

临床荟萃 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (11): 978-987.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.11.003
收稿日期:2025-09-23
出版日期:2025-11-20
发布日期:2025-12-02
通讯作者:
段军
E-mail:13691362130@163.com
基金资助:
Ren Dezhi1,2, Xu Siyao1,2, Wang Shuai3, Duan Jun2( )
)
Received:2025-09-23
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-12-02
Contact:
Duan Jun
E-mail:13691362130@163.com
摘要:
目的 探究天冬氨酸转氨酶/丙氨酸转氨酶(De Ritis比值)在脑卒中患者中28 d病死率的影响关联,并分析合并不同疾病后其具体预测价值。方法 采用回顾性队列研究提取MIMIC-Ⅳ数据库(2008-2019年)中6 165例脑卒中患者(ICD编码:I60/I63/I69),经缺失值筛选后最终纳入1 674例。缺失数据采用均值插补,缺失率>20%的变量被剔除。通过LASSO回归筛选变量,建立多变量Cox比例风险模型(含限制性立方样条函数)评估De Ritis比值与病死率的关系,并调整SOFA/APACHE-Ⅱ评分、器官支持及生物标志物等混杂因素。模型性能通过ROC-AUC和校准度验证,并预设亚组分析检验合并症的修饰效应。结果 De Ritis ratio是28 d病死率的独立预测因子。Kaplan-Meier分析表明,De Ritis最高组(Q4)生存率显著低于其他组(P<0.01)。单因素Cox回归证实,随De Ritis升高,死亡风险递增,其中Q3组HR=2.073(95%CI: 1.477~2.91, P<0.01),Q4组HR=2.066(95%CI: 1.452~2.939, P<0.01)。多因素模型(AUC=0.764)进一步验证其独立性。非线性分析揭示关键转折点(De Ritis=2):比值≤2时死亡风险随比值上升而增加,>2时影响不确定性升高。决策曲线证实其在广泛阈值概率具有临床净效益。亚组分析提示,该比值对高龄、无急性肾损伤/肝硬化/冠心病患者的预测价值更显著。结论 De Ritis比值是一种潜在的、有前景的预后指标,可用于评估脑卒中患者的死亡风险,为临床医生提供更准确的预后信息,从而帮助优化治疗策略,改善患者预后。
中图分类号:
任德志, 徐斯瑶, 王帅, 段军. De Ritis比值与卒中患者28 d病死率的关联:一项MIMIC-Ⅳ数据库分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2025, 40(11): 978-987.
Ren Dezhi, Xu Siyao, Wang Shuai, Duan Jun. Association between the De Ritis ratio and 28-day mortality in patients with cerebrovascular accident: A MIMIC-Ⅳ database analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(11): 978-987.
| 项目 | 总体 | Q1:0.791(0~1.037) | Q2:1.219(1.038~1.426) | Q3:1.675(1.429~2.000) | Q4: 2.462(2.000~3.429) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 例数 | 1 674 | 432 | 421 | 454 | 367 | |
| 年龄(岁) | 72(22~104) | 69(22~104) | 73(27~93) | 74(24~104) | 73(26~97) | <0.01 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 27.257(12.24~95.84) | 28.439(14.06~61.592) | 27.218(14.985~95.84) | 26.607(16.005~50.529) | 26.91(12.24~54.444) | 0.013 |
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||||
| 女性 男性 | 700(41.82) 974(58.18) | 157(36.34) 275(63.66) | 179(42.52) 242(57.48) | 188(41.41) 266(58.59) | 176(47.96) 191(52.04) | 0.011 |
| CRRT天数(d) | 0(0~33) | 0(0~17) | 0(0~32) | 0(0~24) | 0(0~33) | 0.034 |
| 生命体征 | ||||||
| HR(次/min) | 85(28~166) | 85(28~148) | 85(41~150) | 85.5(39~154) | 86(37~166) | 0.581 |
| 平均动脉压(mmHg) | 85.667(33.333~210.667) | 91.333(40.667~149.667) | 85.5(33.333~210.667) | 84.667(37~198.667) | 80.833(33.667~175.333) | <0.01 |
| RR(次/min) | 18(0~73) | 19(0~50) | 18(0~48) | 18(0~40) | 18(0~73) | 0.828 |
| 温度(°F) | 98.1(34.9~106) | 98.2(92.4~103.1) | 98.1(34.9~104.3) | 98.2(93~103.9) | 98.1(85.4~106) | 0.105 |
| 评分系统(分) | ||||||
| OASIS | 34(10~72) | 32(15~72) | 34(10~60) | 36(15~64) | 36(15~58) | <0.01 |
| SAPSⅡ | 40(9~98) | 36(9~98) | 39(13~88) | 41(13~93) | 42(15~90) | <0.01 |
| CHARLSON | 6(0~17) | 6(0~14) | 6(0~15) | 7(0~17) | 6(0~16) | 0.001 |
| SOFA | 5(0~20) | 4(0~17) | 5(0~17) | 6(0~18) | 6(0~20) | <0.01 |
| GCS | 15(3~15) | 15(3~15) | 15(3~15) | 15(3~15) | 15(3~15) | 0.651 |
| APACHEⅡ | 19(2~49) | 17(2~49) | 18(5~45) | 19.5(4~48) | 21(7~48) | <0.01 |
| 合并症 | ||||||
| 心肌梗死[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 497(89.43) 177(10.57) | 393(90.97) 39(9.03) | 384(91.21) 37(8.79) | 404(88.99) 50(11.01) | 316(86.10) 51(13.90) | 0.076 |
| 高血压[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 913(54.54) 761(45.46) | 229(53.01) 203(46.99) | 214(50.83) 207(49.17) | 261(57.49) 193(42.51) | 209(56.95) 158(43.05) | 0.158 |
| 肝硬化[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 587(94.80) 87(5.20) | 427(98.84) 5(1.16) | 408(96.91) 13(3.09) | 427(94.05) 27(5.95) | 325(88.56) 42(11.44) | <0.001 |
| 2型糖尿病[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 056(63.08) 618(36.92) | 271(62.73) 161(37.27) | 258(61.28) 163(38.72) | 305(67.18) 149(32.82) | 222(60.49) 145(39.51) | 0.176 |
| COPD[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 350(80.65) 324(19.35) | 356(82.41) 76(17.59) | 331(78.62) 90(21.38) | 369(81.28) 85(18.72) | 294(80.11) 73(19.89) | 0.542 |
| 心力衰竭[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 012(60.45) 662(39.55) | 277(64.12) 155(35.88) | 269(63.90) 152(36.10) | 255(56.17) 199(43.83) | 211(57.49) 156(42.51) | 0.025 |
| 实验室参数 | ||||||
| 血红蛋白(g/dl) | 10.5(4.6~20) | 11(5~16.3) | 10.8(4.6~18.6) | 10.2(4.8~20) | 9.9(4.7~17.2) | <0.01 |
| RBC(×1012/L) | 3.53(1.15~7.25) | 3.77(1.52~6.17) | 3.635(1.54~6.2) | 3.42(1.45~5.82) | 3.32(1.15~7.25) | <0.01 |
| WBC(×109/L) | 11.3(0.1~59.7) | 10.8(0.1~59.7) | 11.65(0.3~52.3) | 11(0.6~56.3) | 11.9(0.6~47) | 0.317 |
| 白蛋白(g/dl) | 3.1(1.1~4.9) | 3.2(1.2~4.9) | 3.1(1.5~4.7) | 3.1(1.1~4.9) | 3(1.4~4.9) | <0.01 |
| pH值 | 7.38(6.89~7.65) | 7.39(6.95~7.59) | 7.38(6.98~7.61) | 7.39(6.97~7.56) | 7.37(6.89~7.65) | 0.004 |
| 凝血酶原时间(s) | 14.4(8.9~150) | 13.7(9.3~124.6) | 14(10.4~92.2) | 14.9(10.1~150) | 15.1(8.9~84.5) | 0.015 |
| 总胆红素(mg/dl) | 0.6(0.1~31.3) | 0.5(0.1~22) | 0.5(0.1~14) | 0.6(0.1~20.5) | 0.6(0.1~31.3) | 0.003 |
| BUN(mg/dl) | 22(3~212) | 23(6~212) | 21(5~139) | 23(5~200) | 22(3~159) | 0.236 |
| 血小板计数(×109/L) | 193(5~1647) | 200(31~796) | 204(16~855) | 189(5~1592) | 165(17~1647) | <0.01 |
| SIRS[例(%)] | ||||||
| 0 | 18(1.08) | 6(1.39) | 3(0.71) | 7(1.54) | 2(0.54) | |
| 1 | 168(10.04) | 55(12.73) | 45(10.69) | 45(9.91) | 23(6.27) | |
| 2 | 495(29.57) | 134(31.02) | 126(29.93) | 140(30.84) | 95(25.89) | 0.029 |
| 3 | 677(40.44) | 169(39.12) | 174(41.33) | 175(38.55) | 159(43.32) | |
| 4 | 316(18.88) | 68(15.74) | 73(17.34) | 87(19.16) | 88(23.98) |
表1 各组患者一般临床资料比较
Tab.1 Baseline characteristics between groups
| 项目 | 总体 | Q1:0.791(0~1.037) | Q2:1.219(1.038~1.426) | Q3:1.675(1.429~2.000) | Q4: 2.462(2.000~3.429) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 例数 | 1 674 | 432 | 421 | 454 | 367 | |
| 年龄(岁) | 72(22~104) | 69(22~104) | 73(27~93) | 74(24~104) | 73(26~97) | <0.01 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 27.257(12.24~95.84) | 28.439(14.06~61.592) | 27.218(14.985~95.84) | 26.607(16.005~50.529) | 26.91(12.24~54.444) | 0.013 |
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||||
| 女性 男性 | 700(41.82) 974(58.18) | 157(36.34) 275(63.66) | 179(42.52) 242(57.48) | 188(41.41) 266(58.59) | 176(47.96) 191(52.04) | 0.011 |
| CRRT天数(d) | 0(0~33) | 0(0~17) | 0(0~32) | 0(0~24) | 0(0~33) | 0.034 |
| 生命体征 | ||||||
| HR(次/min) | 85(28~166) | 85(28~148) | 85(41~150) | 85.5(39~154) | 86(37~166) | 0.581 |
| 平均动脉压(mmHg) | 85.667(33.333~210.667) | 91.333(40.667~149.667) | 85.5(33.333~210.667) | 84.667(37~198.667) | 80.833(33.667~175.333) | <0.01 |
| RR(次/min) | 18(0~73) | 19(0~50) | 18(0~48) | 18(0~40) | 18(0~73) | 0.828 |
| 温度(°F) | 98.1(34.9~106) | 98.2(92.4~103.1) | 98.1(34.9~104.3) | 98.2(93~103.9) | 98.1(85.4~106) | 0.105 |
| 评分系统(分) | ||||||
| OASIS | 34(10~72) | 32(15~72) | 34(10~60) | 36(15~64) | 36(15~58) | <0.01 |
| SAPSⅡ | 40(9~98) | 36(9~98) | 39(13~88) | 41(13~93) | 42(15~90) | <0.01 |
| CHARLSON | 6(0~17) | 6(0~14) | 6(0~15) | 7(0~17) | 6(0~16) | 0.001 |
| SOFA | 5(0~20) | 4(0~17) | 5(0~17) | 6(0~18) | 6(0~20) | <0.01 |
| GCS | 15(3~15) | 15(3~15) | 15(3~15) | 15(3~15) | 15(3~15) | 0.651 |
| APACHEⅡ | 19(2~49) | 17(2~49) | 18(5~45) | 19.5(4~48) | 21(7~48) | <0.01 |
| 合并症 | ||||||
| 心肌梗死[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 497(89.43) 177(10.57) | 393(90.97) 39(9.03) | 384(91.21) 37(8.79) | 404(88.99) 50(11.01) | 316(86.10) 51(13.90) | 0.076 |
| 高血压[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 913(54.54) 761(45.46) | 229(53.01) 203(46.99) | 214(50.83) 207(49.17) | 261(57.49) 193(42.51) | 209(56.95) 158(43.05) | 0.158 |
| 肝硬化[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 587(94.80) 87(5.20) | 427(98.84) 5(1.16) | 408(96.91) 13(3.09) | 427(94.05) 27(5.95) | 325(88.56) 42(11.44) | <0.001 |
| 2型糖尿病[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 056(63.08) 618(36.92) | 271(62.73) 161(37.27) | 258(61.28) 163(38.72) | 305(67.18) 149(32.82) | 222(60.49) 145(39.51) | 0.176 |
| COPD[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 350(80.65) 324(19.35) | 356(82.41) 76(17.59) | 331(78.62) 90(21.38) | 369(81.28) 85(18.72) | 294(80.11) 73(19.89) | 0.542 |
| 心力衰竭[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 012(60.45) 662(39.55) | 277(64.12) 155(35.88) | 269(63.90) 152(36.10) | 255(56.17) 199(43.83) | 211(57.49) 156(42.51) | 0.025 |
| 实验室参数 | ||||||
| 血红蛋白(g/dl) | 10.5(4.6~20) | 11(5~16.3) | 10.8(4.6~18.6) | 10.2(4.8~20) | 9.9(4.7~17.2) | <0.01 |
| RBC(×1012/L) | 3.53(1.15~7.25) | 3.77(1.52~6.17) | 3.635(1.54~6.2) | 3.42(1.45~5.82) | 3.32(1.15~7.25) | <0.01 |
| WBC(×109/L) | 11.3(0.1~59.7) | 10.8(0.1~59.7) | 11.65(0.3~52.3) | 11(0.6~56.3) | 11.9(0.6~47) | 0.317 |
| 白蛋白(g/dl) | 3.1(1.1~4.9) | 3.2(1.2~4.9) | 3.1(1.5~4.7) | 3.1(1.1~4.9) | 3(1.4~4.9) | <0.01 |
| pH值 | 7.38(6.89~7.65) | 7.39(6.95~7.59) | 7.38(6.98~7.61) | 7.39(6.97~7.56) | 7.37(6.89~7.65) | 0.004 |
| 凝血酶原时间(s) | 14.4(8.9~150) | 13.7(9.3~124.6) | 14(10.4~92.2) | 14.9(10.1~150) | 15.1(8.9~84.5) | 0.015 |
| 总胆红素(mg/dl) | 0.6(0.1~31.3) | 0.5(0.1~22) | 0.5(0.1~14) | 0.6(0.1~20.5) | 0.6(0.1~31.3) | 0.003 |
| BUN(mg/dl) | 22(3~212) | 23(6~212) | 21(5~139) | 23(5~200) | 22(3~159) | 0.236 |
| 血小板计数(×109/L) | 193(5~1647) | 200(31~796) | 204(16~855) | 189(5~1592) | 165(17~1647) | <0.01 |
| SIRS[例(%)] | ||||||
| 0 | 18(1.08) | 6(1.39) | 3(0.71) | 7(1.54) | 2(0.54) | |
| 1 | 168(10.04) | 55(12.73) | 45(10.69) | 45(9.91) | 23(6.27) | |
| 2 | 495(29.57) | 134(31.02) | 126(29.93) | 140(30.84) | 95(25.89) | 0.029 |
| 3 | 677(40.44) | 169(39.12) | 174(41.33) | 175(38.55) | 159(43.32) | |
| 4 | 316(18.88) | 68(15.74) | 73(17.34) | 87(19.16) | 88(23.98) |
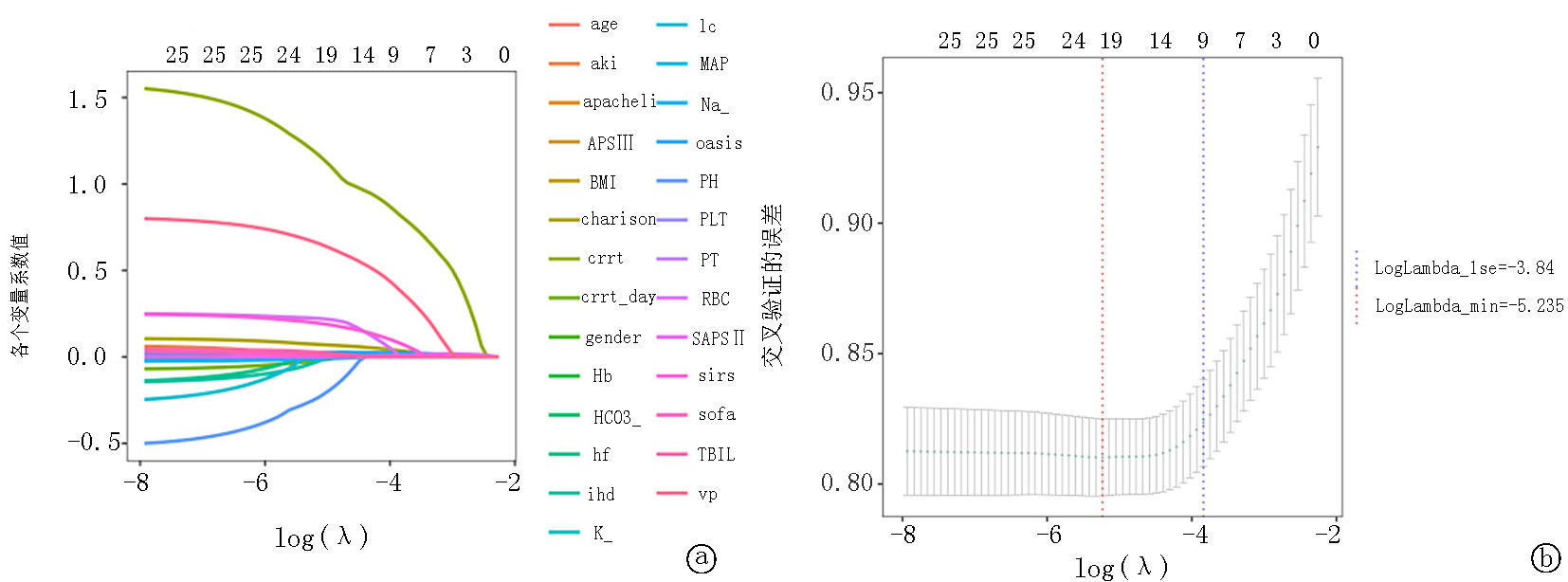
图4 LASSO回归分析,lambda 1se=-4.508,lambda min=-7.113 a. Lasso 回归的系数路径图; b.Lasso 回归的交叉验证曲线
Fig.4 LASSO regression analysis, lambda 1se=-4.508, lambda min=-7.113 a.Lasso regression coefficients trajectory plot b.Lasso regression cross-validation plot
| 项目 | 数值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||
| 年龄(岁) | 70.87±13.71 | 1.03 | 1.018 | 1.043 | 0 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 28.32±7.02 | 0.985 | 0.967 | 1.004 | 0.118 |
| Na+ | 138.83±5.34 | 0.984 | 0.963 | 1.004 | 0.122 |
| MAP(mmHg) | 87.89±20.11 | 1.003 | 0.998 | 1.009 | 0.275 |
| 血红蛋白(mmol/L) | 10.62±2.27 | 1.007 | 0.892 | 1.136 | 0.916 |
| pH | 7.36±0.09 | 0.381 | 0.12 | 1.213 | 0.102 |
| 血小板计数(×109/L) | 210.97±116.40 | 1 | 0.999 | 1.001 | 0.991 |
| 总胆红素 | 0.96±1.67 | 1.042 | 0.993 | 1.094 | 0.096 |
| 凝血酶原时间(s) | 17.73±10.78 | 1.004 | 0.994 | 1.014 | 0.44 |
| OASIS | 34.69±8.60 | 1.023 | 1.003 | 1.043 | 0.023 |
| APACHE Ⅱ | 41.04±13.83 | 0.994 | 0.978 | 1.009 | 0.435 |
| APS Ⅲ | 50.21±21.74 | 1.009 | 1 | 1.018 | 0.044 |
| Charlson | 6.32±2.73 | 1.077 | 1.021 | 1.136 | 0.006 |
| 冠心病(例) | |||||
| 否 是 | 911 763 | 0.9 | 0.703 | 1.152 | 0.402 |
| 急性肾衰竭(例) | |||||
| 否 是 | 948 726 | 1 | 0.775 | 1.29 | 0.999 |
| CRRT天数(d) | 0.40±2.15 | 0.929 | 0.868 | 0.994 | 0.032 |
| CRRT(例) | |||||
| 否 是 | 1 549 125 | 3.443 | 2.201 | 5.387 | 0 |
| SIRS(例) | |||||
| 0 | 18 | ||||
| 1 | 168 | 0.334 | 0.121 | 0.917 | 0.033 |
| 2 | 495 | 0.37 | 0.147 | 0.929 | 0.034 |
| 3 | 677 | 0.367 | 0.147 | 0.914 | 0.031 |
| 4 | 316 | 0.723 | 0.288 | 1.816 | 0.49 |
| 机械通气(例) | |||||
| 否 是 | 690 984 | 2.095 | 1.536 | 2.857 | 0 |
表2 CVA患者28 d病死率的多变量Cox回归分析
Tab.2 Multivariable Cox regression analysis for 28-day mortality in CVA patients
| 项目 | 数值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||
| 年龄(岁) | 70.87±13.71 | 1.03 | 1.018 | 1.043 | 0 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 28.32±7.02 | 0.985 | 0.967 | 1.004 | 0.118 |
| Na+ | 138.83±5.34 | 0.984 | 0.963 | 1.004 | 0.122 |
| MAP(mmHg) | 87.89±20.11 | 1.003 | 0.998 | 1.009 | 0.275 |
| 血红蛋白(mmol/L) | 10.62±2.27 | 1.007 | 0.892 | 1.136 | 0.916 |
| pH | 7.36±0.09 | 0.381 | 0.12 | 1.213 | 0.102 |
| 血小板计数(×109/L) | 210.97±116.40 | 1 | 0.999 | 1.001 | 0.991 |
| 总胆红素 | 0.96±1.67 | 1.042 | 0.993 | 1.094 | 0.096 |
| 凝血酶原时间(s) | 17.73±10.78 | 1.004 | 0.994 | 1.014 | 0.44 |
| OASIS | 34.69±8.60 | 1.023 | 1.003 | 1.043 | 0.023 |
| APACHE Ⅱ | 41.04±13.83 | 0.994 | 0.978 | 1.009 | 0.435 |
| APS Ⅲ | 50.21±21.74 | 1.009 | 1 | 1.018 | 0.044 |
| Charlson | 6.32±2.73 | 1.077 | 1.021 | 1.136 | 0.006 |
| 冠心病(例) | |||||
| 否 是 | 911 763 | 0.9 | 0.703 | 1.152 | 0.402 |
| 急性肾衰竭(例) | |||||
| 否 是 | 948 726 | 1 | 0.775 | 1.29 | 0.999 |
| CRRT天数(d) | 0.40±2.15 | 0.929 | 0.868 | 0.994 | 0.032 |
| CRRT(例) | |||||
| 否 是 | 1 549 125 | 3.443 | 2.201 | 5.387 | 0 |
| SIRS(例) | |||||
| 0 | 18 | ||||
| 1 | 168 | 0.334 | 0.121 | 0.917 | 0.033 |
| 2 | 495 | 0.37 | 0.147 | 0.929 | 0.034 |
| 3 | 677 | 0.367 | 0.147 | 0.914 | 0.031 |
| 4 | 316 | 0.723 | 0.288 | 1.816 | 0.49 |
| 机械通气(例) | |||||
| 否 是 | 690 984 | 2.095 | 1.536 | 2.857 | 0 |
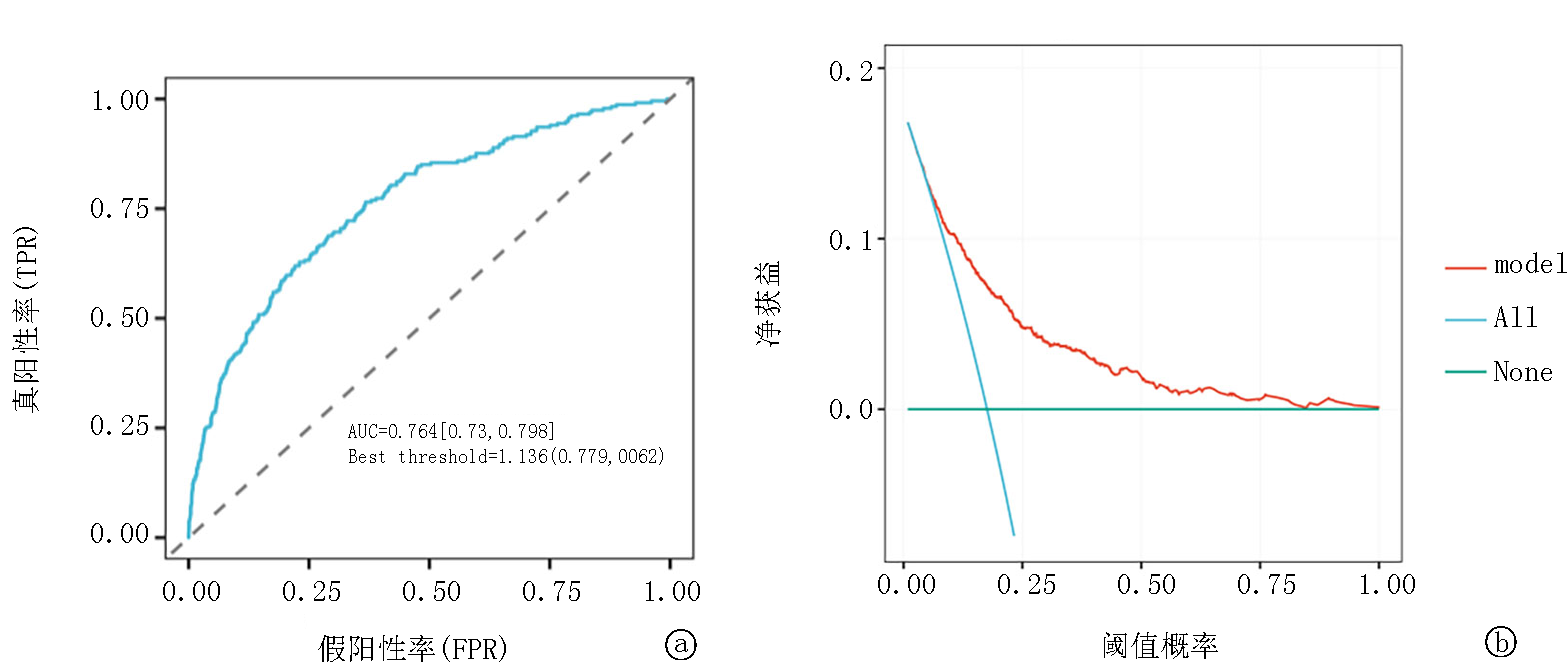
图5 多因素logistic回归分析曲线 a. De Ritis比值预测28 d病死率的ROC曲线; b.使用DCA评价De Ritis比值的有效性
Fig.5 Multivariate logistic regression analysis curve a. ROC curves of De Ritis for predicting 28-day mortality; b. DCA for evaluating De Ritis effectiveness
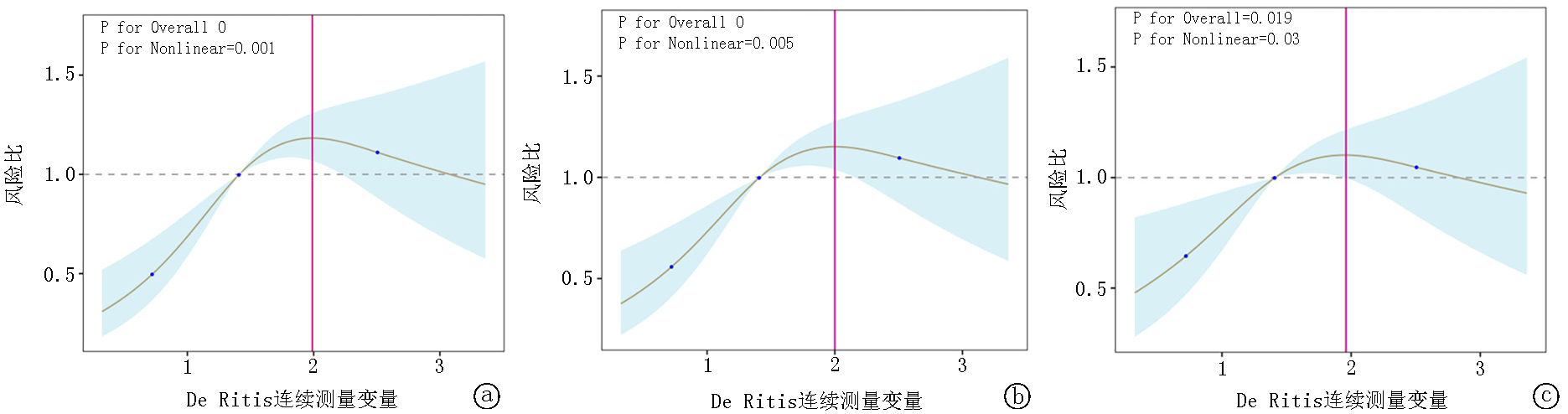
图6 限制性立方样条回归模型分析 a.模型1表示未调整分析;b.模型2包括性别、年龄和体重指数的调整;c.模型3包含模型2的变量,并进一步调整了其他因素,如种族、RR、MAP、HR、SOFA评分、SIRS评分、APSⅢ评分、SAPSⅡ评分、WBC、RBC、BUN、Scr、PCO2、钾、钠、pH和PO2。
Fig.6 Restricted cubic splines regression model for De Ritis a. Model 1 represents the unadjusted analysis; b. Model 2 involves adjustments for sex, age, and BMI; c. Model 3 includes the variables from Model 2 and further adjusts for additional factors such as race, RR, MAP, HR, SOFA score, SIRS score, APSⅢ score, SAPSⅡ score, WHC, RBC, BUN, Scr, PCO2, potassium, sodium, pH, and PO2.
| 项目 | 例数 | 百分比(%) | 死亡风险 | 95% | 交互作用 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 总数 | 1 674 | 100 | 1.15 | 1.08 | 1.22 | <0.01 | |
| 年龄(岁) | |||||||
| <65 ≥65 | 493 1 181 | 29.5 70.5 | 1.34 1.3 | 0.91 1.1 | 1.97 1.55 | 0.133 0.003 | 0.888 |
| 肝硬化 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 1 587 87 | 94.8 5.2 | 1.34 1.58 | 1.14 0.8 | 1.58 3.12 | <0.01 0.191 | 0.633 |
| 急性肾衰竭 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 948 726 | 56.6 43.4 | 1.45 1.22 | 1.14 0.99 | 1.83 1.51 | 0.002 0.057 | 0.291 |
| 心力衰竭 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 1 012 662 | 60.5 39.5 | 1.36 1.32 | 1.1 1.05 | 1.68 1.65 | 0.005 0.019 | 0.842 |
| 冠心病 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 911 763 | 54.4 45.6 | 1.51 1.21 | 1.2 0.97 | 1.89 1.51 | <0.01 0.09 | 0.17 |
| SOFA | |||||||
| 0 | 1 040 | 62.1 | 1.29 | 1.02 | 1.65 | 0.036 | |
| 1 | 552 | 33 | 1.16 | 0.9 | 1.49 | 0.245 | 0.775 |
| 2 | 82 | 4.9 | 1.12 | 0.74 | 1.69 | 0.599 | |
| Charlson | |||||||
| 0 | 127 | 7.6 | 1.62 | 0.69 | 3.79 | 0.266 | |
| 1 | 311 | 18.6 | 1.64 | 1 | 2.69 | 0.051 | 0.531 |
| 2 | 1 236 | 73.8 | 1.25 | 1.05 | 1.48 | 0.01 | |
| APACHE Ⅱ | |||||||
| 0 | 161 | 9.6 | 1.61 | 0.63 | 4.07 | 0.319 | |
| 1 | 813 | 48.6 | 1.28 | 0.97 | 1.69 | 0.077 | 0.739 |
| 2 | 564 | 33.7 | 1.22 | 0.96 | 1.54 | 0.103 | |
| 3 | 136 | 8.1 | 1.02 | 0.7 | 1.48 | 0.913 | |
| 机械通气 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 690 984 | 41.2 58.8 | 1.64 1.16 | 1.17 0.97 | 2.29 1.38 | 0.004 0.112 | 0.071 |
表3 亚组分析
Tab.3 Subgroup analysis for De Ritis
| 项目 | 例数 | 百分比(%) | 死亡风险 | 95% | 交互作用 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 总数 | 1 674 | 100 | 1.15 | 1.08 | 1.22 | <0.01 | |
| 年龄(岁) | |||||||
| <65 ≥65 | 493 1 181 | 29.5 70.5 | 1.34 1.3 | 0.91 1.1 | 1.97 1.55 | 0.133 0.003 | 0.888 |
| 肝硬化 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 1 587 87 | 94.8 5.2 | 1.34 1.58 | 1.14 0.8 | 1.58 3.12 | <0.01 0.191 | 0.633 |
| 急性肾衰竭 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 948 726 | 56.6 43.4 | 1.45 1.22 | 1.14 0.99 | 1.83 1.51 | 0.002 0.057 | 0.291 |
| 心力衰竭 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 1 012 662 | 60.5 39.5 | 1.36 1.32 | 1.1 1.05 | 1.68 1.65 | 0.005 0.019 | 0.842 |
| 冠心病 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 911 763 | 54.4 45.6 | 1.51 1.21 | 1.2 0.97 | 1.89 1.51 | <0.01 0.09 | 0.17 |
| SOFA | |||||||
| 0 | 1 040 | 62.1 | 1.29 | 1.02 | 1.65 | 0.036 | |
| 1 | 552 | 33 | 1.16 | 0.9 | 1.49 | 0.245 | 0.775 |
| 2 | 82 | 4.9 | 1.12 | 0.74 | 1.69 | 0.599 | |
| Charlson | |||||||
| 0 | 127 | 7.6 | 1.62 | 0.69 | 3.79 | 0.266 | |
| 1 | 311 | 18.6 | 1.64 | 1 | 2.69 | 0.051 | 0.531 |
| 2 | 1 236 | 73.8 | 1.25 | 1.05 | 1.48 | 0.01 | |
| APACHE Ⅱ | |||||||
| 0 | 161 | 9.6 | 1.61 | 0.63 | 4.07 | 0.319 | |
| 1 | 813 | 48.6 | 1.28 | 0.97 | 1.69 | 0.077 | 0.739 |
| 2 | 564 | 33.7 | 1.22 | 0.96 | 1.54 | 0.103 | |
| 3 | 136 | 8.1 | 1.02 | 0.7 | 1.48 | 0.913 | |
| 机械通气 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 690 984 | 41.2 58.8 | 1.64 1.16 | 1.17 0.97 | 2.29 1.38 | 0.004 0.112 | 0.071 |
| [1] | Boursin P, Paternotte S, Dercy B, et al. Semantics, epidemiology and semiology of stroke[J]. Soins, 2018, 63(828): 24-27.doi: 10.1016/j.soin.2018.06.008. |
| [2] | Battaglini D, Robba C, Lopes Da Silva A, et al. Brain-heart interaction after acute ischemic stroke[J]. Crit Care, 2020, 24(1): 163.doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02885-8. |
| [3] |
Chen Z, Venkat P, Seyfried D, et al. Brain-heart interaction: Cardiac complications after stroke[J]. Circ Res, 2017, 121(4): 451-468.doi: 10.1161/circresaha.117.311170.
pmid: 28775014 |
| [4] | Fan X, Cao J, Li M, et al. Stroke related brain-heart crosstalk: Pathophysiology, clinical implications, and underlying mechanisms[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2024, 11(14): e2307698.doi: 10.1002/advs.202307698. |
| [5] |
Sposato LA, Hilz MJ, Aspberg S, et al. Post-stroke cardiovascular complications and neurogenic cardiac injury: JACC state-of-the-art review[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2020, 76(23): 2768-85.doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.10.009.
pmid: 33272372 |
| [6] | Trefts E, Gannon M, Wasserman DH. The liver[J]. Curr Biol, 2017, 27(21): R1147-R1151. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.09.019. |
| [7] | Liu H, Ding C, Hu L, et al. The association between AST/ALT ratio and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with hypertension[J]. Medicine, 2021, 100(31): e26693.doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000026693. |
| [8] | Djakpo DK, Wang ZQ, Shrestha M. The significance of transaminase ratio (AST/ALT) in acute myocardial infarction[J]. Arch Med Sci Atheroscler Dis, 2020, 5: e279-e83.doi: 10.5114/amsad.2020.103028. |
| [9] | Weng SF, Kai J, Guha IN, et al. The value of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase in cardiovascular disease risk assessment[J]. Open Heart, 2015, 2(1): e000272.doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2015-000272. |
| [10] | Chen W, Wang W, Zhou L, et al. Elevated AST/ALT ratio is associated with all-cause mortality and cancer incident[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2022, 36(5): e24356.doi: 10.1002/jcla.24356. |
| [11] | Knittelfelder O, Delago D, Jakse G, et al. The AST/ALT (De Ritis) ratio predicts survival in patients with oral and oropharyngeal cancer[J]. Diagnostics (Basel), 2020, 10(11):973. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10110973. |
| [12] | Li L, Zeng Q, Xue N, et al. A nomogram based on aspartate aminotransferase/alanine aminotransferase (AST/ALT) ratio to predict prognosis after surgery in gastric cancer patients[J]. Cancer Control, 2020, 27(1): 1073274820954458.doi: 10.1177/1073274820954458. |
| [13] | Zhou J, He Z, Ma S, et al. AST/ALT ratio as a significant predictor of the incidence risk of prostate cancer[J]. Cancer Med, 2020, 9(15): 5672-5677.doi: 10.1002/cam4.3086. |
| [14] | Luo J, Yu F, Zhou H, et al. AST/ALT ratio is an independent risk factor for diabetic retinopathy: A cross-sectional study[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2024, 103(26): e38583.doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000038583. |
| [15] | Balling M, Nordestgaard BG, Varbo A, et al. Small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and ischemic stroke[J]. Ann Neurol, 2023, 93(5): 952-964.doi: 10.1002/ana.26598. |
| [16] |
Qie R, Liu L, Zhang D, et al. Dose-response association between high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies[J]. Prev Chronic Dis, 2021, 18: E45.doi: 10.5888/pcd18.200278.
pmid: 33988499 |
| [17] |
El-Sayed OS, Alnajjar AZ, Arafa A, et al. Association between risk of ischemic stroke and liver enzymes levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BMC Neurol, 2025, 25(1): 18. doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-03875-x.
pmid: 39806288 |
| [18] | Jayaraj RL, Azimullah S, Beiram R, et al. Neuroinflammation: Friend and foe for ischemic stroke[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2019, 16(1): 142.doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1516-2. |
| [19] | 殷越, 马一铭, 万晓红. 白细胞介素-1家族在缺血性脑卒中中的研究进展[J]. 中国现代医生, 2025, 63(17): 104-108. |
| [20] | Steven S, Frenis K, Oelze M, et al. Vascular inflammation and oxidative stress: Major triggers for cardiovascular disease[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019, 2019: 7092151.doi: 10.1155/2019/7092151. |
| [21] | 张滕飞, 巩婷, 王黎, 等. 氧化应激在缺血性脑卒中病理进程中的作用[J]. 生命的化学, 2025, 45(6): 1063-1068.doi: 10.13488/j.smhx.20250062. |
| [22] | García N, Zazueta C, Aguilera-Aguirre L. Oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiovascular disease[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2017: 5853238.doi: 10.1155/2017/5853238. |
| [23] |
Willard SS, Koochekpour S. Glutamate, glutamate receptors, and downstream signaling pathways[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2013, 9(9): 948-959.doi: 10.7150/ijbs.6426.
pmid: 24155668 |
| [24] |
Campos F, Rodríguez-Yáñez M, Castellanos M, et al. Blood levels of glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase are more strongly associated with good outcome in acute ischaemic stroke than glutamate pyruvate transaminase levels[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 2011, 121(1): 11-17.doi: 10.1042/cs20100427.
pmid: 21265738 |
| [25] | Gao F, Chen C, Lu J, et al. De Ritis ratio (AST/ALT) as an independent predictor of poor outcome in patients with acute ischemic stroke[J]. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat, 2017, 13: 1551-1557.doi: 10.2147/ndt.S139316. |
| [26] |
Castillo J, Dávalos A, Naveiro J, et al. Neuroexcitatory amino acids and their relation to infarct size and neurological deficit in ischemic stroke[J]. Stroke, 1996, 27(6): 1060-1065.doi: 10.1161/01.str.27.6.1060.
pmid: 8650715 |
| [27] |
Teichberg VI, Cohen-Kashi-Malina K, Cooper I, et al. Homeostasis of glutamate in brain fluids: An accelerated brain-to-blood efflux of excess glutamate is produced by blood glutamate scavenging and offers protection from neuropathologies[J]. Neuroscience, 2009, 158(1): 301-308.doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.02.075.
pmid: 18423998 |
| [1] | 王辉, 夏新建, 刘赛, 魏西福, 张树忠. 颈动脉CTA影像学指标及血脂指标与缺血性脑卒中的关系[J]. 临床荟萃, 2025, 40(9): 790-795. |
| [2] | 陈敏, 宋心荣, 马博戬, 牛慧敏. 对比增强超声评估颈动脉斑块稳定性与缺血性脑卒中相关性的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2025, 40(6): 492-497. |
| [3] | 徐胜, 杨青青, 张敏. 基于功能性近红外光谱技术, 观察脑机接口训练系统对亚急性期脑卒中后上肢功能障碍患者功能连接网络的影响[J]. 临床荟萃, 2025, 40(5): 428-433. |
| [4] | 卜志平, 赵宇, 刘洪峰, 刘光亮, 韩文芹. 家庭成员对急性缺血性脑卒中患者进行康复训练的效果[J]. 临床荟萃, 2025, 40(3): 222-226. |
| [5] | 刘金华, 王春梅, 王莹, 陈凯. 老年营养风险指数对老年急性脑梗死患者静脉溶栓短期转归的预测价值[J]. 临床荟萃, 2025, 40(1): 21-28. |
| [6] | 徐玉萍, 沈滔. 乳脂球表皮生长因子8对缺血性脑卒中后认知功能障碍的预测价值[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(6): 524-530. |
| [7] | 刘秀颖, 崔凯歌, 刘丽莹, 吴艳凯, 于佳琪, 杨冀萍. 基于静息态功能磁共振成像探讨卒中后疲劳的中枢机制[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(5): 401-407. |
| [8] | 宋梦姣, 王睿琪, 曹灿, 程光森, 刘羽, 李忠亮, 杨建豪. 血尿酸与首次急性缺血性脑卒中患者TOAST分型及预后的相关性[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(3): 216-221. |
| [9] | 李雯琳, 张志. 心房颤动患者左心耳形态结构和功能与左心耳血栓及心源性卒中的关系研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(2): 168-171. |
| [10] | 张琦, 孙增鑫, 赵越, 袁野, 秦小露, 吕红香, 尹昱, 张雅文. 经颅直流电刺激对脑卒中患者单侧忽略康复效果的影响: 网状meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(12): 1061-1072. |
| [11] | 任大斌, 周晨辉, 张立国. 缺血性脑卒中发病率不均衡原因探究和预防[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(12): 1119-1124. |
| [12] | 史莎莎, 任昊天, 宋丽菲, 李佳妮, 周岩, 张雁. 重症脑卒中患者肠内营养后高血糖管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(11): 1000-1006. |
| [13] | 朱静, 黄灿. 饮食与复发性缺血性卒中二级预防的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(11): 1040-1046. |
| [14] | 张学谦, 李阳, 徐国栋, 吕佩源. 卵圆孔未闭所致急性脑梗死患者人口学特征、临床及影像学等特征分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(6): 500-503. |
| [15] | 辛燕红, 郎桂艳, 陈子为, 王东玉. 中性粒细胞-淋巴细胞比值和血小板-淋巴细胞比值预测急性轻型缺血性脑卒中患者认知障碍的价值[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(6): 504-509. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||