨酸 | 3-(4-羟基苯基)乳酸 | 尿黑酸 | ||||||||
| 对照组 | 2802.90±1870.56 | 98772.97±53695.87 | 1804.07±838.35 | 72246.58±38762.87 | 582.55±249.04 | 120.45±88.21 | ||||||||
| 观察组 | 1360.91±747.21 | 49167.89±38805.84 | 913.76±747.21 | 37181.64±27278.68 | 298.92±206.05 | 46.54±35.95 | ||||||||
| 变化倍数 (观察组/对照组) | 0.486 | 0.498 | 0.506 | 0.515 | 0.513 | 0.386 | ||||||||
| P值 | 0.036 | 0.029 | 0.022 | 0.031 | 0.012 | 0.024 | ||||||||
Tab.2 Concentration information of 18 differentially expressed organic acid metabolites (ng/ml)
| 组别 | 例数 | 油酸 | 亚油酸 | 棕榈酸 | 壬酸 | 癸二酸 | 草酸 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照组 | 10 | 488.35±155.97 | 195.68±114.64 | 1113.22±674.54 | 104.62±57.66 | 815.26±114.26 | 6542.63±3682.01 | |||||||
| 观察组 | 10 | 309.53±56.15 | 74.40±25.78 | 467.21±460.79 | 1260.79±405.67 | 159.98±67.91 | 10372.78±3894.39 | |||||||
| 变化倍数 (观察组/对照组) | 0.634 | 0.380 | 0.420 | 1.546 | 0.380 | 1.585 | ||||||||
| P值 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.022 | 0.045 | 0.039 | 0.036 | ||||||||
| 组别 | L-苯丙氨酸 | 3-羟基丙酸 | 柠檬酸 | 乙醇酸 | L-苹果酸 | 尿嘧啶 | ||||||||
| 对照组 | 2467.92±985.14 | 47372.17±20851.61 | 141568.05±70636.63 | 61405.95±29008.71 | 2442.89±1682.24 | 3950.87±1648.88 | ||||||||
| 观察组 | 1128.04±604.12 | 15732.55±10120.39 | 66582.48±32340.82 | 29776.15±22874.65 | 1034.51±967.84 | 1793.62±1123.919 | ||||||||
| 变化倍数 (观察组/对照组) | 0.457 | 0.332 | 0.470 | 0.485 | 0.423 | 0.454 | ||||||||
| P值 | 0.002 | <0.001 | 0.007 | 0.014 | 0.034 | 0.003 | ||||||||
| 组别 | L-4-羟脯氨酸 | 顺式乌头酸 | 琥珀酸 | DL-焦谷氨酸 | 3-(4-羟基苯基)乳酸 | 尿黑酸 | ||||||||
| 对照组 | 2802.90±1870.56 | 98772.97±53695.87 | 1804.07±838.35 | 72246.58±38762.87 | 582.55±249.04 | 120.45±88.21 | ||||||||
| 观察组 | 1360.91±747.21 | 49167.89±38805.84 | 913.76±747.21 | 37181.64±27278.68 | 298.92±206.05 | 46.54±35.95 | ||||||||
| 变化倍数 (观察组/对照组) | 0.486 | 0.498 | 0.506 | 0.515 | 0.513 | 0.386 | ||||||||
| P值 | 0.036 | 0.029 | 0.022 | 0.031 | 0.012 | 0.024 | ||||||||
| 影响因素 | TBA | AST | ALT | ALP | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r值 | P值 | r值 | P值 | r值 | P值 | r值 | P值 | ||||
| 壬酸 | 0.827 | 0.000 | 0.728 | 0.000 | 0.713 | 0.000 | 0.371 | 0.107 | |||
| 癸二酸 | 0.369 | 0.110 | 0.532 | 0.016 | 0.357 | 0.122 | 0.289 | 0.217 | |||
| 油酸 | -0.542 | 0.014 | -0.571 | 0.009 | -0.522 | 0.018 | -0.216 | 0.361 | |||
| 亚油酸 | -0.489 | 0.029 | -0.443 | 0.050 | -0.426 | 0.061 | -0.117 | 0.622 | |||
| 棕榈酸 | -0.527 | 0.017 | -0.409 | 0.074 | -0.443 | 0.050 | -0.097 | 0.686 | |||
| 3-羟基丙酸 | -0.605 | 0.005 | -0.440 | 0.052 | -0.427 | 0.061 | -0.174 | 0.462 | |||
| L-苯丙氨酸 | -0.576 | 0.008 | -0.472 | 0.036 | -0.485 | 0.030 | -0.074 | 0.755 | |||
Tab.3 Correlation between seven differentially expressed urinary metabolites and liver function indices in ICP patients
| 影响因素 | TBA | AST | ALT | ALP | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r值 | P值 | r值 | P值 | r值 | P值 | r值 | P值 | ||||
| 壬酸 | 0.827 | 0.000 | 0.728 | 0.000 | 0.713 | 0.000 | 0.371 | 0.107 | |||
| 癸二酸 | 0.369 | 0.110 | 0.532 | 0.016 | 0.357 | 0.122 | 0.289 | 0.217 | |||
| 油酸 | -0.542 | 0.014 | -0.571 | 0.009 | -0.522 | 0.018 | -0.216 | 0.361 | |||
| 亚油酸 | -0.489 | 0.029 | -0.443 | 0.050 | -0.426 | 0.061 | -0.117 | 0.622 | |||
| 棕榈酸 | -0.527 | 0.017 | -0.409 | 0.074 | -0.443 | 0.050 | -0.097 | 0.686 | |||
| 3-羟基丙酸 | -0.605 | 0.005 | -0.440 | 0.052 | -0.427 | 0.061 | -0.174 | 0.462 | |||
| L-苯丙氨酸 | -0.576 | 0.008 | -0.472 | 0.036 | -0.485 | 0.030 | -0.074 | 0.755 | |||
| 影响因素 | 新生儿出生体重 | |
|---|---|---|
| r值 | P值 | |
| 壬酸 | -0.551 | 0.005 |
| 癸二酸 | -0.112 | 0.601 |
| 油酸 | 0.352 | 0.092 |
| 亚油酸 | 0.312 | 0.138 |
| 棕榈酸 | 0.167 | 0.436 |
| 3-羟基丙酸 | 0.456 | 0.025 |
| L-苯丙氨酸 | 0.337 | 0.107 |
Tab.4 Correlation between seven differentially expressed urinary metabolites and neonatal birth weight in ICP patients
| 影响因素 | 新生儿出生体重 | |
|---|---|---|
| r值 | P值 | |
| 壬酸 | -0.551 | 0.005 |
| 癸二酸 | -0.112 | 0.601 |
| 油酸 | 0.352 | 0.092 |
| 亚油酸 | 0.312 | 0.138 |
| 棕榈酸 | 0.167 | 0.436 |
| 3-羟基丙酸 | 0.456 | 0.025 |
| L-苯丙氨酸 | 0.337 | 0.107 |
| [1] | Majsterek M, Wierzchowska-Opoka M, Makosz I, et al. Bile acids in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy[J]. Diagnostics (Basel), 2022, 12(11). |
| [2] | 中华医学会妇产科学分会产科学组, 中华医学会围产医学分会. 妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症临床诊治和管理指南(2024版)[J]. 中华妇产科杂志, 2024, 59(2): 97-107. |
| [3] | Manzotti C, Casazza G, Stimac T, et al. Total serum bile acids or serum bile acid profile, or both, for the diagnosis of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2019, 7(7): Cd012546. |
| [4] | Xiao J, Li Z, Song Y, et al. Molecular pathogenesis of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy[J]. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 2021: 6679322. |
| [5] | Qiu C, Enquobahrie DA, Frederick IO, et al. Early pregnancy urinary biomarkers of fatty acid and carbohydrate metabolism in pregnancies complicated by gestational diabetes[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2014, 104(3): 393-400. |
| [6] | Straub RH. The memory of the fatty acid system[J]. Prog Lipid Res, 2020, 79: 101049. |
| [7] | Cao XY, Li MY, Shao CX, et al. Fatty Acid Metabolism Disruptions: A subtle yet critical factor in adverse pregnancy outcomes[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2024, 20(15): 6018-6037. |
| [8] |
Li M, Xu C, Shi J, et al. Fatty acids promote fatty liver disease via the dysregulation of 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase/hydrogen sulfide pathway[J]. Gut, 2018, 67(12): 2169-2180.
doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-313778 pmid: 28877979 |
| [9] | 中华医学会妇产科学分会产科学组. 妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症诊疗指南(2015)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2015, 31(10): 1575-1578. |
| [10] | 胡翠芳, 朱大伟, 李力. 妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症的研究进展[J]. 中国实用妇科与产科杂志, 2021, 37(2): 248-252. |
| [11] | Gao XX, Ye MY, Liu Y, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy in a Chinese population[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 16307. |
| [12] | Puljic A, Kim E, Page J, et al. The risk of infant and fetal death by each additional week of expectant management in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy by gestational age[J]. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2015, 212(5): 667. |
| [13] |
Arafa A, Dong JY. Association between intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy and risk of gestational diabetes and preeclampsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hypertens Pregnancy, 2020, 39(3): 354-360.
doi: 10.1080/10641955.2020.1758939 pmid: 32326772 |
| [14] |
Avsar HA, Atlıhan U, Ata C, et al. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy and its association with preeclampsia and gestational diabetes: A retrospective analysis[J]. Arch Gynecol Obstet, 2024, 310(1): 221-227.
doi: 10.1007/s00404-024-07507-0 pmid: 38625544 |
| [15] | Chen Y, Zhang H, Ning W, et al. The impact of intrahepatic cholestasis on pregnancy outcomes: A retrospective cohort study[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2023, 23(1): 16. |
| [16] | 龚燕, 龚杰. 妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症的致病因素和药物治疗进展[J]. 肝脏, 2022, 27(2): 247-9+254. |
| [17] | 施秋洁. 常用肝功能项目在妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症中的变化及临床意义[J]. 系统医学, 2022, 7(3): 13-16. |
| [18] | Piccinin E, Cariello M, De Santis S, et al. Role of oleic acid in the gut-liver axis: From diet to the regulation of its synthesis via stearoyl-coa desaturase 1 (SCD1)[J]. Nutrients, 2019, 11(10). |
| [19] |
Sales-Campos H, Souza PR, Peghini BC, et al. An overview of the modulatory effects of oleic acid in health and disease[J]. Mini Rev Med Chem, 2013, 13(2): 201-210.
pmid: 23278117 |
| [20] | Szczuko M, Kikut J, Komorniak N, et al. The role of arachidonic and linoleic acid derivatives in pathological pregnancies and the human reproduction process[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(24):9628. |
| [21] | Shrestha N, Holland OJ, Kent NL, et al. Maternal high linoleic acid alters placental fatty acid composition[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(8):2183. |
| [22] | Dong R, Ye N, Zhao S, et al. Studies on novel diagnostic and predictive biomarkers of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy through metabolomics and proteomics[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 733225. |
| [23] |
Ennis MA, Rasmussen BF, Lim K, et al. Dietary phenylalanine requirements during early and late gestation in healthy pregnant women[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2020, 111(2): 351-359.
doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqz288 pmid: 31758682 |
| [24] | Tessari P, Vettore M, Millioni R, et al. Effect of liver cirrhosis on phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolism[J]. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care, 2010, 13(1): 81-86. |
| [25] | Wilson KA, Han Y, Zhang M, et al. Inter-relations between 3-hydroxypropionate and propionate metabolism in rat liver: Relevance to disorders of propionyl-CoA metabolism[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2017, 313(4): E413-428. |
| [1] | Kong Li, Zhao Suxian, Zhang Ying, Jin Meng, Wang Shanshan, Ren Weiguang, Zhang Yuguo, Kong Lingbo, Han Fang, Ji Lei. Expression levels of TIPE2 and FOXP3 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis and their clinical significance [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(5): 412-416. |
| [2] | Zhao Xueting, Bai Jiawen, Sun Jun. Analysis of risk factors for liver fibrosis in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and construction of a nomogram [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(5): 417-422. |
| [3] | Su Rui, Wang Cunkai, Wang Dingxin, Cai Conghui, Zhang Jian, Hou Hongtao, Bai Yun. Efficacy and safety of anticoagulant therapy in patients with cirrhosis: A meta-analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(4): 293-303. |
| [4] | Lin Tao, Du Taoming, Li Ya, Feng Yuling, Song Huizhen, Yu Qin. Value of T2WI signal intensity and gadobemeglumine enhanced MRI hepatobiliary phase parameters in evaluating liver function of cirrhosis patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(3): 251-256. |
| [5] | Tong Mingxia, Chen Ke, Xiang Xiaocong, Zhou Lifeng. Analysis of lean metabolic-associated fatty liver disease among young and middle-aged people and its risk factors [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(2): 128-132. |
| [6] | Qian Chenying, Yan Wenjun, Huang Yan, Zhao Zhi. Analysis of risk factors for multidrug-resistant bacterial infection in patients with decompensated cirrhosis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(2): 143-146. |
| [7] | Sun Ya, Yang Shuang. Value of ultrasound-guided attenuation parameter in the quantitative assessment of hepatic steatosis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(2): 158-161. |
| [8] | Gou Caixia, Zhang Jie, Baoyixiamu·Ababaikeli , Wang Yiming, Yao Lei, Zheng Rongjiong, Pan Jinliang, Lu Xiaobo. Analysis of influencing factors of sleep quality and metabolically associated fatty liver disease in the physical examination population [J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(1): 33-38. |
| [9] | Zhang Shasha, Zhao Yingchun, Zhou Hongxia. Effect of low-level viremia on the incidence of hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis treated with entecavir [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(11): 980-983. |
| [10] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(10): 935-939. |
| [11] | Qin Qiaoling, Mo Ranghui, Chen Xinyi. Efficacy and safety of the direct-acting anti-HCV therapy based on efavirenz-containing regimen on HIV/HCV co-infected patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(10): 921-924. |
| [12] | Wu Qiupin, Yan Shiwei, He Xiaoyin, Li Yun, LU Liju, Wu Yi. Analysis of hepatitis associated aplastic anemia in children [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(7): 640-643. |
| [13] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(7): 658-663. |
| [14] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(2): 177-182. |
| [15] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(1): 84-87. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||