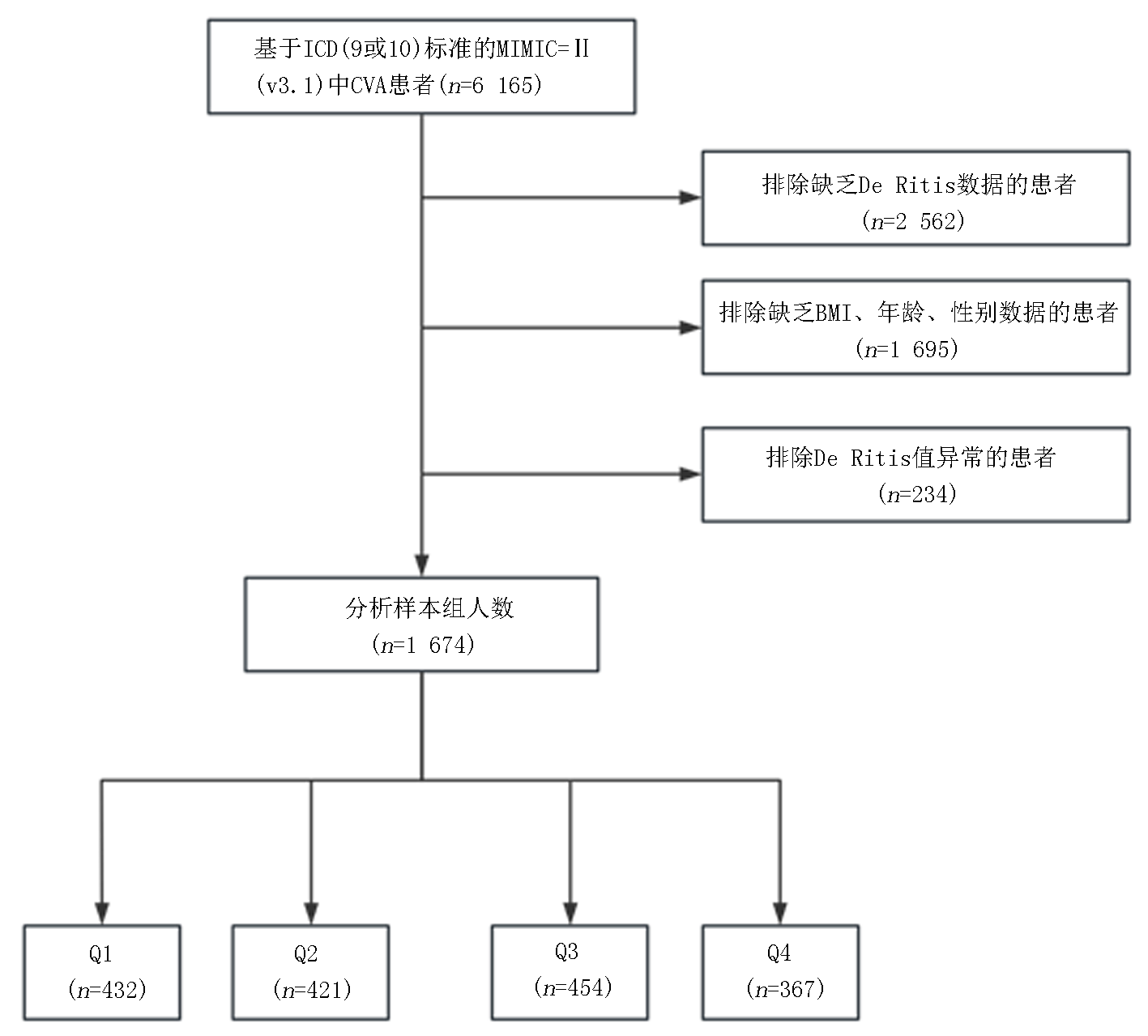
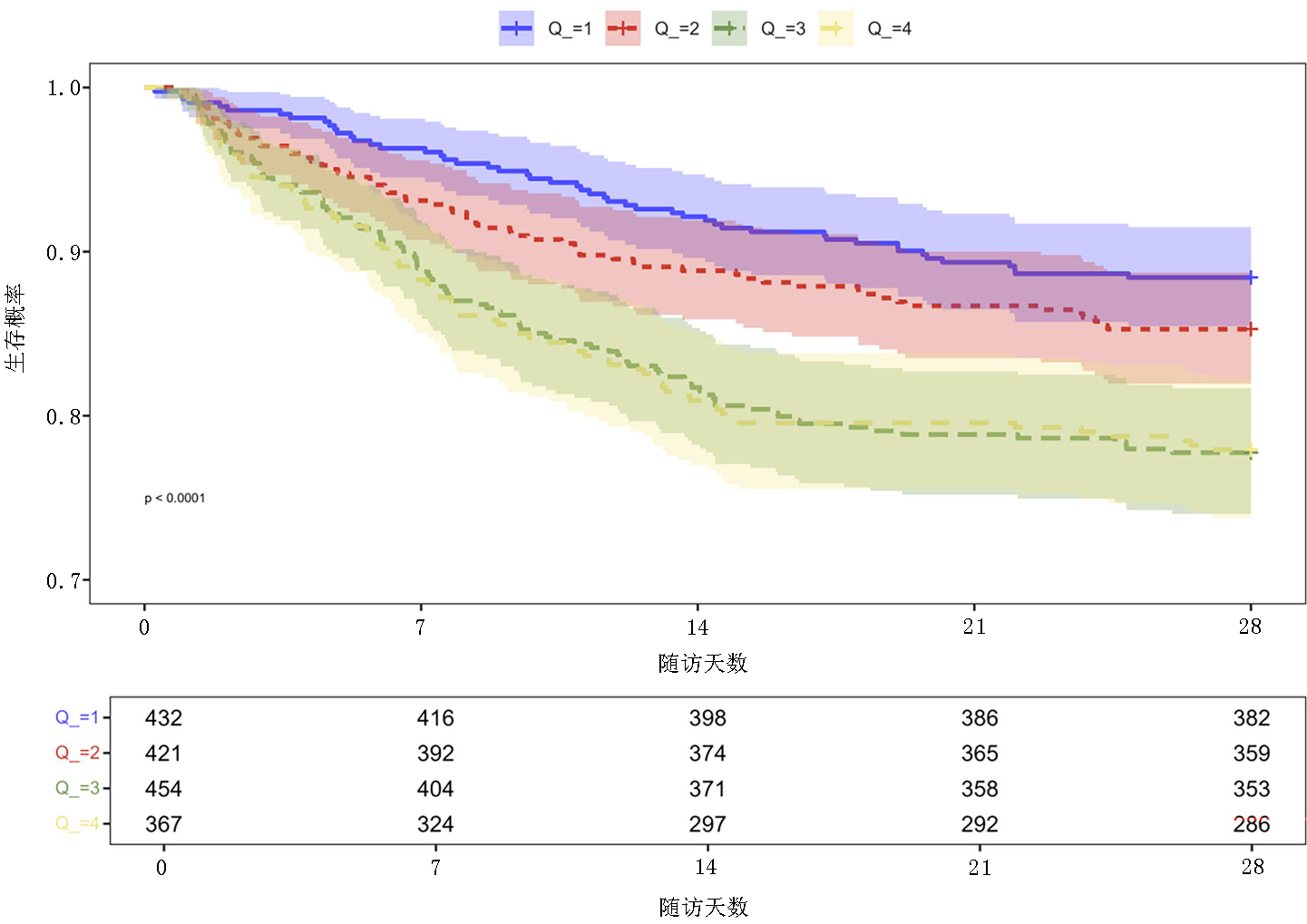
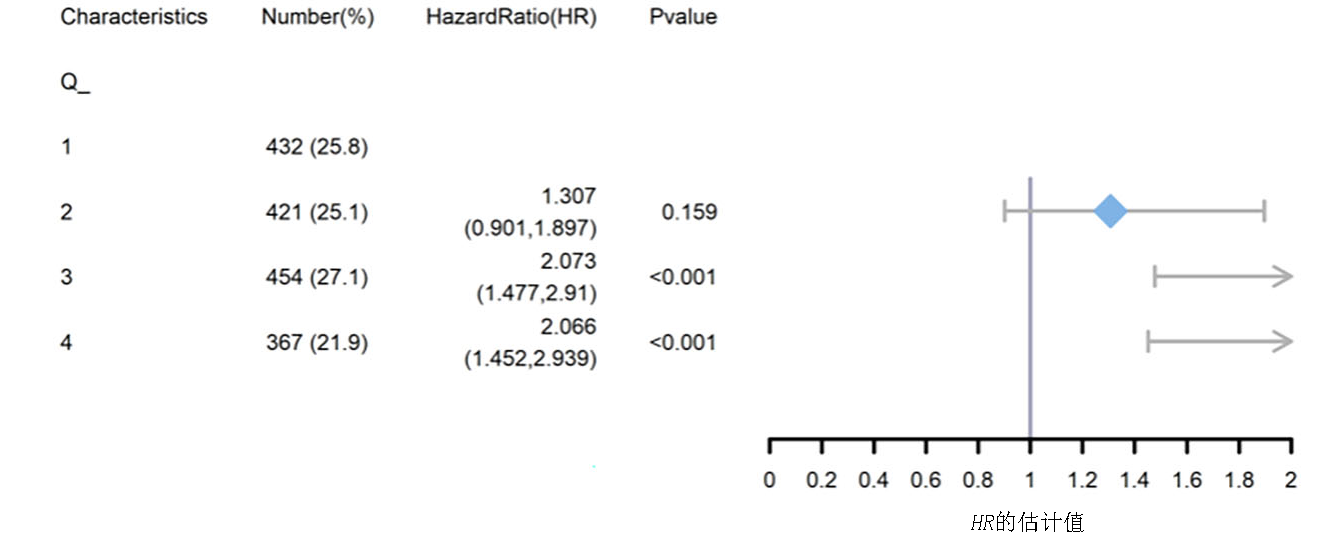
Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (11): 978-987.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.11.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Association between the De Ritis ratio and 28-day mortality in patients with cerebrovascular accident: A MIMIC-Ⅳ database analysis
Ren Dezhi1,2, Xu Siyao1,2, Wang Shuai3, Duan Jun2( )
)
- 1. China-Japan Friendship Hospital (Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences), Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100029,China
2. Department of Critical Care Medicine, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029,China
3. Department of Emergency, Tongren Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200336, China
-
Received:2025-09-23Online:2025-11-20Published:2025-12-02 -
Contact:Duan Jun E-mail:13691362130@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ren Dezhi, Xu Siyao, Wang Shuai, Duan Jun. Association between the De Ritis ratio and 28-day mortality in patients with cerebrovascular accident: A MIMIC-Ⅳ database analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2025, 40(11): 978-987.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.lchc.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.11.003
| 项目 | 总体 | Q1:0.791(0~1.037) | Q2:1.219(1.038~1.426) | Q3:1.675(1.429~2.000) | Q4: 2.462(2.000~3.429) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 例数 | 1 674 | 432 | 421 | 454 | 367 | |
| 年龄(岁) | 72(22~104) | 69(22~104) | 73(27~93) | 74(24~104) | 73(26~97) | <0.01 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 27.257(12.24~95.84) | 28.439(14.06~61.592) | 27.218(14.985~95.84) | 26.607(16.005~50.529) | 26.91(12.24~54.444) | 0.013 |
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||||
| 女性 男性 | 700(41.82) 974(58.18) | 157(36.34) 275(63.66) | 179(42.52) 242(57.48) | 188(41.41) 266(58.59) | 176(47.96) 191(52.04) | 0.011 |
| CRRT天数(d) | 0(0~33) | 0(0~17) | 0(0~32) | 0(0~24) | 0(0~33) | 0.034 |
| 生命体征 | ||||||
| HR(次/min) | 85(28~166) | 85(28~148) | 85(41~150) | 85.5(39~154) | 86(37~166) | 0.581 |
| 平均动脉压(mmHg) | 85.667(33.333~210.667) | 91.333(40.667~149.667) | 85.5(33.333~210.667) | 84.667(37~198.667) | 80.833(33.667~175.333) | <0.01 |
| RR(次/min) | 18(0~73) | 19(0~50) | 18(0~48) | 18(0~40) | 18(0~73) | 0.828 |
| 温度(°F) | 98.1(34.9~106) | 98.2(92.4~103.1) | 98.1(34.9~104.3) | 98.2(93~103.9) | 98.1(85.4~106) | 0.105 |
| 评分系统(分) | ||||||
| OASIS | 34(10~72) | 32(15~72) | 34(10~60) | 36(15~64) | 36(15~58) | <0.01 |
| SAPSⅡ | 40(9~98) | 36(9~98) | 39(13~88) | 41(13~93) | 42(15~90) | <0.01 |
| CHARLSON | 6(0~17) | 6(0~14) | 6(0~15) | 7(0~17) | 6(0~16) | 0.001 |
| SOFA | 5(0~20) | 4(0~17) | 5(0~17) | 6(0~18) | 6(0~20) | <0.01 |
| GCS | 15(3~15) | 15(3~15) | 15(3~15) | 15(3~15) | 15(3~15) | 0.651 |
| APACHEⅡ | 19(2~49) | 17(2~49) | 18(5~45) | 19.5(4~48) | 21(7~48) | <0.01 |
| 合并症 | ||||||
| 心肌梗死[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 497(89.43) 177(10.57) | 393(90.97) 39(9.03) | 384(91.21) 37(8.79) | 404(88.99) 50(11.01) | 316(86.10) 51(13.90) | 0.076 |
| 高血压[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 913(54.54) 761(45.46) | 229(53.01) 203(46.99) | 214(50.83) 207(49.17) | 261(57.49) 193(42.51) | 209(56.95) 158(43.05) | 0.158 |
| 肝硬化[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 587(94.80) 87(5.20) | 427(98.84) 5(1.16) | 408(96.91) 13(3.09) | 427(94.05) 27(5.95) | 325(88.56) 42(11.44) | <0.001 |
| 2型糖尿病[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 056(63.08) 618(36.92) | 271(62.73) 161(37.27) | 258(61.28) 163(38.72) | 305(67.18) 149(32.82) | 222(60.49) 145(39.51) | 0.176 |
| COPD[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 350(80.65) 324(19.35) | 356(82.41) 76(17.59) | 331(78.62) 90(21.38) | 369(81.28) 85(18.72) | 294(80.11) 73(19.89) | 0.542 |
| 心力衰竭[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 012(60.45) 662(39.55) | 277(64.12) 155(35.88) | 269(63.90) 152(36.10) | 255(56.17) 199(43.83) | 211(57.49) 156(42.51) | 0.025 |
| 实验室参数 | ||||||
| 血红蛋白(g/dl) | 10.5(4.6~20) | 11(5~16.3) | 10.8(4.6~18.6) | 10.2(4.8~20) | 9.9(4.7~17.2) | <0.01 |
| RBC(×1012/L) | 3.53(1.15~7.25) | 3.77(1.52~6.17) | 3.635(1.54~6.2) | 3.42(1.45~5.82) | 3.32(1.15~7.25) | <0.01 |
| WBC(×109/L) | 11.3(0.1~59.7) | 10.8(0.1~59.7) | 11.65(0.3~52.3) | 11(0.6~56.3) | 11.9(0.6~47) | 0.317 |
| 白蛋白(g/dl) | 3.1(1.1~4.9) | 3.2(1.2~4.9) | 3.1(1.5~4.7) | 3.1(1.1~4.9) | 3(1.4~4.9) | <0.01 |
| pH值 | 7.38(6.89~7.65) | 7.39(6.95~7.59) | 7.38(6.98~7.61) | 7.39(6.97~7.56) | 7.37(6.89~7.65) | 0.004 |
| 凝血酶原时间(s) | 14.4(8.9~150) | 13.7(9.3~124.6) | 14(10.4~92.2) | 14.9(10.1~150) | 15.1(8.9~84.5) | 0.015 |
| 总胆红素(mg/dl) | 0.6(0.1~31.3) | 0.5(0.1~22) | 0.5(0.1~14) | 0.6(0.1~20.5) | 0.6(0.1~31.3) | 0.003 |
| BUN(mg/dl) | 22(3~212) | 23(6~212) | 21(5~139) | 23(5~200) | 22(3~159) | 0.236 |
| 血小板计数(×109/L) | 193(5~1647) | 200(31~796) | 204(16~855) | 189(5~1592) | 165(17~1647) | <0.01 |
| SIRS[例(%)] | ||||||
| 0 | 18(1.08) | 6(1.39) | 3(0.71) | 7(1.54) | 2(0.54) | |
| 1 | 168(10.04) | 55(12.73) | 45(10.69) | 45(9.91) | 23(6.27) | |
| 2 | 495(29.57) | 134(31.02) | 126(29.93) | 140(30.84) | 95(25.89) | 0.029 |
| 3 | 677(40.44) | 169(39.12) | 174(41.33) | 175(38.55) | 159(43.32) | |
| 4 | 316(18.88) | 68(15.74) | 73(17.34) | 87(19.16) | 88(23.98) |
Tab.1 Baseline characteristics between groups
| 项目 | 总体 | Q1:0.791(0~1.037) | Q2:1.219(1.038~1.426) | Q3:1.675(1.429~2.000) | Q4: 2.462(2.000~3.429) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 例数 | 1 674 | 432 | 421 | 454 | 367 | |
| 年龄(岁) | 72(22~104) | 69(22~104) | 73(27~93) | 74(24~104) | 73(26~97) | <0.01 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 27.257(12.24~95.84) | 28.439(14.06~61.592) | 27.218(14.985~95.84) | 26.607(16.005~50.529) | 26.91(12.24~54.444) | 0.013 |
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||||
| 女性 男性 | 700(41.82) 974(58.18) | 157(36.34) 275(63.66) | 179(42.52) 242(57.48) | 188(41.41) 266(58.59) | 176(47.96) 191(52.04) | 0.011 |
| CRRT天数(d) | 0(0~33) | 0(0~17) | 0(0~32) | 0(0~24) | 0(0~33) | 0.034 |
| 生命体征 | ||||||
| HR(次/min) | 85(28~166) | 85(28~148) | 85(41~150) | 85.5(39~154) | 86(37~166) | 0.581 |
| 平均动脉压(mmHg) | 85.667(33.333~210.667) | 91.333(40.667~149.667) | 85.5(33.333~210.667) | 84.667(37~198.667) | 80.833(33.667~175.333) | <0.01 |
| RR(次/min) | 18(0~73) | 19(0~50) | 18(0~48) | 18(0~40) | 18(0~73) | 0.828 |
| 温度(°F) | 98.1(34.9~106) | 98.2(92.4~103.1) | 98.1(34.9~104.3) | 98.2(93~103.9) | 98.1(85.4~106) | 0.105 |
| 评分系统(分) | ||||||
| OASIS | 34(10~72) | 32(15~72) | 34(10~60) | 36(15~64) | 36(15~58) | <0.01 |
| SAPSⅡ | 40(9~98) | 36(9~98) | 39(13~88) | 41(13~93) | 42(15~90) | <0.01 |
| CHARLSON | 6(0~17) | 6(0~14) | 6(0~15) | 7(0~17) | 6(0~16) | 0.001 |
| SOFA | 5(0~20) | 4(0~17) | 5(0~17) | 6(0~18) | 6(0~20) | <0.01 |
| GCS | 15(3~15) | 15(3~15) | 15(3~15) | 15(3~15) | 15(3~15) | 0.651 |
| APACHEⅡ | 19(2~49) | 17(2~49) | 18(5~45) | 19.5(4~48) | 21(7~48) | <0.01 |
| 合并症 | ||||||
| 心肌梗死[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 497(89.43) 177(10.57) | 393(90.97) 39(9.03) | 384(91.21) 37(8.79) | 404(88.99) 50(11.01) | 316(86.10) 51(13.90) | 0.076 |
| 高血压[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 913(54.54) 761(45.46) | 229(53.01) 203(46.99) | 214(50.83) 207(49.17) | 261(57.49) 193(42.51) | 209(56.95) 158(43.05) | 0.158 |
| 肝硬化[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 587(94.80) 87(5.20) | 427(98.84) 5(1.16) | 408(96.91) 13(3.09) | 427(94.05) 27(5.95) | 325(88.56) 42(11.44) | <0.001 |
| 2型糖尿病[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 056(63.08) 618(36.92) | 271(62.73) 161(37.27) | 258(61.28) 163(38.72) | 305(67.18) 149(32.82) | 222(60.49) 145(39.51) | 0.176 |
| COPD[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 350(80.65) 324(19.35) | 356(82.41) 76(17.59) | 331(78.62) 90(21.38) | 369(81.28) 85(18.72) | 294(80.11) 73(19.89) | 0.542 |
| 心力衰竭[例(%)] | ||||||
| 否 是 | 1 012(60.45) 662(39.55) | 277(64.12) 155(35.88) | 269(63.90) 152(36.10) | 255(56.17) 199(43.83) | 211(57.49) 156(42.51) | 0.025 |
| 实验室参数 | ||||||
| 血红蛋白(g/dl) | 10.5(4.6~20) | 11(5~16.3) | 10.8(4.6~18.6) | 10.2(4.8~20) | 9.9(4.7~17.2) | <0.01 |
| RBC(×1012/L) | 3.53(1.15~7.25) | 3.77(1.52~6.17) | 3.635(1.54~6.2) | 3.42(1.45~5.82) | 3.32(1.15~7.25) | <0.01 |
| WBC(×109/L) | 11.3(0.1~59.7) | 10.8(0.1~59.7) | 11.65(0.3~52.3) | 11(0.6~56.3) | 11.9(0.6~47) | 0.317 |
| 白蛋白(g/dl) | 3.1(1.1~4.9) | 3.2(1.2~4.9) | 3.1(1.5~4.7) | 3.1(1.1~4.9) | 3(1.4~4.9) | <0.01 |
| pH值 | 7.38(6.89~7.65) | 7.39(6.95~7.59) | 7.38(6.98~7.61) | 7.39(6.97~7.56) | 7.37(6.89~7.65) | 0.004 |
| 凝血酶原时间(s) | 14.4(8.9~150) | 13.7(9.3~124.6) | 14(10.4~92.2) | 14.9(10.1~150) | 15.1(8.9~84.5) | 0.015 |
| 总胆红素(mg/dl) | 0.6(0.1~31.3) | 0.5(0.1~22) | 0.5(0.1~14) | 0.6(0.1~20.5) | 0.6(0.1~31.3) | 0.003 |
| BUN(mg/dl) | 22(3~212) | 23(6~212) | 21(5~139) | 23(5~200) | 22(3~159) | 0.236 |
| 血小板计数(×109/L) | 193(5~1647) | 200(31~796) | 204(16~855) | 189(5~1592) | 165(17~1647) | <0.01 |
| SIRS[例(%)] | ||||||
| 0 | 18(1.08) | 6(1.39) | 3(0.71) | 7(1.54) | 2(0.54) | |
| 1 | 168(10.04) | 55(12.73) | 45(10.69) | 45(9.91) | 23(6.27) | |
| 2 | 495(29.57) | 134(31.02) | 126(29.93) | 140(30.84) | 95(25.89) | 0.029 |
| 3 | 677(40.44) | 169(39.12) | 174(41.33) | 175(38.55) | 159(43.32) | |
| 4 | 316(18.88) | 68(15.74) | 73(17.34) | 87(19.16) | 88(23.98) |
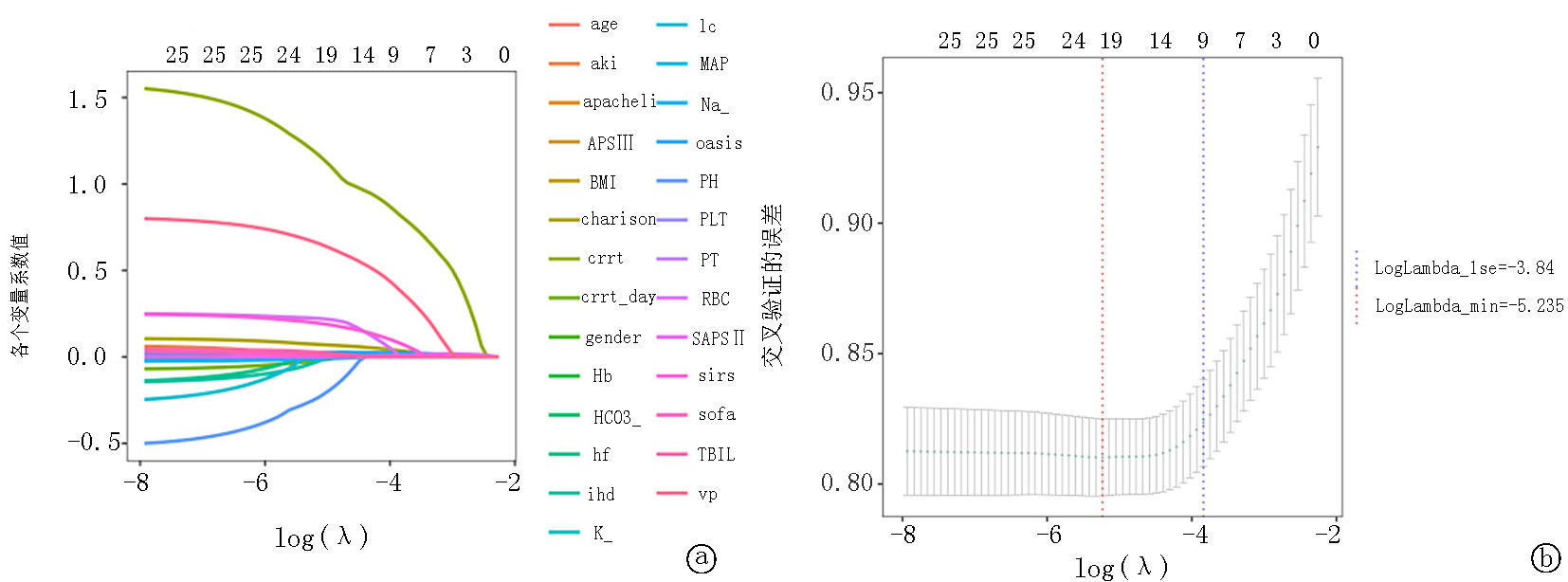
Fig.4 LASSO regression analysis, lambda 1se=-4.508, lambda min=-7.113 a.Lasso regression coefficients trajectory plot b.Lasso regression cross-validation plot
| 项目 | 数值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||
| 年龄(岁) | 70.87±13.71 | 1.03 | 1.018 | 1.043 | 0 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 28.32±7.02 | 0.985 | 0.967 | 1.004 | 0.118 |
| Na+ | 138.83±5.34 | 0.984 | 0.963 | 1.004 | 0.122 |
| MAP(mmHg) | 87.89±20.11 | 1.003 | 0.998 | 1.009 | 0.275 |
| 血红蛋白(mmol/L) | 10.62±2.27 | 1.007 | 0.892 | 1.136 | 0.916 |
| pH | 7.36±0.09 | 0.381 | 0.12 | 1.213 | 0.102 |
| 血小板计数(×109/L) | 210.97±116.40 | 1 | 0.999 | 1.001 | 0.991 |
| 总胆红素 | 0.96±1.67 | 1.042 | 0.993 | 1.094 | 0.096 |
| 凝血酶原时间(s) | 17.73±10.78 | 1.004 | 0.994 | 1.014 | 0.44 |
| OASIS | 34.69±8.60 | 1.023 | 1.003 | 1.043 | 0.023 |
| APACHE Ⅱ | 41.04±13.83 | 0.994 | 0.978 | 1.009 | 0.435 |
| APS Ⅲ | 50.21±21.74 | 1.009 | 1 | 1.018 | 0.044 |
| Charlson | 6.32±2.73 | 1.077 | 1.021 | 1.136 | 0.006 |
| 冠心病(例) | |||||
| 否 是 | 911 763 | 0.9 | 0.703 | 1.152 | 0.402 |
| 急性肾衰竭(例) | |||||
| 否 是 | 948 726 | 1 | 0.775 | 1.29 | 0.999 |
| CRRT天数(d) | 0.40±2.15 | 0.929 | 0.868 | 0.994 | 0.032 |
| CRRT(例) | |||||
| 否 是 | 1 549 125 | 3.443 | 2.201 | 5.387 | 0 |
| SIRS(例) | |||||
| 0 | 18 | ||||
| 1 | 168 | 0.334 | 0.121 | 0.917 | 0.033 |
| 2 | 495 | 0.37 | 0.147 | 0.929 | 0.034 |
| 3 | 677 | 0.367 | 0.147 | 0.914 | 0.031 |
| 4 | 316 | 0.723 | 0.288 | 1.816 | 0.49 |
| 机械通气(例) | |||||
| 否 是 | 690 984 | 2.095 | 1.536 | 2.857 | 0 |
Tab.2 Multivariable Cox regression analysis for 28-day mortality in CVA patients
| 项目 | 数值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||
| 年龄(岁) | 70.87±13.71 | 1.03 | 1.018 | 1.043 | 0 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 28.32±7.02 | 0.985 | 0.967 | 1.004 | 0.118 |
| Na+ | 138.83±5.34 | 0.984 | 0.963 | 1.004 | 0.122 |
| MAP(mmHg) | 87.89±20.11 | 1.003 | 0.998 | 1.009 | 0.275 |
| 血红蛋白(mmol/L) | 10.62±2.27 | 1.007 | 0.892 | 1.136 | 0.916 |
| pH | 7.36±0.09 | 0.381 | 0.12 | 1.213 | 0.102 |
| 血小板计数(×109/L) | 210.97±116.40 | 1 | 0.999 | 1.001 | 0.991 |
| 总胆红素 | 0.96±1.67 | 1.042 | 0.993 | 1.094 | 0.096 |
| 凝血酶原时间(s) | 17.73±10.78 | 1.004 | 0.994 | 1.014 | 0.44 |
| OASIS | 34.69±8.60 | 1.023 | 1.003 | 1.043 | 0.023 |
| APACHE Ⅱ | 41.04±13.83 | 0.994 | 0.978 | 1.009 | 0.435 |
| APS Ⅲ | 50.21±21.74 | 1.009 | 1 | 1.018 | 0.044 |
| Charlson | 6.32±2.73 | 1.077 | 1.021 | 1.136 | 0.006 |
| 冠心病(例) | |||||
| 否 是 | 911 763 | 0.9 | 0.703 | 1.152 | 0.402 |
| 急性肾衰竭(例) | |||||
| 否 是 | 948 726 | 1 | 0.775 | 1.29 | 0.999 |
| CRRT天数(d) | 0.40±2.15 | 0.929 | 0.868 | 0.994 | 0.032 |
| CRRT(例) | |||||
| 否 是 | 1 549 125 | 3.443 | 2.201 | 5.387 | 0 |
| SIRS(例) | |||||
| 0 | 18 | ||||
| 1 | 168 | 0.334 | 0.121 | 0.917 | 0.033 |
| 2 | 495 | 0.37 | 0.147 | 0.929 | 0.034 |
| 3 | 677 | 0.367 | 0.147 | 0.914 | 0.031 |
| 4 | 316 | 0.723 | 0.288 | 1.816 | 0.49 |
| 机械通气(例) | |||||
| 否 是 | 690 984 | 2.095 | 1.536 | 2.857 | 0 |
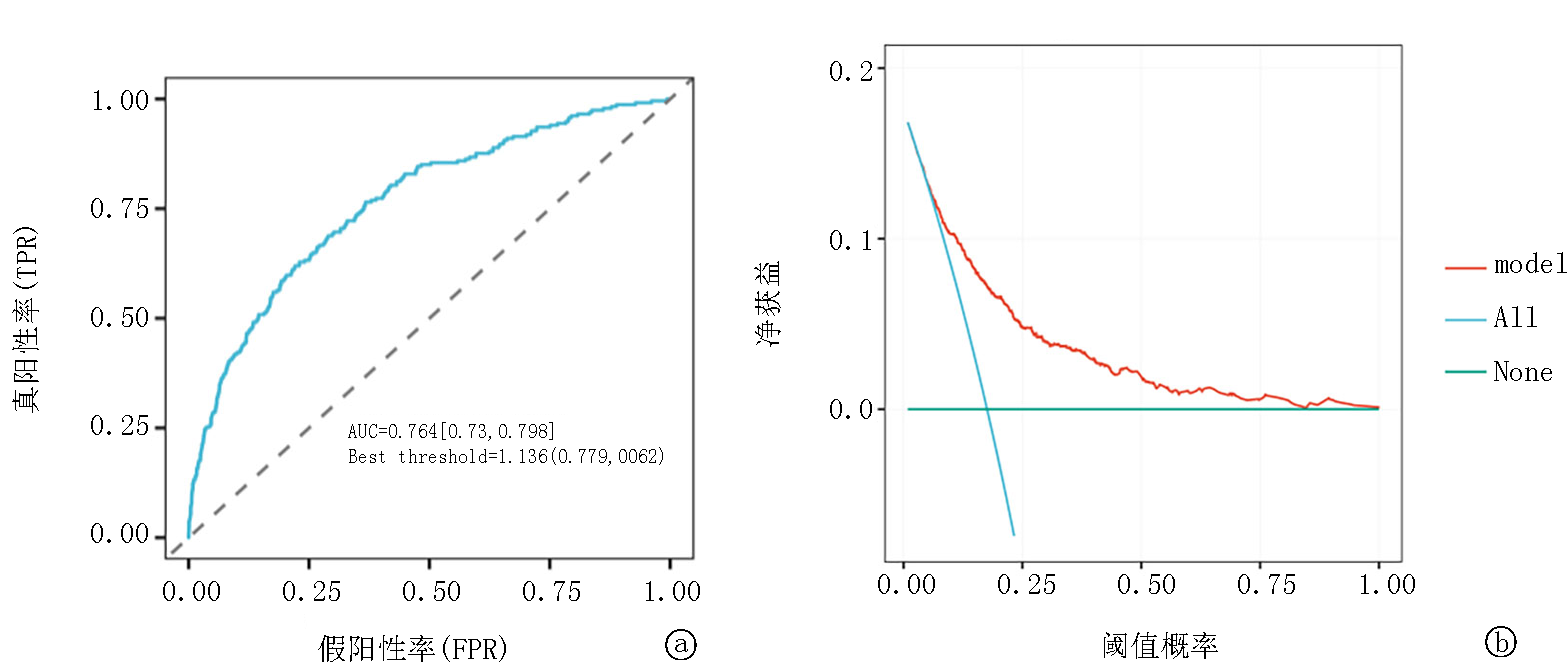
Fig.5 Multivariate logistic regression analysis curve a. ROC curves of De Ritis for predicting 28-day mortality; b. DCA for evaluating De Ritis effectiveness
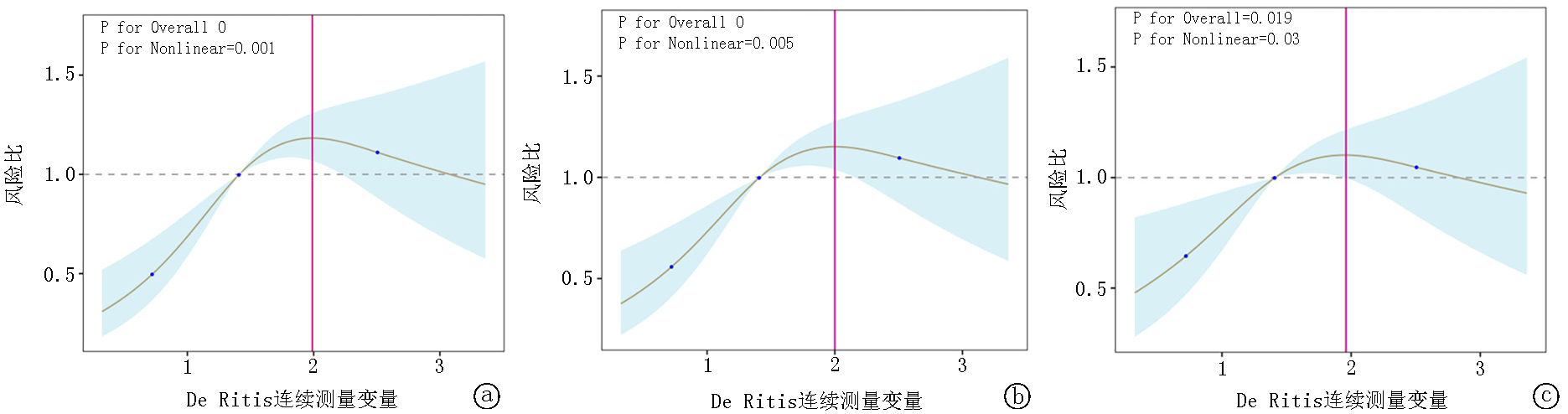
Fig.6 Restricted cubic splines regression model for De Ritis a. Model 1 represents the unadjusted analysis; b. Model 2 involves adjustments for sex, age, and BMI; c. Model 3 includes the variables from Model 2 and further adjusts for additional factors such as race, RR, MAP, HR, SOFA score, SIRS score, APSⅢ score, SAPSⅡ score, WHC, RBC, BUN, Scr, PCO2, potassium, sodium, pH, and PO2.
| 项目 | 例数 | 百分比(%) | 死亡风险 | 95% | 交互作用 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 总数 | 1 674 | 100 | 1.15 | 1.08 | 1.22 | <0.01 | |
| 年龄(岁) | |||||||
| <65 ≥65 | 493 1 181 | 29.5 70.5 | 1.34 1.3 | 0.91 1.1 | 1.97 1.55 | 0.133 0.003 | 0.888 |
| 肝硬化 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 1 587 87 | 94.8 5.2 | 1.34 1.58 | 1.14 0.8 | 1.58 3.12 | <0.01 0.191 | 0.633 |
| 急性肾衰竭 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 948 726 | 56.6 43.4 | 1.45 1.22 | 1.14 0.99 | 1.83 1.51 | 0.002 0.057 | 0.291 |
| 心力衰竭 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 1 012 662 | 60.5 39.5 | 1.36 1.32 | 1.1 1.05 | 1.68 1.65 | 0.005 0.019 | 0.842 |
| 冠心病 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 911 763 | 54.4 45.6 | 1.51 1.21 | 1.2 0.97 | 1.89 1.51 | <0.01 0.09 | 0.17 |
| SOFA | |||||||
| 0 | 1 040 | 62.1 | 1.29 | 1.02 | 1.65 | 0.036 | |
| 1 | 552 | 33 | 1.16 | 0.9 | 1.49 | 0.245 | 0.775 |
| 2 | 82 | 4.9 | 1.12 | 0.74 | 1.69 | 0.599 | |
| Charlson | |||||||
| 0 | 127 | 7.6 | 1.62 | 0.69 | 3.79 | 0.266 | |
| 1 | 311 | 18.6 | 1.64 | 1 | 2.69 | 0.051 | 0.531 |
| 2 | 1 236 | 73.8 | 1.25 | 1.05 | 1.48 | 0.01 | |
| APACHE Ⅱ | |||||||
| 0 | 161 | 9.6 | 1.61 | 0.63 | 4.07 | 0.319 | |
| 1 | 813 | 48.6 | 1.28 | 0.97 | 1.69 | 0.077 | 0.739 |
| 2 | 564 | 33.7 | 1.22 | 0.96 | 1.54 | 0.103 | |
| 3 | 136 | 8.1 | 1.02 | 0.7 | 1.48 | 0.913 | |
| 机械通气 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 690 984 | 41.2 58.8 | 1.64 1.16 | 1.17 0.97 | 2.29 1.38 | 0.004 0.112 | 0.071 |
Tab.3 Subgroup analysis for De Ritis
| 项目 | 例数 | 百分比(%) | 死亡风险 | 95% | 交互作用 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 总数 | 1 674 | 100 | 1.15 | 1.08 | 1.22 | <0.01 | |
| 年龄(岁) | |||||||
| <65 ≥65 | 493 1 181 | 29.5 70.5 | 1.34 1.3 | 0.91 1.1 | 1.97 1.55 | 0.133 0.003 | 0.888 |
| 肝硬化 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 1 587 87 | 94.8 5.2 | 1.34 1.58 | 1.14 0.8 | 1.58 3.12 | <0.01 0.191 | 0.633 |
| 急性肾衰竭 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 948 726 | 56.6 43.4 | 1.45 1.22 | 1.14 0.99 | 1.83 1.51 | 0.002 0.057 | 0.291 |
| 心力衰竭 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 1 012 662 | 60.5 39.5 | 1.36 1.32 | 1.1 1.05 | 1.68 1.65 | 0.005 0.019 | 0.842 |
| 冠心病 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 911 763 | 54.4 45.6 | 1.51 1.21 | 1.2 0.97 | 1.89 1.51 | <0.01 0.09 | 0.17 |
| SOFA | |||||||
| 0 | 1 040 | 62.1 | 1.29 | 1.02 | 1.65 | 0.036 | |
| 1 | 552 | 33 | 1.16 | 0.9 | 1.49 | 0.245 | 0.775 |
| 2 | 82 | 4.9 | 1.12 | 0.74 | 1.69 | 0.599 | |
| Charlson | |||||||
| 0 | 127 | 7.6 | 1.62 | 0.69 | 3.79 | 0.266 | |
| 1 | 311 | 18.6 | 1.64 | 1 | 2.69 | 0.051 | 0.531 |
| 2 | 1 236 | 73.8 | 1.25 | 1.05 | 1.48 | 0.01 | |
| APACHE Ⅱ | |||||||
| 0 | 161 | 9.6 | 1.61 | 0.63 | 4.07 | 0.319 | |
| 1 | 813 | 48.6 | 1.28 | 0.97 | 1.69 | 0.077 | 0.739 |
| 2 | 564 | 33.7 | 1.22 | 0.96 | 1.54 | 0.103 | |
| 3 | 136 | 8.1 | 1.02 | 0.7 | 1.48 | 0.913 | |
| 机械通气 | |||||||
| 否 是 | 690 984 | 41.2 58.8 | 1.64 1.16 | 1.17 0.97 | 2.29 1.38 | 0.004 0.112 | 0.071 |
| [1] | Boursin P, Paternotte S, Dercy B, et al. Semantics, epidemiology and semiology of stroke[J]. Soins, 2018, 63(828): 24-27.doi: 10.1016/j.soin.2018.06.008. |
| [2] | Battaglini D, Robba C, Lopes Da Silva A, et al. Brain-heart interaction after acute ischemic stroke[J]. Crit Care, 2020, 24(1): 163.doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02885-8. |
| [3] |
Chen Z, Venkat P, Seyfried D, et al. Brain-heart interaction: Cardiac complications after stroke[J]. Circ Res, 2017, 121(4): 451-468.doi: 10.1161/circresaha.117.311170.
pmid: 28775014 |
| [4] | Fan X, Cao J, Li M, et al. Stroke related brain-heart crosstalk: Pathophysiology, clinical implications, and underlying mechanisms[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2024, 11(14): e2307698.doi: 10.1002/advs.202307698. |
| [5] |
Sposato LA, Hilz MJ, Aspberg S, et al. Post-stroke cardiovascular complications and neurogenic cardiac injury: JACC state-of-the-art review[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2020, 76(23): 2768-85.doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.10.009.
pmid: 33272372 |
| [6] | Trefts E, Gannon M, Wasserman DH. The liver[J]. Curr Biol, 2017, 27(21): R1147-R1151. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.09.019. |
| [7] | Liu H, Ding C, Hu L, et al. The association between AST/ALT ratio and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with hypertension[J]. Medicine, 2021, 100(31): e26693.doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000026693. |
| [8] | Djakpo DK, Wang ZQ, Shrestha M. The significance of transaminase ratio (AST/ALT) in acute myocardial infarction[J]. Arch Med Sci Atheroscler Dis, 2020, 5: e279-e83.doi: 10.5114/amsad.2020.103028. |
| [9] | Weng SF, Kai J, Guha IN, et al. The value of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase in cardiovascular disease risk assessment[J]. Open Heart, 2015, 2(1): e000272.doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2015-000272. |
| [10] | Chen W, Wang W, Zhou L, et al. Elevated AST/ALT ratio is associated with all-cause mortality and cancer incident[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2022, 36(5): e24356.doi: 10.1002/jcla.24356. |
| [11] | Knittelfelder O, Delago D, Jakse G, et al. The AST/ALT (De Ritis) ratio predicts survival in patients with oral and oropharyngeal cancer[J]. Diagnostics (Basel), 2020, 10(11):973. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10110973. |
| [12] | Li L, Zeng Q, Xue N, et al. A nomogram based on aspartate aminotransferase/alanine aminotransferase (AST/ALT) ratio to predict prognosis after surgery in gastric cancer patients[J]. Cancer Control, 2020, 27(1): 1073274820954458.doi: 10.1177/1073274820954458. |
| [13] | Zhou J, He Z, Ma S, et al. AST/ALT ratio as a significant predictor of the incidence risk of prostate cancer[J]. Cancer Med, 2020, 9(15): 5672-5677.doi: 10.1002/cam4.3086. |
| [14] | Luo J, Yu F, Zhou H, et al. AST/ALT ratio is an independent risk factor for diabetic retinopathy: A cross-sectional study[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2024, 103(26): e38583.doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000038583. |
| [15] | Balling M, Nordestgaard BG, Varbo A, et al. Small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and ischemic stroke[J]. Ann Neurol, 2023, 93(5): 952-964.doi: 10.1002/ana.26598. |
| [16] |
Qie R, Liu L, Zhang D, et al. Dose-response association between high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies[J]. Prev Chronic Dis, 2021, 18: E45.doi: 10.5888/pcd18.200278.
pmid: 33988499 |
| [17] |
El-Sayed OS, Alnajjar AZ, Arafa A, et al. Association between risk of ischemic stroke and liver enzymes levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BMC Neurol, 2025, 25(1): 18. doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-03875-x.
pmid: 39806288 |
| [18] | Jayaraj RL, Azimullah S, Beiram R, et al. Neuroinflammation: Friend and foe for ischemic stroke[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2019, 16(1): 142.doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1516-2. |
| [19] | 殷越, 马一铭, 万晓红. 白细胞介素-1家族在缺血性脑卒中中的研究进展[J]. 中国现代医生, 2025, 63(17): 104-108. |
| [20] | Steven S, Frenis K, Oelze M, et al. Vascular inflammation and oxidative stress: Major triggers for cardiovascular disease[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019, 2019: 7092151.doi: 10.1155/2019/7092151. |
| [21] | 张滕飞, 巩婷, 王黎, 等. 氧化应激在缺血性脑卒中病理进程中的作用[J]. 生命的化学, 2025, 45(6): 1063-1068.doi: 10.13488/j.smhx.20250062. |
| [22] | García N, Zazueta C, Aguilera-Aguirre L. Oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiovascular disease[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2017: 5853238.doi: 10.1155/2017/5853238. |
| [23] |
Willard SS, Koochekpour S. Glutamate, glutamate receptors, and downstream signaling pathways[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2013, 9(9): 948-959.doi: 10.7150/ijbs.6426.
pmid: 24155668 |
| [24] |
Campos F, Rodríguez-Yáñez M, Castellanos M, et al. Blood levels of glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase are more strongly associated with good outcome in acute ischaemic stroke than glutamate pyruvate transaminase levels[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 2011, 121(1): 11-17.doi: 10.1042/cs20100427.
pmid: 21265738 |
| [25] | Gao F, Chen C, Lu J, et al. De Ritis ratio (AST/ALT) as an independent predictor of poor outcome in patients with acute ischemic stroke[J]. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat, 2017, 13: 1551-1557.doi: 10.2147/ndt.S139316. |
| [26] |
Castillo J, Dávalos A, Naveiro J, et al. Neuroexcitatory amino acids and their relation to infarct size and neurological deficit in ischemic stroke[J]. Stroke, 1996, 27(6): 1060-1065.doi: 10.1161/01.str.27.6.1060.
pmid: 8650715 |
| [27] |
Teichberg VI, Cohen-Kashi-Malina K, Cooper I, et al. Homeostasis of glutamate in brain fluids: An accelerated brain-to-blood efflux of excess glutamate is produced by blood glutamate scavenging and offers protection from neuropathologies[J]. Neuroscience, 2009, 158(1): 301-308.doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.02.075.
pmid: 18423998 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||